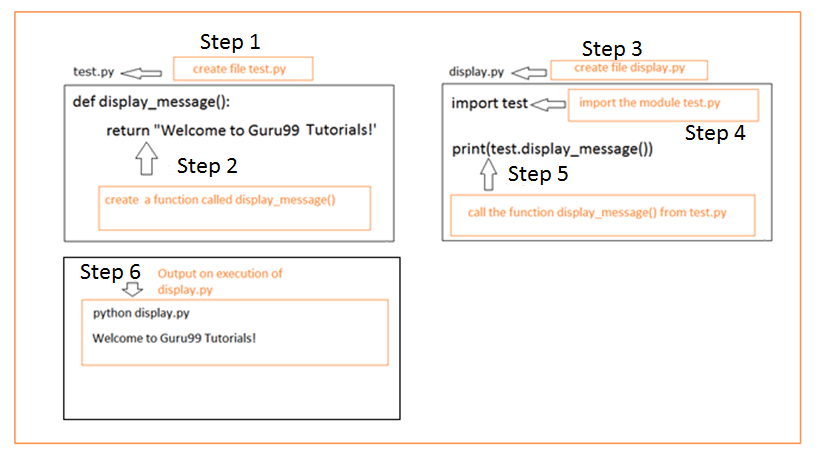
What does import os path do in Python?
What does import os path do in Python?
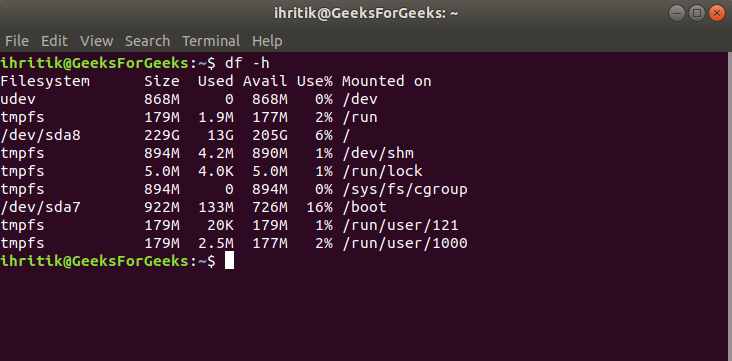
The import os and import path statements in Python are used to access the functions and variables provided by these modules.
Importing the "os" Module:
When you import the os module, you gain access to a wide range of operating system-related functionalities. The os module provides a way to use Python programs that can run on multiple platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux. Here are some key features of the os module:
os.chdir().
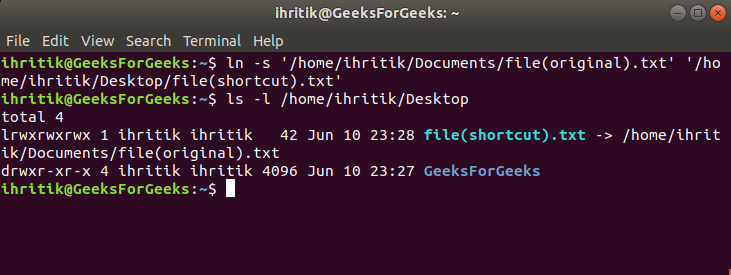
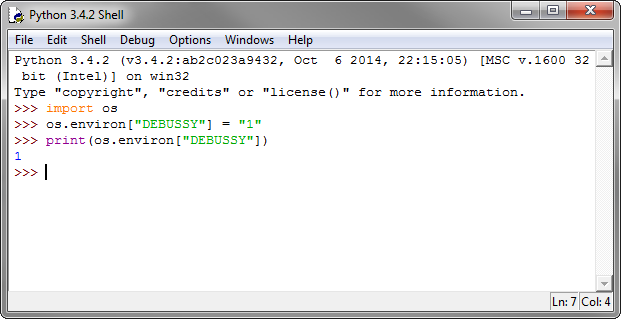
os module provides functions for performing file operations such as creating (os.mkdir()), renaming (os.rename()), and deleting (os.remove()) files. Environment Variables: You can access environment variables using os.environ. Process Execution: You can execute system-level commands (e.g., shell scripts) using os.system() or run subprocesses with subprocess.Popen.
Importing the "path" Module:
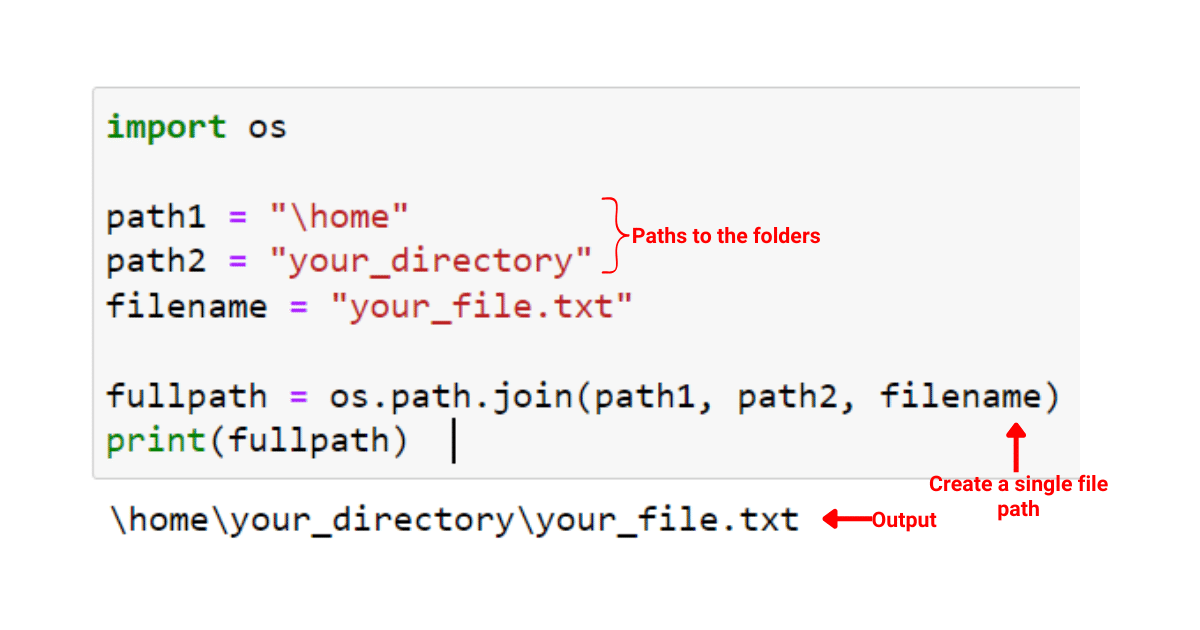
The path module is a part of the Python standard library and provides functionality for manipulating file paths. The path module is often used in conjunction with the os module. Some key features of the path module include:
os.path.join() and os.path.split().
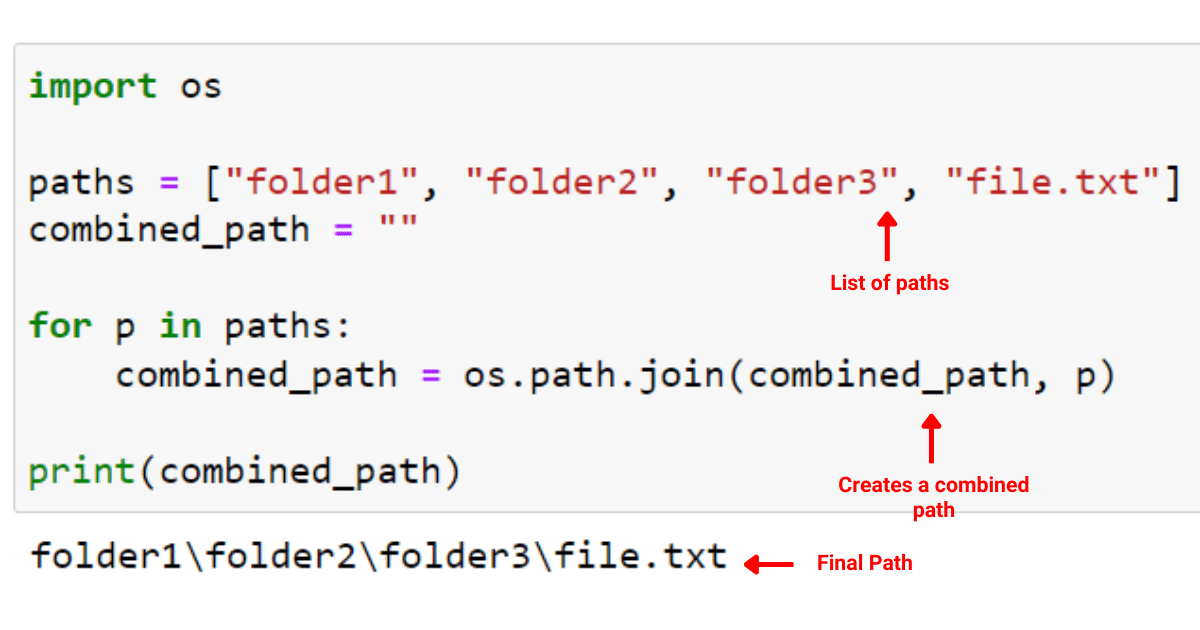
path module provides functions for performing path-related operations such as expanding (~), simplifying (i.e., removing redundant directory separators), and checking if a path is absolute. Common Path Functions: The path module includes a range of useful path-related functions, such as os.path.exists() to check if a file exists, or os.path.isdir() to check if a directory exists.
When to Use Import os path:
In general, you'll want to use the import os statement when:
On the other hand, you might use import path when:
In summary, the import os and import path statements provide a range of operating system-related functionalities that can be used in Python programs to interact with files, directories, environment variables, and more.
Import os python example
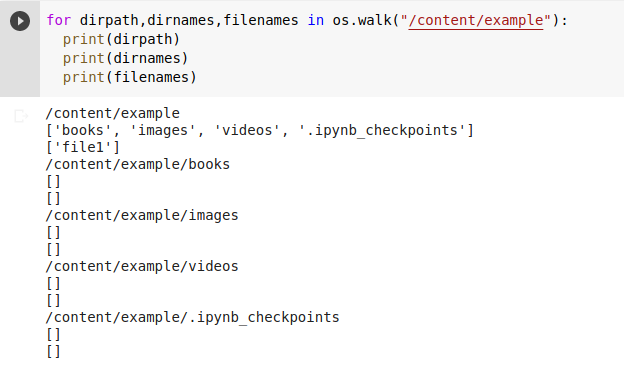
Here is an example of using the os module in Python to interact with the operating system and perform various tasks:
import os
Print current working directory
print("Current Working Directory:", os.getcwd())
Change directory
os.chdir("/path/to/new/directory")
print("New Current Working Directory:", os.getcwd())
List files and directories in a directory
print("Files and Directories in", os.getcwd(),":")
for file_name in os.listdir():
print(file_name)
Check if a file exists
file_path = "/path/to/file.txt"
if os.path.exists(file_path):
print(f"{file_path} exists.")
else:
print(f"{file_path} does not exist.")
Create a new directory
os.mkdir("/path/to/new/directory")
print("Directory created successfully!")
Remove an empty directory
os.rmdir("/path/to/empty/directory")
print("Empty directory removed successfully!")
Copy a file
source_file = "/path/to/source/file.txt"
destination_file = "/path/to/destination/file.txt"
os.system(f"cp {source_file} {destination_file}")
Move or rename a file
file_name = "old_file.txt"
new_file_name = "new_file.txt"
os.rename(file_name, new_file_name)
print("File renamed successfully!")
Get the size of a file
file_size = os.path.getsize(source_file)
print(f"Size of {source_file} is {file_size} bytes.")
Get the creation date and time of a file
creation_time = os.path.getctime(source_file)
print(f"{source_file} was created on {creation_time}")
Get the modification date and time of a file
modification_time = os.path.getmtime(source_file)
print(f"{source_file} was last modified on {modification_time}")
This example shows how to:
Print the current working directory usingos.getcwd(). Change the current working directory using os.chdir(). List files and directories in a directory using os.listdir() and iterate over the results. Check if a file exists using os.path.exists(). Create a new directory using os.mkdir(). Remove an empty directory using os.rmdir(). Copy a file using os.system() with the cp command. Rename or move a file using os.rename(). Get the size of a file using os.path.getsize(). Get the creation and modification dates/times of a file using os.path.getctime() and os.path.getmtime().