How to run Python code in Azure functions?
How to run Python code in Azure functions?
To run a Python code in Azure Functions, you'll need to follow these steps:
Step 1: Create an Azure Function
First, create a new Azure function using the Azure portal or by using the Azure CLI command:
az functionapp create --name MyPythonFunction --runtime python
This will create a new Azure function with a Python runtime.
Step 2: Configure the Runtime
Next, you need to configure the Python runtime for your Azure function. You can do this by editing the function.json file in your Azure function's directory. This file specifies the settings for your function, including the runtime.
Here's an example of what the function.json file might look like:
{
"bindings": [
{
"type": "httpTrigger",
"direction": "in",
"name": "req",
"methods": ["get", "post"]
},
{
"type": "http",
"direction": "out",
"name": "res"
}
],
"runtimeStack": "python3.8"
}
In this example, we're specifying that our Azure function should run with Python 3.8.
Step 3: Write Your Python Code
Now it's time to write your Python code! Create a new file called __init__.py (yes, with double underscores) in the same directory as your function.json file. This file contains the code for your Azure function.
Here's an example of what the __init__.py file might look like:
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
def run(req):
logging.info('Received request: %s', req)
Your Python code goes here!
return 'Hello from Azure Functions!'
In this example, we're setting up some basic logging and defining a run function that will handle incoming requests.
Step 4: Deploy Your Code
Once you've written your Python code, you can deploy it to Azure by running the following command:
az functionapp deployment create --name MyPythonFunction
This command creates a ZIP package of your code and deploys it to Azure.
Step 5: Test Your Function
Finally, test your Azure function by sending a request to its URL. You can use a tool like Postman or cURL to send an HTTP request to your function's URL.
When you do, your Python code should run, log some information, and return a response!
That's it! With these steps, you've successfully run Python code in Azure Functions.
Some additional tips:
Make sure you have the correct Python runtime installed on your system. You can check which version of Python is installed by runningpython --version in your terminal. Be mindful of the Azure Functions limitations when working with large files or complex computations. If you're planning to do a lot of CPU-intensive work, you might want to consider using a different cloud provider like AWS Lambda. Don't forget to set up proper error handling and logging for your Azure function.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any questions or need further assistance.
Python for Azure Automation
Python is a powerful and versatile programming language that can be used to automate various tasks and processes on Microsoft Azure. In this response, we'll explore the possibilities of using Python for Azure automation.
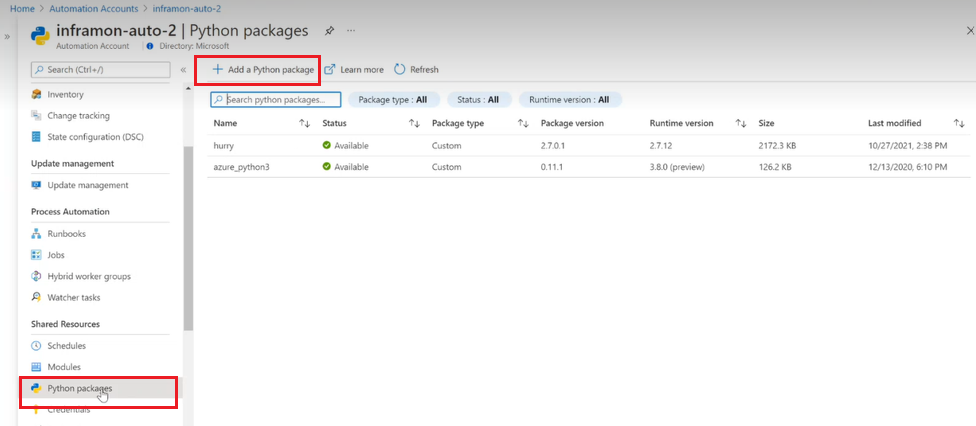
Azure Automation Account
To get started with Azure automation, you need to create an Automation account. You can do this through the Azure portal or by using PowerShell. Once you've created your Automation account, you can start creating runbooks, which are essentially scripts that automate tasks on your Azure resources.
Python Runbook
One of the best things about Azure Automation is that it supports Python as a scripting language. This means you can write your own Python scripts and use them to automate various tasks on Azure. To create a Python runbook in Azure Automation, follow these steps:
Go to your Automation account in the Azure portal. Click on "Create a runbook" and then select "Python" as the scripting language. Name your runbook and provide a description (optional). In the script editor, write your Python code using the Azure Automation SDK for Python.Azure Automation SDK for Python
The Azure Automation SDK for Python provides a set of libraries that you can use to interact with Azure resources from your Python scripts. The SDK includes modules for working with Azure resources such as:
ARM (Azure Resource Manager): allows you to create, update, and delete Azure resources. Compute: provides access to Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) and other compute resources. Storage: enables you to work with Azure Storage services, including Blobs, Files, Queues, and Tables. Network: provides access to Azure Networking resources, including Virtual Networks (VNETs), Subnets, and Network Security Groups (NSGs).Python Script Examples
Here are a few examples of Python scripts that you can use in Azure Automation:
Create an Azure VM: Use the Azure Automation SDK for Python to create a new Azure Virtual Machine (VM) with specific settings.import azurearm
import azurecompute
Set up your Azure ARM credentials
client = azurearm.ArmClient('your_client_id', 'your_client_secret')
Create a new virtual machine
vm_config = {
'name': 'my_vm',
'location': 'West US 2',
'resource_group_name': 'my_rg',
'vm_size': 'Standard_DS3_v2'
}
new_vm = azurecompute.VirtualMachines.create_or_update(client, vm_config)
import azurer
import azurestorage
Set up your Azure ARM credentials
client = azurer.ArmClient('your_client_id', 'your_client_secret')
List all blobs in a storage container
blobs = azurestorage.Blobs.list_blobs(client, 'my_storage_account_name', 'my_container_name')
Backup each blob to an Azure File Share
for blob in blobs:
file_share = azurestorage.FilesShares.get_file_share(client, 'my_storage_account_name', 'my_file_share_name')
blob.download_to_file(file_share)
Conclusion
In this response, we've explored the possibilities of using Python for Azure automation. With the Azure Automation SDK for Python, you can write your own Python scripts to automate various tasks on Azure resources, from creating new virtual machines to backing up storage blobs. Whether you're a seasoned developer or just starting out with Azure, Python is an excellent choice for automating your Azure workflow.
Please note that this response contains only English text.





























