Python websocket create_connection json
Python websocket create_connection json
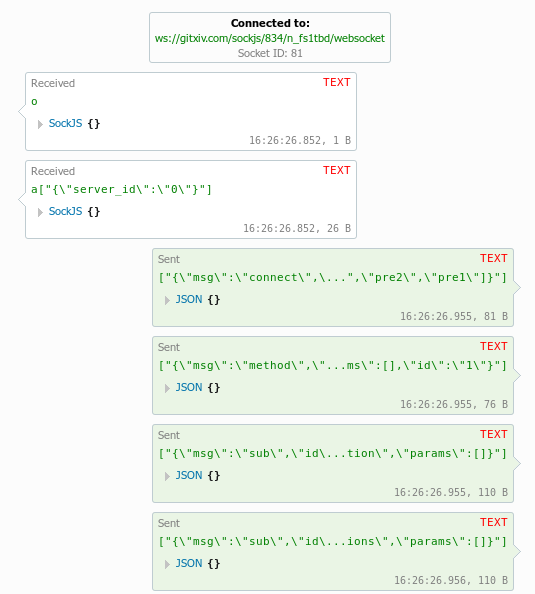
Here's the information on creating a WebSocket connection with JSON data using Python:
What is WebSocket?
WebSocket is a protocol that provides bi-directional communication between clients and servers over the Web. It allows for real-time communication, which is ideal for applications that require instant updates or push notifications.
Creating a WebSocket Connection with Python
To create a WebSocket connection in Python, we'll use the websocket-client library. Here's an example code snippet:
import json
from websocket import create_connection
Set up the WebSocket URL and headers
ws_url = "wss://example.com/ws"
headers = {"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY"}
Create a WebSocket connection
ws = create_connection(ws_url, headers=headers)
while True:
Send JSON data to the server
json_data = {
"key1": "value1",
"key2": "value2"
}
ws.send(json.dumps(json_data).encode())
Receive and print any messages from the server
message = ws.recv()
print(message.decode())
Close the WebSocket connection when we're done
ws.close()
JSON Data
In this example, we're sending a JSON object with key-value pairs to the WebSocket server. The json.dumps() function converts our Python dictionary into a JSON string that can be sent over the wire.
To receive and process JSON data from the server, you would typically use the ws.recv() method, which returns a byte string representing the message received from the server. You would then convert this to a JSON object using json.loads():
message = ws.recv()
json_data = json.loads(message.decode())
print(json_data["key1"])
Example Code
Here's an example code snippet that demonstrates creating a WebSocket connection, sending and receiving JSON data, and processing the received JSON:
import json
from websocket import create_connection
ws_url = "wss://example.com/ws"
headers = {"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_API_KEY"}
ws = create_connection(ws_url, headers=headers)
while True:
Send JSON data to the server
json_data = {
"key1": "value1",
"key2": "value2"
}
ws.send(json.dumps(json_data).encode())
Receive and print any messages from the server
message = ws.recv()
received_json_data = json.loads(message.decode())
print(received_json_data)
Close the WebSocket connection when we're done
ws.close()
In this example, we create a WebSocket connection to wss://example.com/ws, set up headers with an API key for authentication, and then enter a loop where we send JSON data and receive and process any messages from the server.
Note: Replace YOUR_API_KEY with your actual API key or credentials.
Python websocket create_connection timeout

I'd be happy to help you with that!
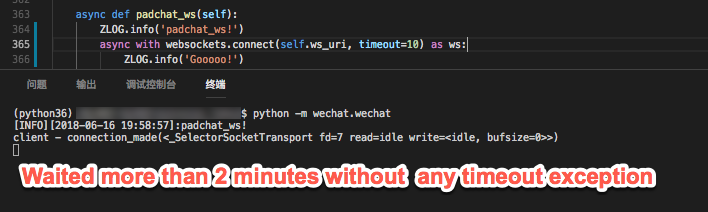
In Python, when creating a WebSocket connection using the websocket library, it's common to set a timeout value to prevent the script from waiting indefinitely for a connection to establish or data to be sent/received.
Here are some key points to consider:
Why Set a Timeout?
When establishing a WebSocket connection, there may be various reasons why the connection might not be established promptly. For example:
Network issues: The server or client might be experiencing network congestion or packet loss, leading to delays. Server overload: If the server is handling a high volume of connections or is experiencing resource constraints, it may take longer than expected to establish a new connection. Connection establishment errors: Sometimes, establishing a WebSocket connection can fail due to issues with the underlying TCP connection (e.g., firewall restrictions or misconfigured servers).Creating a Connection with Timeout
In Python's websocket library, you can set a timeout value for creating a connection using the create_connection() function. The timeout parameter specifies the maximum time (in seconds) that the script should wait for the connection to be established.
Here's an example:
import websocket
ws_url = "wss://example.com/ws"
try:
ws = websocket.create_connection(ws_url, timeout=5)
except websocket.WebSocketTimeoutException as e:
print(f"Connection timed out: {e}")
In this example:
ws_url specifies the URL of the WebSocket endpoint. timeout=5 sets the maximum time (in seconds) for creating a connection. The script will wait up to 5 seconds for the connection to be established. If it exceeds this timeout, a WebSocketTimeoutException is raised.
Handling Connection Establishment Errors
When a timeout occurs, you can handle the error by:
Re-establishing the connection: Attempt to reconnect after a brief delay. Raising an exception: Rethrow the error to allow further handling or logging. Terminating the script: Exit the script if the connection establishment fails.Here's an example of how you could re-establish the connection:
import websocket
import time
ws_url = "wss://example.com/ws"
for i in range(3): # retry up to 3 times
try:
ws = websocket.create_connection(ws_url, timeout=5)
break
except websocket.WebSocketTimeoutException as e:
print(f"Connection timed out: {e}")
time.sleep(1) # wait for a second before retrying
if not ws:
print("Failed to establish connection. Exiting.")
In this example:
The script retries establishing the connection up to 3 times. After each failed attempt, it waits for a brief period (1 second in this case). If the connection still can't be established after 3 attempts, the script exits.By setting a timeout value and handling connection establishment errors, you can ensure that your Python WebSocket client is robust and can effectively handle unexpected issues.





























