How to get a part of a list in Python?
How to get a part of a list in Python?
I'd be happy to help! Getting a part of a list in Python can be achieved through various methods, which I'll outline below.
Method 1: Using Slicing
One way to get a part of a list is by using slicing. This method allows you to specify the start and end indices of the range you want to retrieve from the original list. The basic syntax for slicing is as follows:
list_name[start:stop]
In this syntax, start represents the starting index (inclusive), and stop represents the ending index (exclusive). If you omit the start index, it defaults to 0, which means the first element in the list. If you omit the stop index, it defaults to the end of the list.
Here's an example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
print(my_list[1:3]) # Output: [2, 3]
In this example, we're retrieving elements 1 and 2 from the my_list. Note that the stop index is exclusive, which means it doesn't include element 3.
Method 2: Using Negative Indices
Another way to get a part of a list is by using negative indices. When you use negative indices, Python counts from the end of the list instead of the beginning.
The syntax for using negative indices is as follows:
list_name[-n:]
In this syntax, n represents the number of elements you want to retrieve from the end of the list.
Here's an example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
print(my_list[-2:]) # Output: [4, 5]
In this example, we're retrieving the last two elements from the my_list.
Method 3: Using List Comprehensions
If you want to get a part of a list based on certain conditions or transformations, you can use list comprehensions. This method allows you to create new lists by iterating over an existing list and applying specific operations.
Here's an example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
even_numbers = [x for x in my_list if x % 2 == 0]
print(even_numbers) # Output: [2, 4]
In this example, we're creating a new list called even_numbers that only includes the even numbers from the original my_list.
Method 4: Using the random Module
If you want to randomly select elements from a list, you can use the random module. This method allows you to specify the number of elements you want to retrieve and the probability of each element being selected.
Here's an example:
import random
my_list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
selected_elements = random.sample(my_list, 2)
print(selected_elements) # Output: [randomly selected elements, e.g., [3, 5]]
In this example, we're randomly selecting two elements from the my_list.
In conclusion, Python provides various ways to get a part of a list. By using slicing, negative indices, list comprehensions, or the random module, you can extract specific elements or ranges of elements from an original list.
What is list slicing in Python?
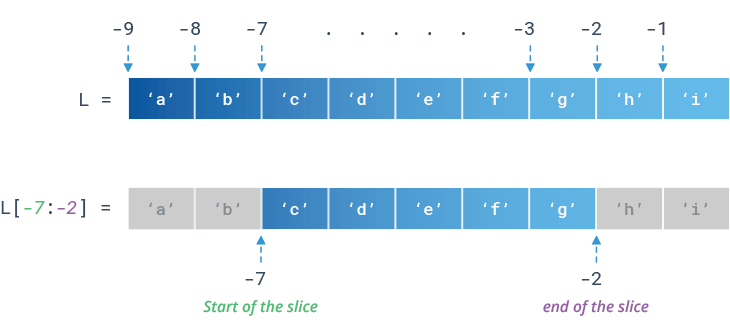
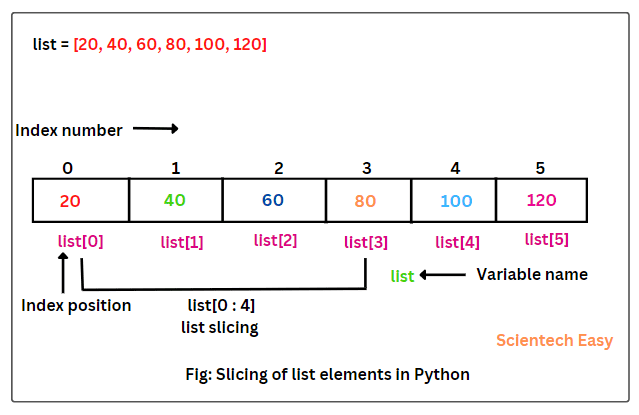
List slicing in Python refers to the process of selecting a subset of elements from a list and returning them as a new list. This is achieved by specifying a range or a set of indices that define the portion of the original list you want to extract.
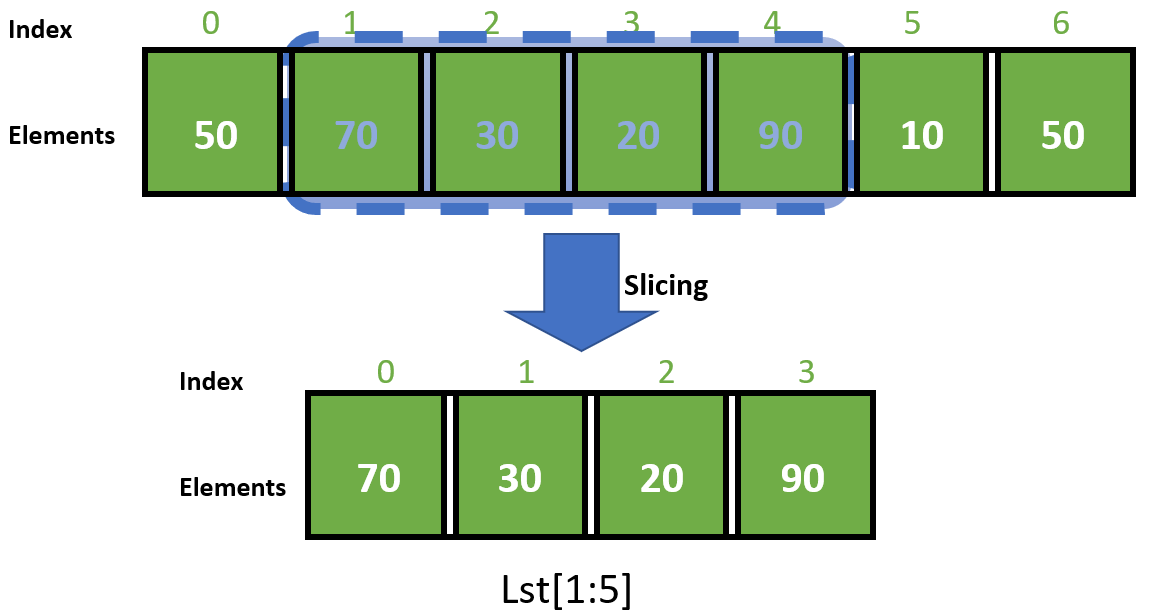
In its most basic form, list slicing involves using square brackets [] to enclose the indices or range you want to select. The general syntax is as follows:
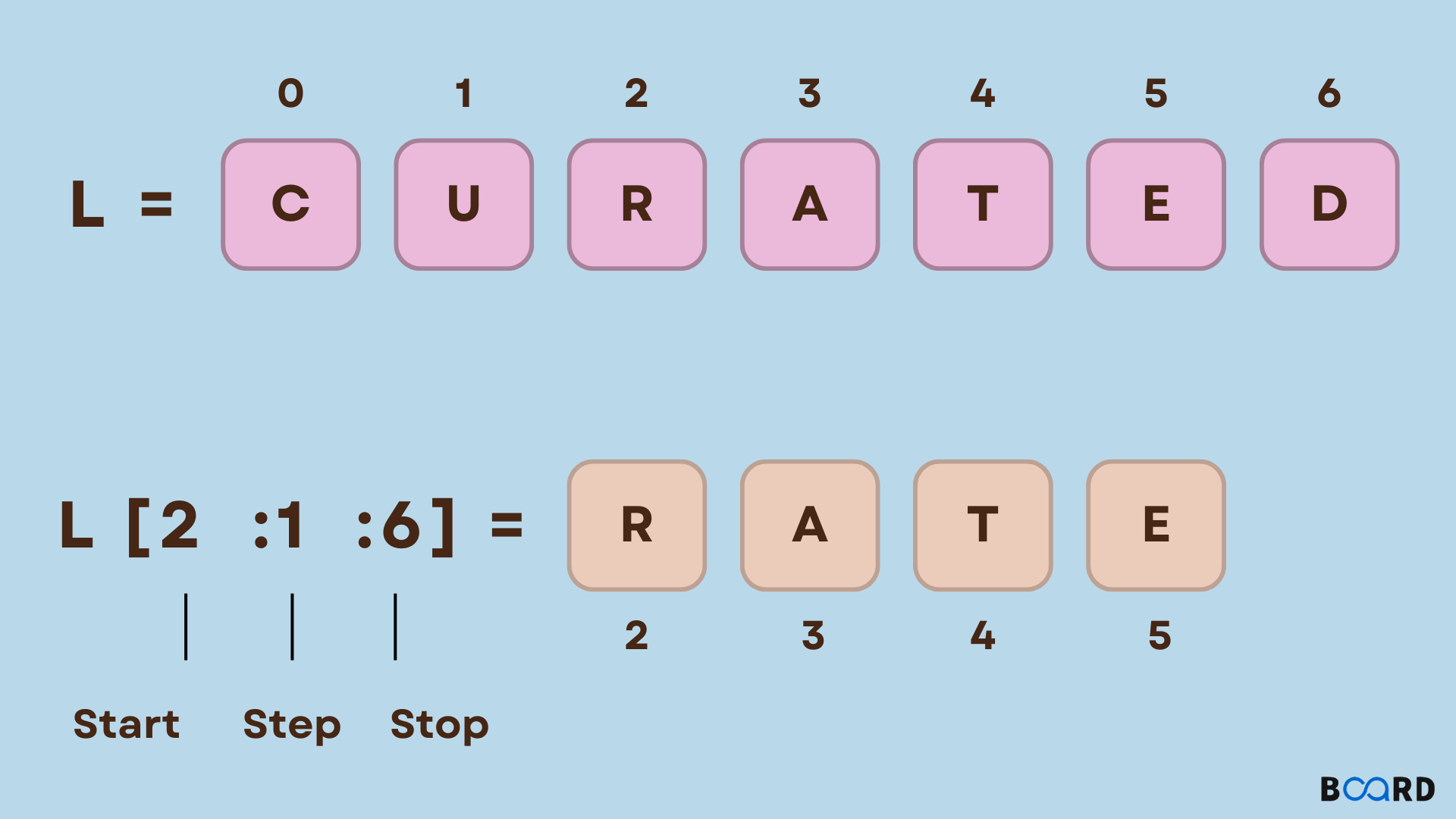
list[start:stop:step]

start: This is the index where the slice starts (inclusive). If omitted, it defaults to 0. stop: This is the index where the slice ends (exclusive). If omitted, it defaults to the end of the list. step: This is the interval between elements in the slice. If omitted, it defaults to 1.
Here are some examples of how you can use list slicing:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
Get the first two elements
print(numbers[:2]) # Output: [1, 2]
Get the last two elements
print(numbers[-2:]) # Output: [5, 6]
Get every other element starting from the second one
print(numbers[1::2]) # Output: [2, 4, 6]
Get a range of elements (from 1 to 3)
print(numbers[1:3]) # Output: [2, 3]
You can also use negative indices to count from the end of the list. For instance:
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]
Get the last two elements
print(numbers[-2:]) # Output: [5, 6]
Get every other element starting from the second one from the end
print(numbers[-1::2]) # Output: [6, 4]
List slicing is a powerful tool in Python that allows you to manipulate and extract data from lists with ease. It's commonly used in data processing, manipulation, and analysis tasks.
Note that list slicing does not modify the original list; it creates a new list containing the selected elements.