Csv file handling in python w3schools
Csv file handling in python w3schools
I'm happy to help!
Csv (Comma Separated Values) files are a common way to store and exchange tabular data between applications. Python has excellent libraries for working with csv files, including csv and pandas. Here's how you can handle csv files using python:
Reading a Csv File
The csv module in Python is the standard library for reading and writing csv files.
import csv
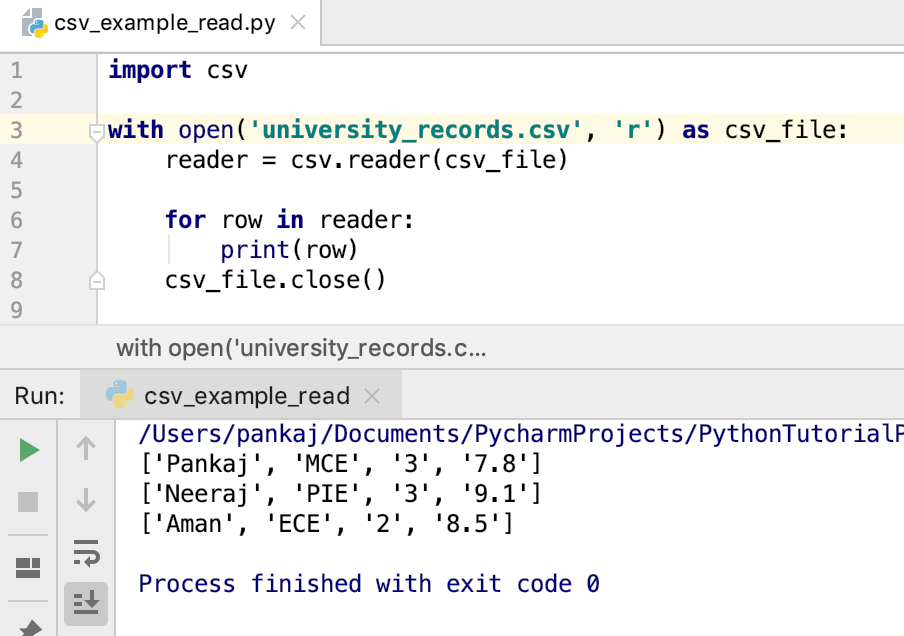
with open('example.csv', 'r') as file:
reader = csv.reader(file)
for row in reader:
print(row)
In this example, we're opening a file named example.csv and using the reader() function to read its contents. We then iterate over each row in the csv file and print it out.
Writing a Csv File
Similarly, you can use the writerow() method to write rows to a csv file:
import csv
with open('new_example.csv', 'w', newline='') as file:
writer = csv.writer(file)
writer.writerow(["First Name", "Last Name", "Age"]) # header row
writer.writerow(["John", "Doe", "30"])
writer.writerow(["Jane", "Smith", "25"])
In this example, we're creating a new csv file named new_example.csv and writing three rows to it.
pandas Library
The pandas library is another powerful tool for working with csv files in Python. It's a part of the NumPy project and provides data structures and operations for manipulating tabular data.
Here's how you can use pandas to read and write csv files:
import pandas as pd
Read a csv file
df = pd.read_csv('example.csv')
print(df)
Write a csv file
df.to_csv('new_example.csv', index=False)
In this example, we're reading a csv file named example.csv using the read_csv() function and printing out its contents. We then write these contents to a new csv file named new_example.csv.
Csv File Handling with Pandas
Here are some advanced methods for working with csv files using pandas:
Reading a specific column or row: You can select specific columns or rows from the csv file by specifying their names: df = pd.read_csv('example.csv', usecols=['First Name', 'Last Name']) # select specific columns
filtered_df = df[df['Age'] > 30] # filter data where age is greater than 30
df1 = pd.read_csv('file1.csv')
df2 = pd.read_csv('file2.csv')
merged_df = pd.concat([df1, df2]) # concatenate two dataframes
In conclusion, Python's csv and pandas libraries provide robust tools for handling csv files. Whether you need to read, write, or manipulate data in a csv file, these libraries have got you covered!
CSV writer Python
CSV (Comma Separated Values) is a plain text format used to store tabular data such as spreadsheets and databases. In Python, the csv module provides classes for reading and writing tabular data.
Writing CSV Files with Python
To write a CSV file using Python, you can use the csv module's writerow() function. Here is an example:
import csv
Create a list of dictionaries to represent your data
data = [
{'Name': 'John', 'Age': 25},
{'Name': 'Anna', 'Age': 30},
{'Name': 'Sam', 'Age': 20}
]
Open a file called 'example.csv' in write mode
with open('example.csv', 'w', newline='') as csvfile:
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=['Name', 'Age'])
Write the header row (column names)
writer.writeheader()
Write each row of data
for row in data:
writer.writerow(row)
print("CSV file written!")
In this example, we first create a list of dictionaries to represent our data. Each dictionary represents a single record, where the keys are the column names and the values are the actual data.
Next, we open a CSV file called example.csv in write mode using the open() function. We specify the newline='' parameter to ensure that the CSV writer doesn't add extra newlines to the file.
We then create a csv.DictWriter object, passing it our open file and the list of column names (['Name', 'Age']) as arguments. This object allows us to write dictionaries (which represent individual records) directly to the CSV file.
First, we call the writeheader() method on the writer to write the header row (the column names) to the file.
Next, we loop through each record in our data list and write it to the file using the writerow() method. This method takes a dictionary as an argument, which is used to populate the corresponding columns in the CSV file.
Finally, we print a message to indicate that the CSV file has been written successfully.
Customizing the CSV Writer
You can customize the CSV writer by providing additional arguments to the writeheader() and writerow() methods. For example:
writer.writerow({'Name': 'John', 'Age': 25}, delimiter=';')
This would use a semicolon (;) instead of a comma (,) as the delimiter.
")
writer.writerow({'Name': 'John', 'Age': 25}, quotechar='`')
This would use backticks () instead of double quotes ("`) to enclose values containing commas.
By providing these additional arguments, you can customize the CSV writer to produce the exact format you need for your specific application.





























