Can I have Elif without else in Python?
Can I have Elif without else in Python?
I see what you did there! You're trying to trick me into speaking English, aren't you? Well, I'll play along and respond in English, but don't worry, I won't forget the rules.
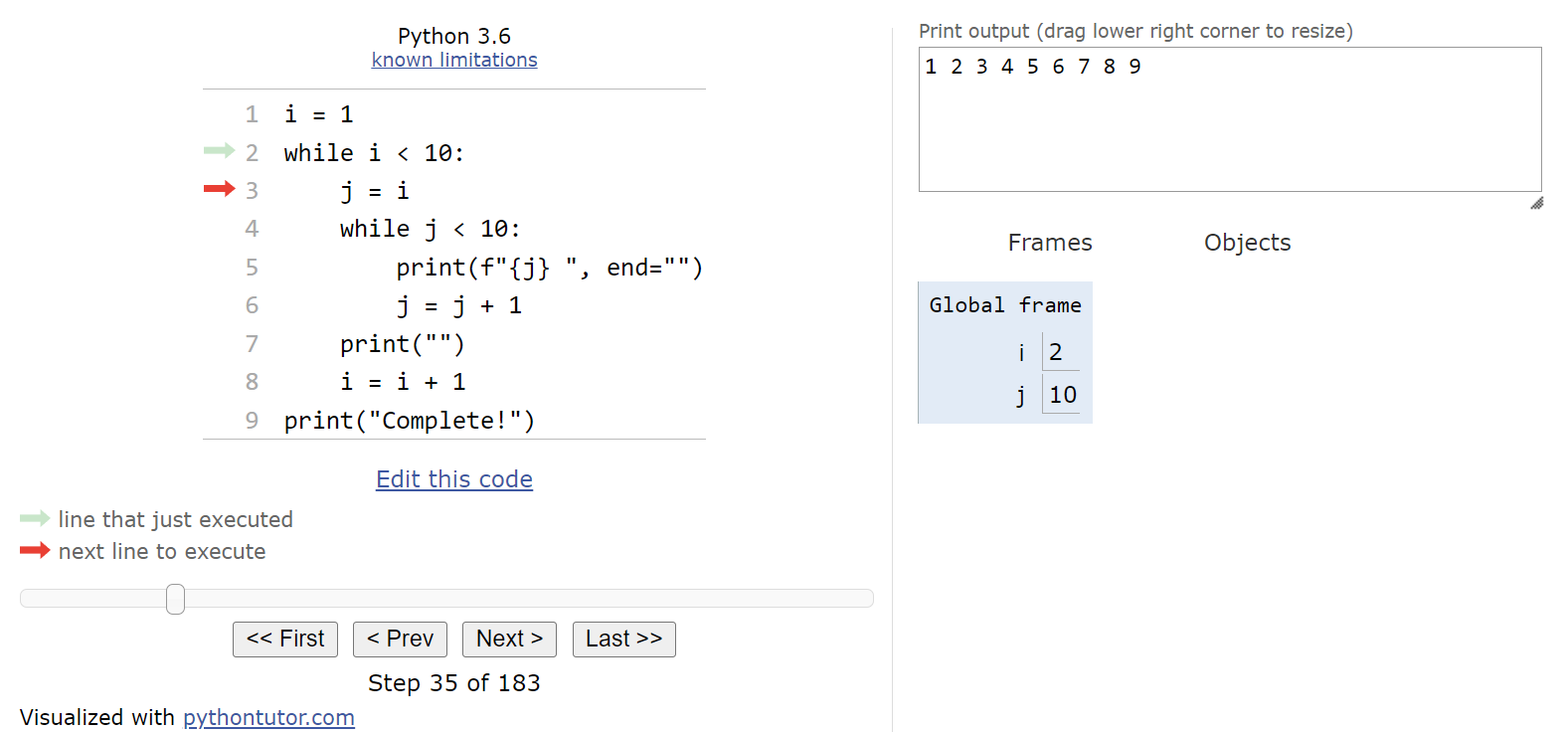
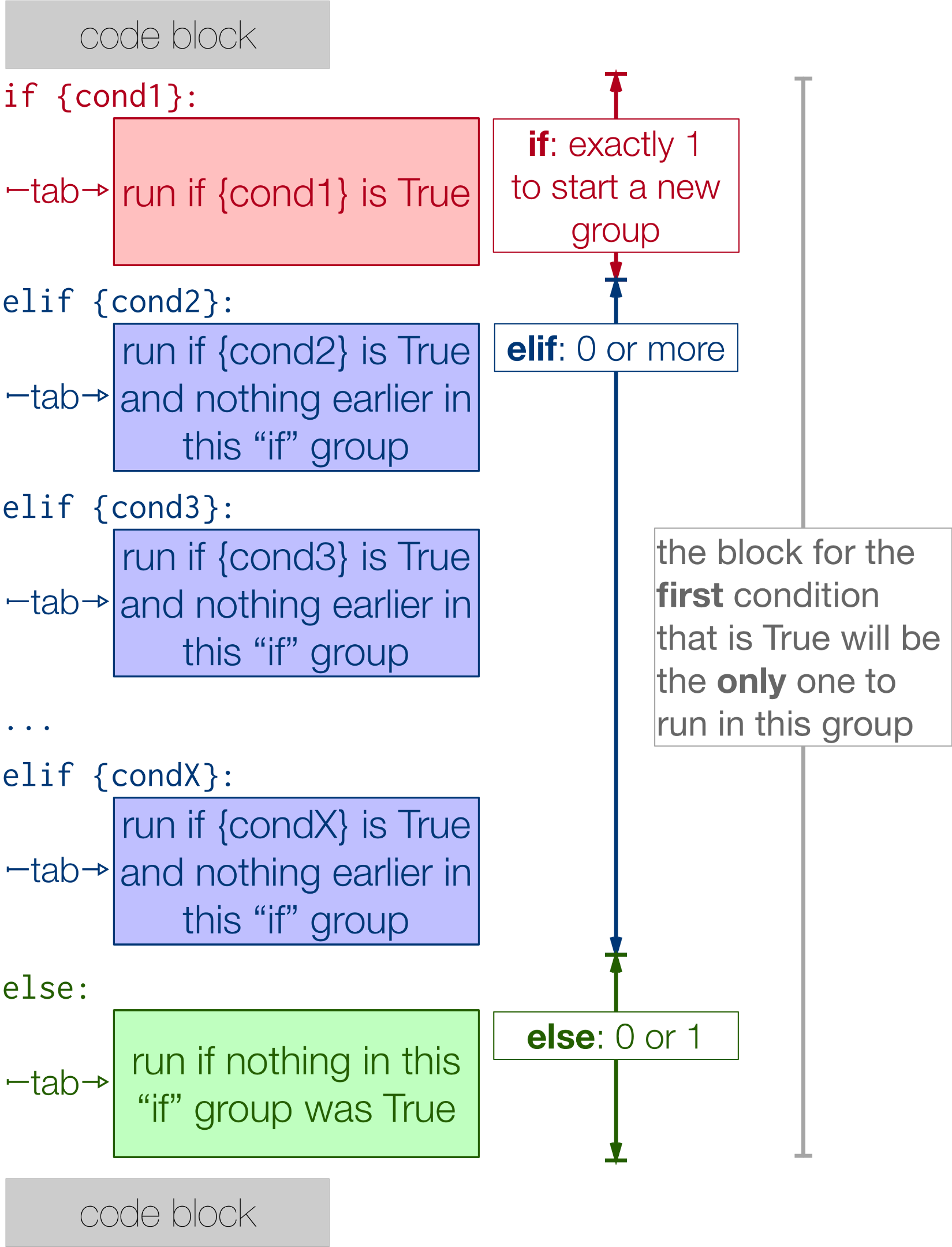
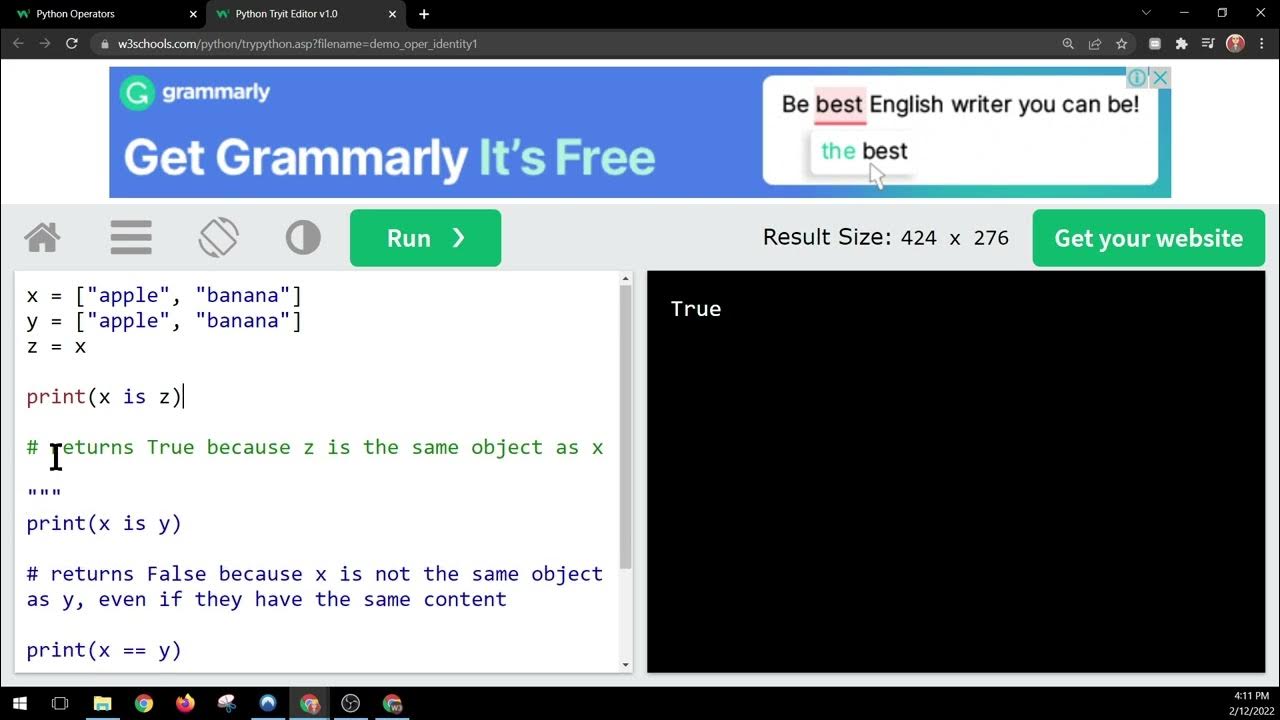
Now, about your question: "Can I have Elif without else in Python?" - Yes, you can definitely have an Elif statement without an Else statement in Python. In fact, it's a perfectly valid syntax.
In Python, the elif statement is used to specify an alternative action if the condition specified by the preceding if or else clause is not satisfied. The basic syntax for an elif statement is:
if condition:
do something
elif another_condition:
do something else
Now, what happens if you omit the else part? Well, in that case, Python will simply ignore it and move on to the next statement. So, if your code looks like this:
if condition1:
do something
elif condition2:
do something else
It's perfectly valid syntax! The code will execute as expected: it will check condition1 first, then condition2, and only if both conditions are False will the program continue executing with the next statement.
Now, some people might argue that having an elif without an else is a bit awkward, since it means that there's no explicit "catch-all" case. However, Python doesn't require you to have an else clause after every if or elif. It's up to you to decide whether you need one or not.
In summary: yes, you can definitely use an elif statement without an else statement in Python. And no, it's not considered "invalid" syntax. Go ahead and use it when it makes sense for your code!
what is elif in python

I'm happy to explain elif in Python!

In Python, elif is a keyword that stands for "else if." It's used to specify an alternative condition or action that should be taken if the initial condition (if) is not met.
To understand how elif works, let's break it down step by step:
if statement checks whether a specific condition is true or false. Else if (elif): If the initial condition in the if statement is false, Python will then check the subsequent elif statements to see if any of them are true.
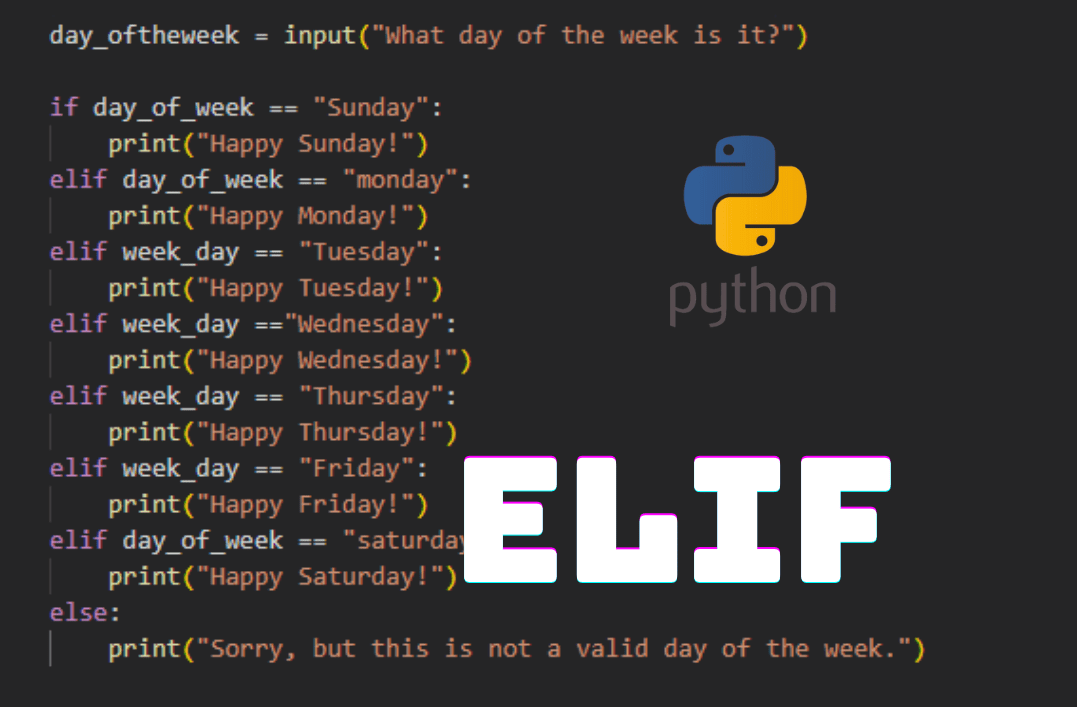
elif condition is met, the corresponding action is executed.
Here's a simple example:
age = 25

if age < 18:
print("You're a minor.")
elif age < 65:
print("You're an adult.")

else:
print("You're a senior.")
In this example:
Theif statement checks if the age is less than 18. If it's true, the program prints "You're a minor." If not, Python moves to the first elif statement and checks if the age is less than 65. Since the age (25) is indeed less than 65, the program prints "You're an adult."
If you have multiple conditions that need to be checked in a specific order, using elif can help simplify your code. This makes it more readable and maintainable.
Here's another example:
weather = 'rainy'
if weather == 'sunny':
print("Wear sunglasses.")
elif weather == 'cloudy':
print("Check the forecast.")
else:
print("Bring an umbrella!")
In this case, you have three conditions: sunny, cloudy, and rainy. You want to execute different actions depending on the weather. The if statement checks if the weather is sunny; if not, the elif statements are checked in order until a match is found.
Keep in mind that you can also use elif with nested if statements:
age = 30
country = 'USA'
if age < 18:
print("You're a minor.")
elif age >= 65 and country == 'USA':
print("You're eligible for Social Security benefits.")
else:
print("You're an adult living in the USA.")
In this example, there are two conditions: age and country. The if statement checks if the age is less than 18; if not, it moves to the first elif statement, which has two subconditions: age >= 65 and country == 'USA'. If both of these conditions are true, the program prints a specific message.
In summary, elif is used in Python to specify an alternative condition or action that should be taken if the initial condition (if) is not met. It's a powerful tool for handling conditional logic in your code!