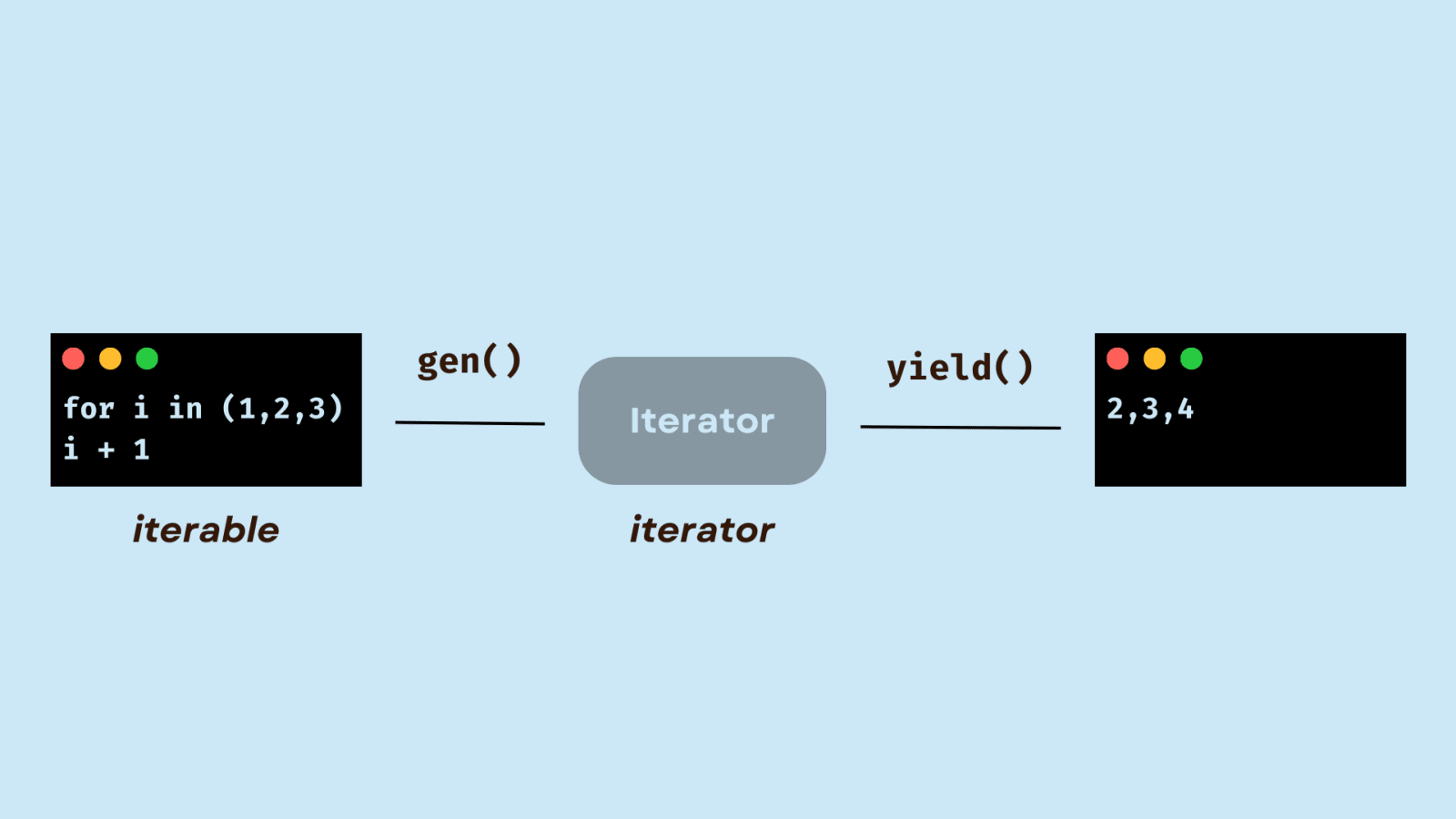
What are shell commands Python?
What are shell commands Python?
Shell commands, also known as command-line interfaces (CLI), are an essential part of using the Python programming language. While Python is a high-level language and doesn't have built-in support for shells like Bash or Zsh, you can still interact with your operating system's shell from within Python.
There are two main ways to use shell commands in Python: the os module and the subprocess module. Let's take a closer look at each:
1. The os Module
The os (Operating System) module provides a way to use shell commands directly in your Python code. This is done by using functions like system(), execv(), execl(), and others that execute shell commands.
For example, you can use the system() function to run a shell command:
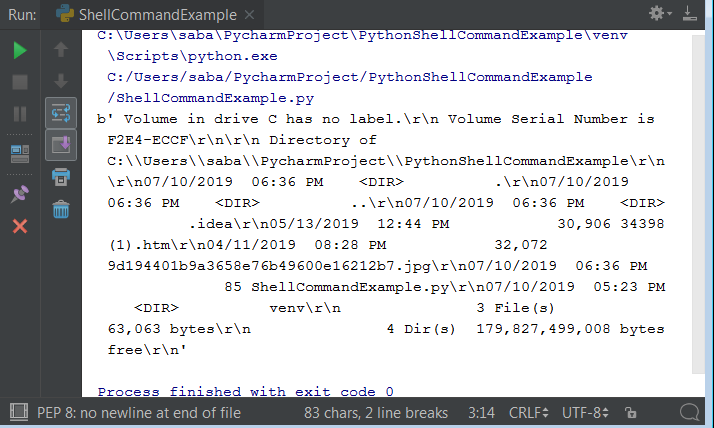
import os
os.system('ls -l') # Lists all files in the current directory
However, be aware that using os.system() can be insecure. If you're running a command with user-controlled input, an attacker could inject malicious code. To avoid this, use the subprocess module instead.
2. The subprocess Module
The subprocess module is generally considered safer than the os module for several reasons:
To use the subprocess module, you'll typically follow these steps:
Popen() object, passing the command string (e.g., "ls -l") as an argument. Use methods like communicate(), wait(), or read() to interact with the process.
Here's an example:
import subprocess
process = subprocess.Popen(['ls', '-l'], stdout=subprocess.PIPE, stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
output, errors = process.communicate()
print(output.decode()) # Output of the command
print(errors.decode()) # Errors from the command (if any)
Additional Tips and Considerations
When working with shell commands in Python, keep these best practices in mind:
Always use thesubprocess module instead of os.system(), as it's safer and more flexible. When running shell commands with user-controlled input, ensure you properly sanitize or escape special characters to avoid injection attacks. Be mindful of the potential security implications of executing shell commands from Python code.
By mastering the use of shell commands in Python, you'll be better equipped to automate tasks, interact with your operating system, and tackle complex programming projects.
How do I run a sh command in Python?
I see you're trying to get some coding done!
You can indeed execute shell commands using Python's built-in modules, specifically os and subprocess. Let me break it down for you.
Option 1: Using the os module
import os
Shell command to run
cmd = "ls -l"
Execute the command
os.system(cmd)
Output will be printed in your terminal
In this example, we're using the os.system() function to execute a simple shell command (ls -l in this case) and capture its output.
Option 2: Using the subprocess module
import subprocess
Shell command to run
cmd = "ls -l"
Execute the command
process = subprocess.Popen(cmd, shell=True, stdout=subprocess.PIPE)
Get the output as a string
output = process.stdout.read().decode('utf-8')
print(output)
In this example, we're using the subprocess module to create a new process that runs the shell command. We specify shell=True to indicate that we want to execute the command through the shell. The output will be captured and printed as a string.
Tips and Variations:
If you need to pass arguments to the shell command, you can modify thecmd variable accordingly. For example, cmd = "ls -l | grep 'specific_pattern'". You can also capture error messages by redirecting stderr to stdout using the 2>&1 syntax, like this: cmd = "ls -l 2>&1".
Why Use Python's Shell Execution Instead of Running Commands Directly in Your Terminal?
You might be wondering why you'd want to execute shell commands within a Python script. Here are some reasons:
Programmatic Control: You can use Python's control structures (e.g., loops, conditionals) to execute shell commands based on specific conditions or data. Automation: By integrating shell commands with Python code, you can automate repetitive tasks or workflows that involve both programming and system administration. Flexibility: Python scripts can be easily modified, shared, or distributed, making it a great option for scripting and automation tasks.So there you have it! You now know how to run shell commands using Python's built-in modules. Happy coding!