How to make gRPC call in python?
How to make gRPC call in python?
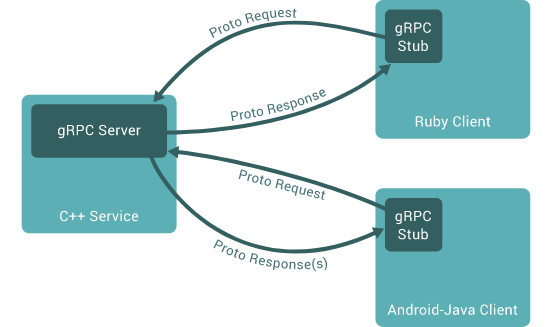
To make a gRPC call in Python, you'll need to use the grpc package and create a client stub that connects to your gRPC server.
Here's a step-by-step guide:
Install the necessary packages:
You'll need to install the following packages using pip:
pip install grpc protobuf
Generate the Python code for your service:
Using the protoc compiler, generate the Python code for your service. For example, if you have a .proto file named greeter.proto, run the following command:
protoc -I=. --python_out=. --grpc_out=. greeter.proto
This will generate two files: greeter_pb2.py and greeter_pb2_grpc.py.
Create a client stub:
In your Python code, import the generated .pb2 file:
import greeter_pb2
from google.protobuf import any
Next, create an instance of your gRPC service using the generated stub:
stub = greeter_pb2.GreeterStub(grpc.insecure_channel('localhost:50051'))
In this example, Greeter is the name of your gRPC service, and localhost:50051 is the address of your gRPC server.
Make a gRPC call:
Now you can make a gRPC call using the client stub. For example, to call the SayHello method:
request = greeter_pb2.HelloRequest(name='John')
response = stub.SayHello(request)
print(response.message) # prints "Hello John!"
In this example, SayHello is a method on your gRPC service that takes a HelloRequest message as input and returns a HelloResponse message.
Handle errors:
When making a gRPC call, you should always handle potential errors:
try:
response = stub.SayHello(request)
except grpc.RpcError as e:
print(f"Error calling SayHello: {e.details()}")
In this example, we catch any RpcError exceptions raised by the gRPC client and print an error message.
Full code example:
Here's a complete Python code example that demonstrates making a gRPC call:
import greeter_pb2
from google.protobuf import any
from grpc import insecure_channel
Create a client stub
stub = greeter_pb2.GreeterStub(insecure_channel('localhost:50051'))
Make a gRPC call
request = greeter_pb2.HelloRequest(name='John')
response = stub.SayHello(request)
print(response.message) # prints "Hello John!"
try:
response = stub.SayHello(request)
except grpc.RpcError as e:
print(f"Error calling SayHello: {e.details()}")
In this example, we assume you have a greeter.proto file containing your gRPC service definition and that you've generated the Python code for your service using the protoc compiler.
gRPC Python tutorial
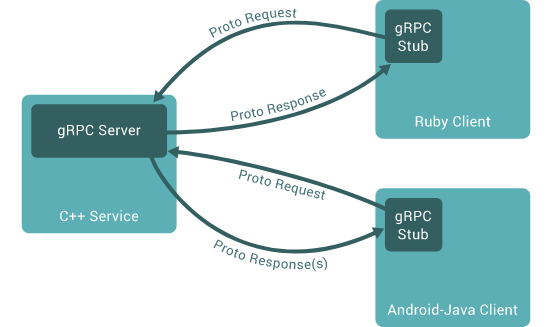
Here is a comprehensive guide to getting started with gRPC Python:
Introduction
gRPC is an open-source framework for building scalable, high-performance APIs that can be used across various platforms, including mobile and web applications. It uses Protocol Buffers (protobuf) as the data serialization format, which ensures efficient and reliable communication between clients and servers.
Prerequisites
Before you begin with gRPC Python, make sure you have:
Python 3.5 or higher installed pip package manager installed (pip is the package installer for Python) A code editor of your choice (e.g., Visual Studio Code, PyCharm)
Step 1: Install gRPC and Protocol Buffers
Run the following command in your terminal/command prompt to install gRPC and Protocol Buffers:
pip install grpc protobuf
This will install both the gRPC library (grpc) and the Protocol Buffers compiler (protoc).
Step 2: Define Your Service Using Protocol Buffers
Create a new file called greeter.proto (or any other name you prefer) with the following content:
syntax = "proto3";
package greeter;
service Greeter {
rpc SayHello(HelloRequest) returns (HelloResponse) {}
}
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
message HelloResponse {
string message = 1;
}
This defines a Greeter service with a single method, SayHello, which takes a HelloRequest object and returns a HelloResponse object. The request contains a name field, while the response contains a message field.
Step 3: Generate Code for Your Service
Use the Protocol Buffers compiler (protoc) to generate code for your service:
protoc -I=. --python_out=. greeter.proto
This will generate a new file called greeter_pb2.py that contains the Python implementation of your service.
Step 4: Implement Your Service
Create a new file called greeter_server.py with the following content:
import grpc
from greeter_pb2 import Greeter
from greeter_pb2 import HelloRequest
from greeter_pb2 import HelloResponse
class GreeterServer(Greeter):
def SayHello(self, request: HelloRequest) -> HelloResponse:
return HelloResponse(message=f"Hello, {request.name}!")
def main():
server = grpc.server(futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10))
GreeterServer.add_to_server(server)
print("gRPC server listening on port 50051...")
server.add_insecure_port("[::]:50051")
server.start()
if name == "main":
main()
This implementation defines a GreeterServer class that implements the SayHello method. The main function sets up a gRPC server that listens on port 50051.
Step 5: Create a Client
Create a new file called greeter_client.py with the following content:
import grpc
from greeter_pb2 import Greeter
from greeter_pb2 import HelloRequest
from greeter_pb2 import HelloResponse
def main():
channel = grpc.insecure_channel('localhost:50051')
client = Greeter(channel)
request = HelloRequest(name='John')
response = client.SayHello(request)
print(response.message)
if name == "main":
main()
This implementation defines a main function that sets up a gRPC client that connects to the server on port 50051. It then sends a HelloRequest message and prints the response.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you learned how to install gRPC and Protocol Buffers, define your service using protocol buffers, generate code for your service, implement your service, and create a client. This is just the beginning of your gRPC journey, but with these basics under your belt, you're ready to start building more complex APIs and applications!