Python list vs tuple reddit
Python list vs tuple reddit
Here's a comprehensive comparison of Python lists and tuples on Reddit:
What are Lists and Tuples?
A fundamental question for any Python programmer! Let's start by understanding what these two data structures are.
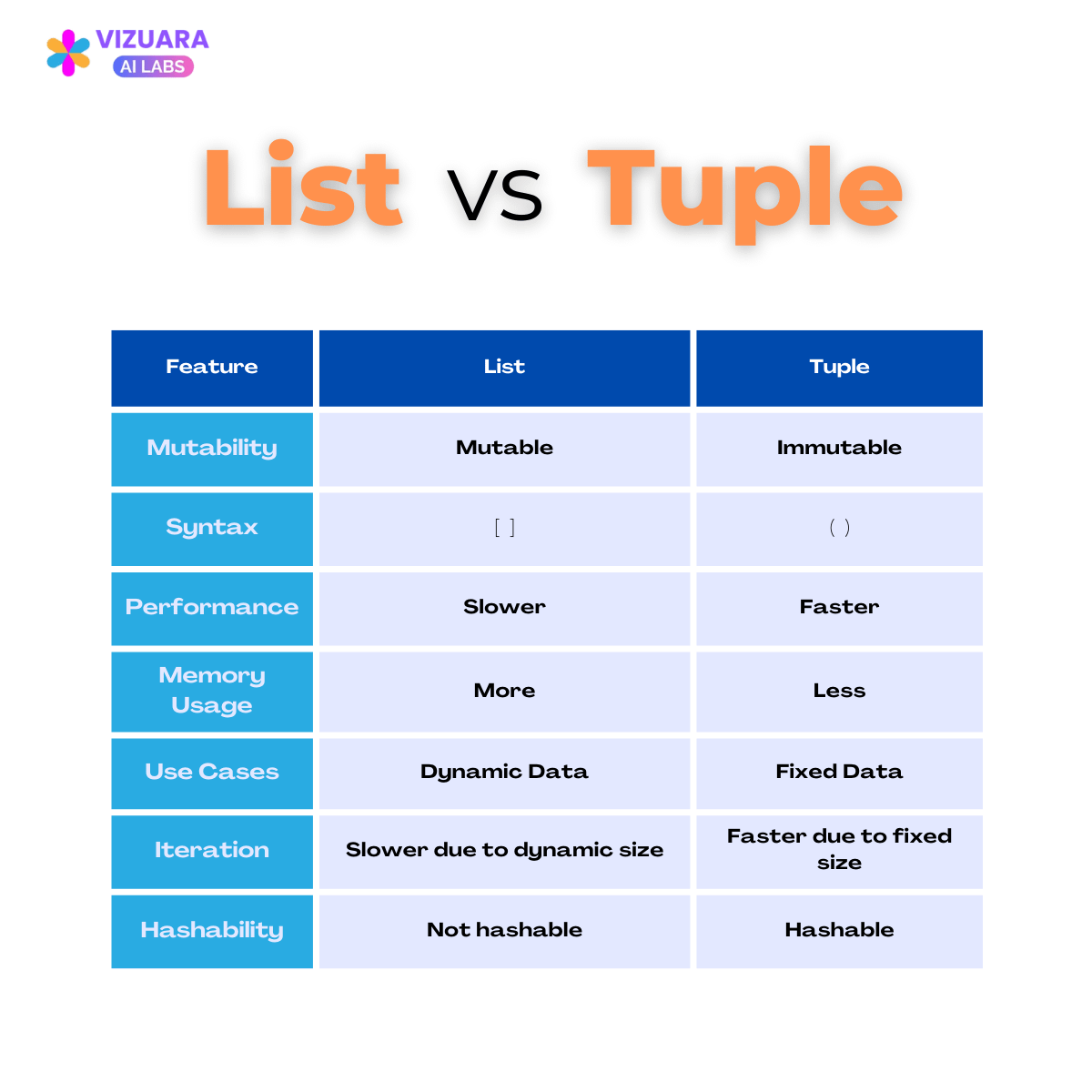
In Python, lists (denoted as []) are ordered collections of items. Each item is an object that can be a string, integer, float, or even another list. Lists are dynamic in nature, meaning they can grow or shrink at runtime. You can add, remove, or modify elements using various methods.
On the other hand, tuples (denoted as ()) are ordered collections of items similar to lists. However, tuples are immutable; once a tuple is created, its contents cannot be changed. Tuples are often used when you need to group several values together without allowing changes.
When to use Lists?
Here are some scenarios where you'd want to use lists:
Dynamic data: When the number of items or their type isn't fixed beforehand, a list is a good choice. Frequent insertion/deletion: If you need to add or remove elements frequently, lists' dynamic nature makes them suitable for this purpose. Ordered collection: Lists allow you to maintain an ordered collection of items.When to use Tuples?
Here are some cases where tuples shine:
Immutable data: When you want to ensure the integrity of your data and prevent accidental changes, a tuple is ideal. Constant-size collections: If you know exactly how many elements you'll be working with upfront, a tuple is a better choice. Performance-critical code: Since tuples are immutable, they can provide a performance boost in scenarios where constant-time access to data is essential.Comparison Chart
Here's a summary of key differences between lists and tuples:
| | Lists | Tuples |
| --- | --- | --- |
| Immutability | No | Yes |
| Dynamic size | Yes | No |
| Ordered collection | Yes | Yes |
| Insertion/deletion | Yes | No |
| Constant-time access | No | Yes |
Conclusion
In conclusion, Python lists and tuples serve distinct purposes. Lists are suitable when you need dynamic data structures with frequent insertion or deletion of elements, while tuples excel in situations where immutability is crucial.
Reddit users often ask questions like:
"What's the difference between a list and a tuple?" "When should I use a list vs. a tuple in Python?" "Are there any performance benefits to using tuples instead of lists?"By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each data structure, you'll be better equipped to choose the right tool for your Python programming tasks.
References:
Python documentation: Lists Python documentation: Tuples Reddit threads: r/learnpython: "What's the difference between a list and a tuple?" r/AskScience: "Why use tuples instead of lists in Python?"Python list vs tuple vs set
I'd be happy to help you with that!
Python's built-in data structures include lists, tuples, and sets. While they share some similarities, each has its unique characteristics, use cases, and advantages.
List
A list is a collection of items that can be of any data type, including strings, integers, floats, and even other lists. Lists are denoted by square brackets [] and are ordered, meaning their elements have a specific order.
Pros:
Dynamic size: Lists can grow or shrink dynamically as elements are added or removed. Mutable: Lists can be modified after creation (e.g., appending, inserting, removing elements). Easy indexing: Accessing individual list elements by their index is straightforward using square brackets[].
Cons:
Slow lookup: Searching for a specific element in a large list can be slow due to the need to iterate through all elements. Memory usage: Lists can consume more memory compared to other data structures, especially when containing many large objects.Use cases: When you need a dynamic collection of items that can be modified frequently (e.g., processing user input or generating reports).
Tuple
A tuple is an ordered, immutable collection of items, similar to a list. Tuples are denoted by parentheses () and are also indexed using square brackets [].
Pros:
Fast lookup: Tuples support fast lookups due to their immutability, making them suitable for data structures that require quick access. Low memory usage: Tuples generally consume less memory than lists since they don't store unnecessary metadata. Thread-safe: Tuples are inherently thread-safe since they're immutable, reducing the need for explicit synchronization.Cons:
Immutable: Once created, tuples cannot be modified (e.g., no appending or inserting elements). Limited dynamic size: Tuples have a fixed size when created and cannot grow dynamically like lists can.Use cases: When you require an efficient, immutable collection of items with fast lookup capabilities, such as in data analysis or scientific computing applications.
Set
A set is an unordered collection of unique items, allowing for fast membership testing and element removal. Sets are denoted by curly braces {} and support operations like union, intersection, and difference.
Pros:
Fast membership testing: Sets provide O(1) lookup times to check if a specific element exists within the set. Efficient element removal: Removing an element from a set is relatively quick (O(n) in the worst case). Unique elements: Sets automatically eliminate duplicates, making them ideal for working with large datasets.Cons:
Unordered: Sets don't preserve the original order of elements. No indexing: Accessing individual elements by index is not supported.Use cases: When you need to quickly verify if an element exists in a collection (e.g., checking user input) or maintain a unique set of items without duplicates (e.g., processing logs).
In summary, lists are dynamic and mutable but can be slow for lookups. Tuples offer fast lookup and low memory usage at the cost of immutability. Sets provide fast membership testing and efficient element removal, with the trade-off being unordered and no indexing.
I hope this helps you understand the differences between Python's list, tuple, and set data structures!





























