What is abstract method in Python example?
What is abstract method in Python example?
I'd be happy to explain abstract methods in Python.
In Python, an abstract class is a special type of class that cannot be instantiated on its own. It's designed to provide a blueprint for other classes to inherit from and implement the abstract methods.
An abstract method is a method defined inside an abstract class that has no implementation. In other words, it's just a declaration with no body or code behind it. This means when you try to create an instance of an abstract class using its constructor (__init__), Python will raise a TypeError.
Here's an example:
pythonfrom abc import ABC, abstractmethod class AbstractClass(ABC): @abstractmethod def do_something(self): pass # this is a placeholder for the actual implementation def init(self): pass class ConcreteClass(AbstractClass): def do_something(self): print("Doing something concrete!") obj = ConcreteClass() obj.do_something() # Output: Doing something concrete!
In this example, AbstractClass is an abstract class with one abstract method (do_something). It has no implementation for that method. ConcreteClass inherits from AbstractClass and provides its own implementation of the abstract method.
When you try to create an instance of the abstract class using its constructor:
python# obj = AbstractClass() # raises a TypeError
Python will raise a TypeError because it can't create an instance of an abstract class. Instead, you need to inherit from the abstract class and provide your own implementation for the abstract methods.
This is useful when you want to define a hierarchy of classes where certain methods are required but can be implemented differently by subclasses. This way, you ensure that any concrete subclass provides its own implementation for those critical methods.
In summary, an abstract method in Python is a declaration without an implementation within an abstract class. You cannot instantiate the abstract class itself but must create concrete subclasses that implement these methods.
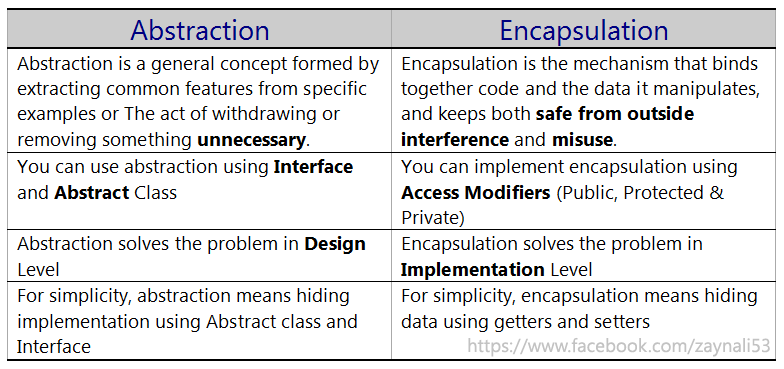
Difference between encapsulation and Abstraction in Python
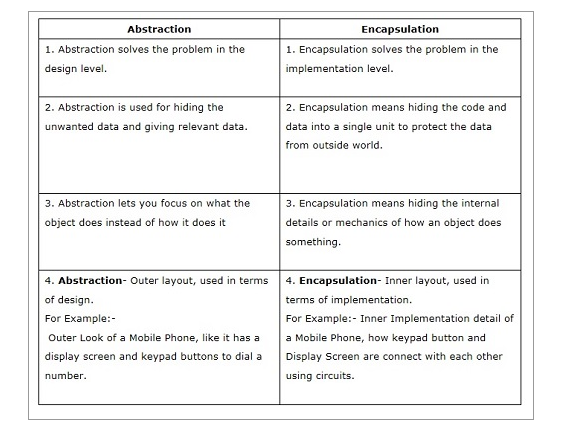
The age-old confusion between encapsulation and abstraction in programming! While they are often used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings in the context of object-oriented programming (OOP). Let's dive into the world of Python to clarify these concepts.
Abstraction
Abstraction is a fundamental concept in OOP that focuses on hiding complex implementation details from the outside world while only exposing essential information. In Python, you can achieve abstraction by using classes and objects to represent abstract concepts. Think of it as wrapping a complex problem into a neat package, making it easier to understand and interact with.
In Python, you can create an abstract class using the abc module (Abstract Base Classes). An abstract class serves as a blueprint for other classes that inherit from it, forcing them to implement specific methods or properties. This is useful when you want to define a common interface for a group of related classes without worrying about their concrete implementation.
For example:
pythonimport abc class AbstractShape(abc.ABC): @abc.abstractmethod def area(self): pass class Circle(AbstractShape): def init(self, radius): self.radius = radius def area(self): return 3.14 * (self.radius ** 2) class Rectangle(AbstractShape): def init(self, width, height): self.width = width self.height = height def area(self): return self.width * self.height
In this example, the AbstractShape class is an abstract class that defines the area() method. The Circle and Rectangle classes inherit from AbstractShape and implement their own version of the area() method.
Encapsulation
Encapsulation is the concept of hiding an object's internal state (data) and behavior (methods) from the outside world while only exposing a controlled interface through which other objects can interact with it. In Python, you can achieve encapsulation by using private variables (__) and public methods to manipulate them.
In Python, you can use the underscore prefix (_) to indicate that a variable or method is intended to be private. This does not provide complete encapsulation, but it serves as a convention for other developers to respect the object's internal state.
For example:
pythonclass Person: def init(self, name, age): self.__name = name self.__age = age def get_name(self): return self.__name def set_age(self, new_age): if 0 < new_age < 120: self.__age = new_age
In this example, the Person class encapsulates its internal state (__name and __age) by using private variables. The public methods get_name() and set_age() allow controlled access to these internal variables.
Key differences
To recap:
Abstraction is about hiding complex implementation details while only exposing essential information, often through abstract classes or interfaces. Encapsulation is about hiding an object's internal state and behavior from the outside world, controlling access through a public interface.While both concepts are crucial in OOP, they serve different purposes. Abstraction helps define common interfaces for related classes, whereas encapsulation ensures that objects maintain control over their internal state and behavior.
I hope this explanation has helped clarify the difference between encapsulation and abstraction in Python!





























