Python package manager
Python package manager

The Python Package Manager!
What is it?
The Python Package Manager, also known as pip (short for "Pip Installs Packages"), is a command-line tool used to install and manage packages for Python projects. It's the primary package manager for Python and is widely used in the Python community.
How does it work?
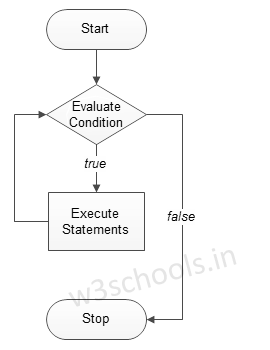
When you run pip with an install command, it searches for the requested package in various locations:
If a package is found, pip downloads and installs it. If not found, it raises an error.
Key features:
Package installation: Install packages from PyPI or local directories usingpip install <package_name>. Package management: Update (pip install --upgrade <package_name>), uninstall (pip uninstall <package_name>), and list all installed packages (pip freeze). Dependency resolution: Automatically resolve dependencies between packages, ensuring correct installation order. Customizable behavior: User-defined configuration files allow fine-tuning of package installation and management.
Advantages:
Easy package management: Simplifies the process of installing, updating, and removing packages for Python projects. Wide package availability: Access a vast repository of open-source packages on PyPI, including popular libraries like NumPy and Pandas. Community-driven:pip is maintained by the Python community, ensuring that it stays up-to-date with the latest developments in package management.
Common use cases:
New project setup: Install required packages for a new Python project usingpip install -r requirements.txt. Package updates: Update all installed packages to their latest versions using pip install --upgrade. Dependency troubleshooting: Resolve issues with package dependencies using pip freeze and manual inspection.
In summary, pip is an essential tool for any Python developer, providing a convenient way to manage packages and dependencies in Python projects.
How's that?
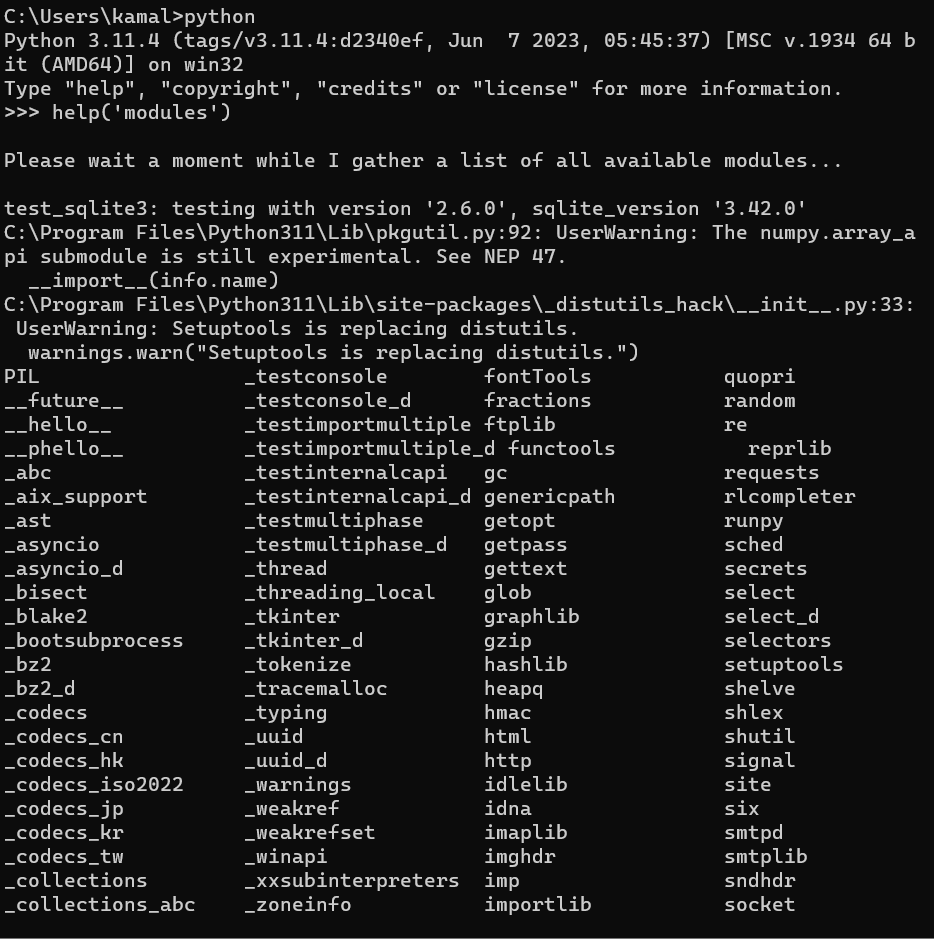
What are all the packages in Python?
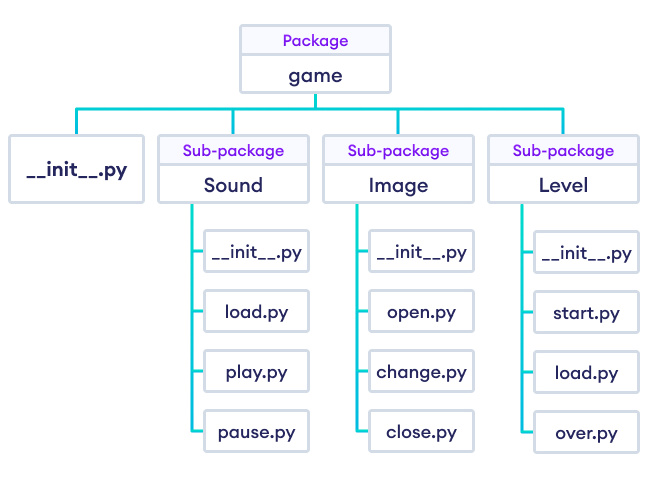
Here's a comprehensive list of packages in Python:
Built-in Modules
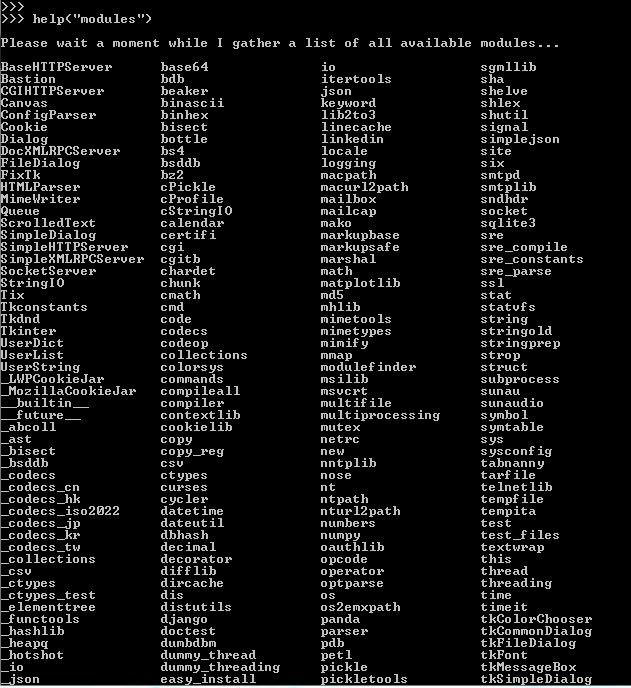
Python has several built-in modules that come bundled with the interpreter, including:
math for mathematical operations
time for working with timestamps and scheduling random for generating random numbers re (regular expressions) os for interacting with the operating system sys for accessing internal Python variables json for parsing JSON data
Utilities
Python has several utility modules that provide useful functionality, including:
argparse for handling command-line arguments datetime for working with dates and times hashlib for calculating message digests (e.g., MD5, SHA256) collections provides specialized container classes such as deque and defaultdict
File I/O
Python has several modules that provide support for file input/output operations:
open allows you to open a file in different modes (e.g., read, write, append) os.path helps with working with files and directories shutil provides functions for copying and moving files
Network Programming
Python has several modules that provide support for network programming:
socket provides low-level socket functionality select allows you to monitor multiple sockets for events (e.g., read, write) http.client and urllib are used for making HTTP requests ssl supports secure (TLS/SSL) connections
Database Connectivity
Python has several modules that provide support for connecting to various databases:
sqlite3 for working with SQLite databases psycopg2 for connecting to PostgreSQL databases mysqlclient for connecting to MySQL databases pymssql for connecting to Microsoft SQL Server databases
XML/HTML Processing
Python has several modules that provide support for processing XML and HTML data:
xml.etree.ElementTree provides a simple API for working with XML documents xml.dom.minidom allows you to create and manipulate XML documents html.parser is used for parsing HTML documents
Web Frameworks
Python has several modules that provide support for building web applications:
flask is a lightweight web framework (microframework) django is a high-level web framework with an ORM (Object Relational Mapping)
Scientific Computing
Python has several modules that provide support for scientific computing, including:
numpy provides support for large, multi-dimensional arrays scipy provides functions for scientific and engineering applications pandas provides data structures for working with structured data
Machine Learning
Python has several modules that provide support for machine learning, including:
scikit-learn is a machine learning library keras is an open-source neural network library tensorflow and theano are deep learning libraries (Python wrappers around C++ code)
This list is not exhaustive, but it covers many of the most widely-used packages in Python.