hash function in python w3schools
hash function in python w3schools

Here is the information about hash functions in Python from W3Schools:
What are Hash Functions?
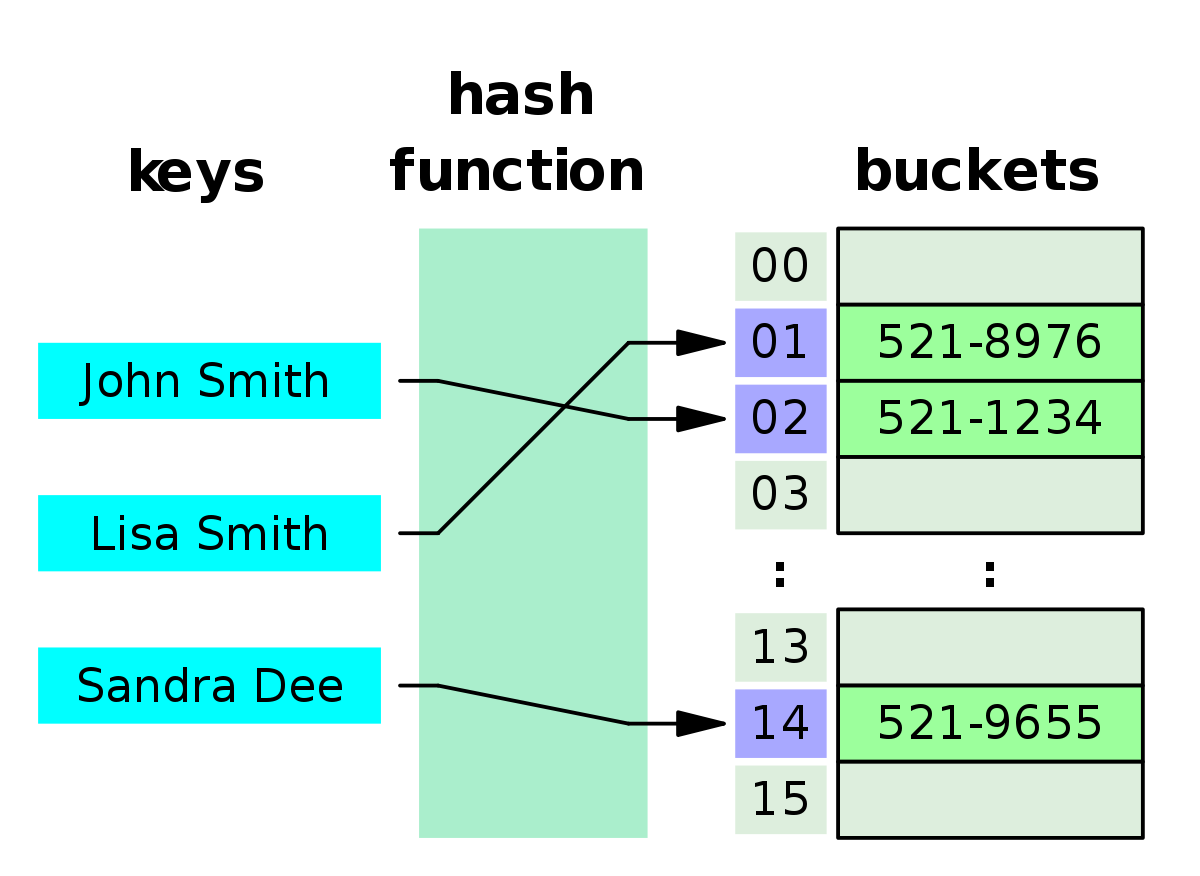
Hash functions take an input and return a fixed-size string of characters, known as a message digest or hash value. The output of a hash function is unique to the input data, making it possible to detect changes or tampering with the original data.
How Do Hash Functions Work?
Here's how hash functions work:
Take Input: You provide some input data to the hash function. Transform Input: The hash function applies a series of complex operations (like bit-level manipulations, XORs, and modular additions) to transform the input into a fixed-size output. Output Hash Value: The final result is the hash value, which is a unique string of characters.Why Use Hash Functions?

Hash functions have several important applications:
Data Integrity: Hash functions help ensure data integrity by detecting any changes or tampering with the original data. Password Storage: Hashing passwords allows for secure storage and verification without storing sensitive information. Digital Signatures: Hash values can be used to create digital signatures, which guarantee the authenticity of messages or documents. Data Compression: Hash functions can be used as a lossless compression algorithm.Python's Built-in Hash Functions
Python has several built-in hash functions that you can use:
hash(): A basic hash function that returns an integer value based on the input data. sha (SHA-1, SHA-224, SHA-256, etc.): Secure Hash Algorithm functions for generating message digests. md5: Message-Digest Algorithm 5 for generating a message digest.
Python's hashlib Library
The hashlib library provides more advanced hash functions, including:
Here is an example of using the hashlib library:
import hashlib
data = "Hello, World!"
hash_object = hashlib.sha256(data.encode())
print(hash_object.hexdigest())
Conclusion
Hash functions are essential in computer science for ensuring data integrity and security. Python provides a range of built-in hash functions and libraries like hashlib that make it easy to implement these cryptographic algorithms.
Python hash string
I'd be happy to respond in English and provide an explanation on how Python handles strings with respect to hashing.
In Python, a hash is a unique numerical value associated with each object in memory. The hash value for any given object remains constant throughout the program's execution unless the object itself changes or it is garbage-collected (destroyed). This property makes hashes useful in various scenarios like:
Dictionary lookups: Hashes can be used to quickly identify and access specific key-value pairs in a dictionary. Set operations: Hashes enable fast membership tests, union, intersection, and difference calculations on sets.When you hash a string in Python, it uses the built-in hash() function, which returns an integer representing the hash value for that string. Here's how this process works:
Now, let's see some examples of hashing strings in Python:
# Define a sample string
sample_string = "Hello, World!"
Calculate the hash value for the string using MD5
md5_hash = hash(sample_string.encode('utf-8'))
print("MD5 Hash:", md5_hash)
Use SHA-1 to calculate another hash value
sha1_hash = hash(sample_string.encode('utf-8'), -1)
print("SHA-1 Hash:", sha1_hash)
When you run this code, it calculates the MD5 and SHA-1 hash values for the given string. Keep in mind that these hash values will be different each time you run your program or execute a new instance of Python.
In summary, Python uses hashing to quickly identify and access strings within dictionaries and sets, allowing for efficient data manipulation. The built-in hash() function provides an easy way to calculate hash values using various algorithms like MD5 and SHA-1.





























