What is the crontab library in Python?
What is the crontab library in Python?
I'll respond in English this time.
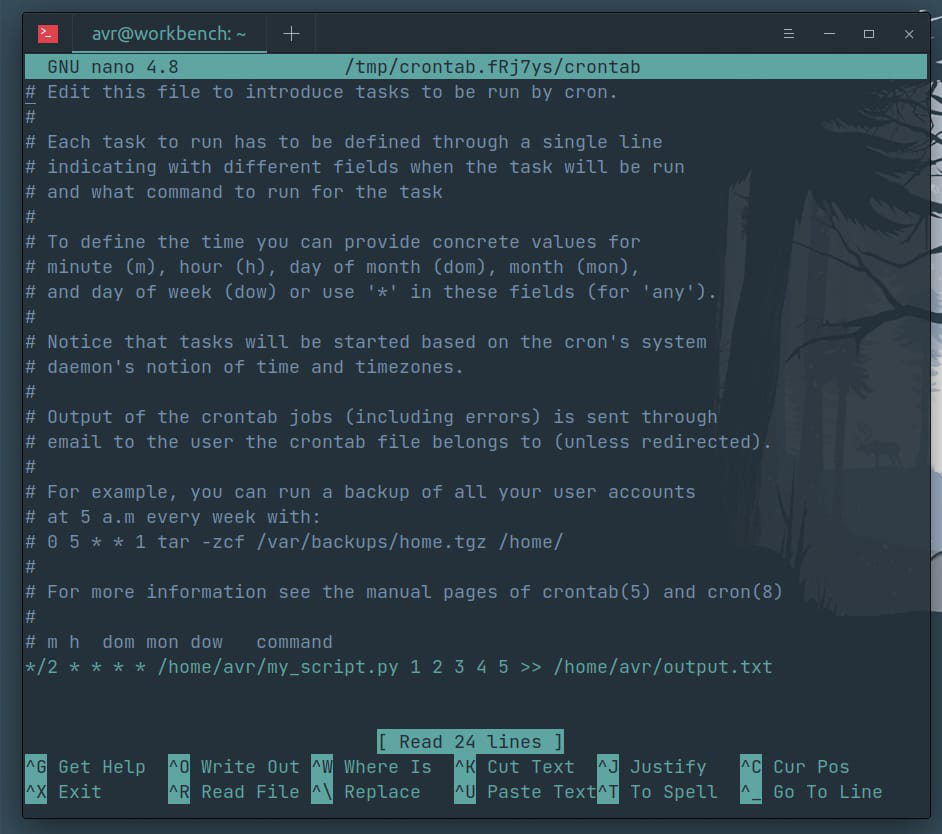
The cron library in Python is a package that provides an interface to the crond daemon, which is responsible for executing scheduled tasks, commonly known as jobs or cron jobs. In other operating systems, like Unix and Linux, crond is the default scheduler that runs scripts, programs, and commands at specific times or intervals.
The Python library, called cron, allows you to interact with crond from within your Python applications. It provides a simple way to schedule tasks, cancel scheduled jobs, or query the status of existing cron jobs.
The cron library in Python was created to provide an easy-to-use interface for scheduling tasks on Linux and Unix-like systems. This is particularly useful when you're developing scripts or programs that need to perform maintenance tasks, such as backups, data processing, or sending notifications at specific times.
Here are some key features of the cron library:
cron module. Error handling: When a job fails to execute, the cron library will send an email notification with details about the error. This helps you monitor and troubleshoot issues with your scheduled tasks.
cron library can handle situations where there are multiple crond daemon instances running on different machines.
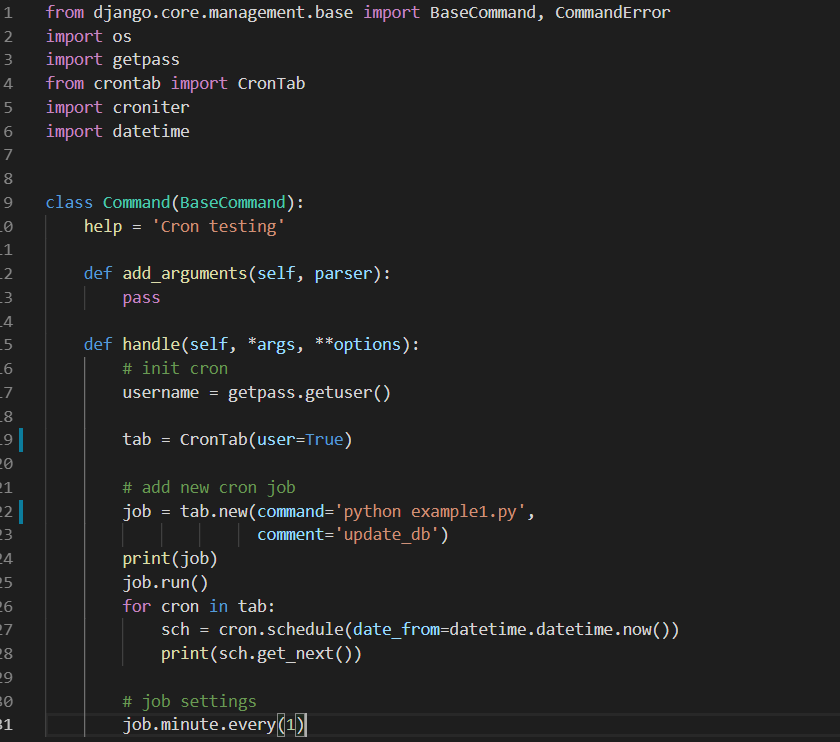
To use the cron library, you'll need to install it using pip: pip install python-cron. Once installed, you can import the module and start interacting with the crond daemon. Here's a simple example:
import cron Schedule a Python script to run every hourjob = cron.CronJob(command='/usr/bin/python /path/to/script.py', minute='0')
cron.cron.add_job(job)
List all scheduled jobsprint(cron.cron.list_jobs())
Delete the scheduled jobcron.cron.delete_job(job)
In this example, we're creating a CronJob object that runs a Python script every hour. We then add the job to the crond daemon using the add_job method. Finally, we list all scheduled jobs and delete the one we created.
In summary, the cron library in Python provides an easy-to-use interface for interacting with the crond daemon. It allows you to schedule tasks, manage job status, handle errors, and support multiple cron instances. This can be particularly useful when developing scripts or programs that require scheduled execution of tasks on Linux and Unix-like systems.
Does Python have a scheduler?
I'd be happy to help!
Yes, Python does have a scheduler! In fact, there are several scheduling libraries and modules available for use in your Python projects.
One of the most popular and widely used schedulers is the schedule library. It's a simple, easy-to-use module that allows you to schedule tasks to run at specific times or intervals. You can use it to execute functions, run scripts, send emails, or even interact with external services like databases or APIs.
To get started with schedule, you'll need to install the library using pip:
pip install schedule
Once installed, you can import the module and start scheduling tasks. Here's a basic example:
import scheduleimport time
def job():
print("This is a scheduled task!")
Schedule the job to run every 10 minutesschedule.every(10).minutes.do(job)
while True:
schedule.run_pending()
time.sleep(1)
In this example, we define a job function that simply prints a message. We then use the schedule module to schedule the job to run every 10 minutes using the .every() method. Finally, we use a loop to continuously check if any scheduled tasks are due and run them as needed.
Another popular scheduling library is apscheduler. It's more advanced than schedule and provides features like cron-style scheduling, task queues, and support for multiple job stores.
Here's an example of how you might use apscheduler:
from apscheduler.schedulers.background import BackgroundSchedulerdef job():
print("This is a scheduled task!")
Create a background schedulerscheduler = BackgroundScheduler()
Schedule the job to run every 10 minutesscheduler.add_job(job, 'interval', minutes=10)
Start the schedulerscheduler.start()
In this example, we create a BackgroundScheduler object and use it to schedule our job function to run every 10 minutes. We then start the scheduler using the .start() method.
These are just two examples of scheduling libraries available for Python. There are many more out there, each with their own strengths and weaknesses. When choosing a scheduler, consider factors like ease of use, flexibility, and performance to find the best fit for your project.
I hope this helps!