Python applications examples
Python applications examples
Here are some examples of Python applications:
Web Development:
Flask: A micro web framework for building small-scale web applications. For example, a blog or a simple e-commerce site.Code snippet:
Django: A high-level web framework for building complex and scalable web applications.from flask import Flask, render_templateapp = Flask(name)
@app.route("/")
def home():
return "Hello World!"
if name == "main":
app.run()
Code snippet:
from django.urls import pathfrom .views import home
urlpatterns = [
path("", home, name="home"),
]
Data Science:
Pandas: A popular library for data manipulation and analysis.Example:
Scikit-learn: A machine learning library for classification, regression, clustering, and more.import pandas as pd Load a CSV filedf = pd.read_csv("data.csv")
Perform some basic operationsprint(df.head()) # Show the first few rows
print(df.describe()) # Show summary statistics
Example:
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionfrom sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
Load the iris datasetiris = load_iris()
Split data into training and testing setsX_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(iris.data, iris.target, test_size=0.2)
Train a logistic regression modellogreg = LogisticRegression()
logreg.fit(X_train, y_train)
Evaluate the model on the test setprint(logreg.score(X_test, y_test))
Automation:
Selenium: A library for automating web browsers.Example:
pyautogui: A library for automating desktop applications.from selenium import webdriver Launch a Chrome browserdriver = webdriver.Chrome()
Navigate to Googledriver.get("https://www.google.com")
Perform some actionsdriver.find_element_by_name("q").send_keys("Python programming")
driver.find_element_by_name("btnG").click()
Close the browserdriver.quit()
Example:
import pyautogui Take a screenshot of the screenpyautogui.screenshot("screenshot.png")
Move the mouse to a specific locationpyautogui.moveTo(100, 200)
Click on an elementpyautogui.click(x=300, y=400)
Gaming:
Pygame: A library for creating games.Example:
import pygame Initialize Pygamepygame.init()
Create a windowscreen = pygame.display.set_mode((640, 480))
Define some colorsWHITE = (255, 255, 255)
RED = (255, 0, 0)
Main game loopwhile True:
Handle eventsfor event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
sys.exit()
Draw something on the screenpygame.draw.circle(screen, RED, (100, 100), 50)
Update the screenpygame.display.flip()
Scientific Computing:
NumPy: A library for numerical computing.Example:
import numpy as np Create a NumPy arrayarr = np.array([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
Perform some basic operationsprint(arr.sum()) # Calculate the sum of the elements
print(arr.mean()) # Calculate the mean of the elements
These are just a few examples of Python applications. Python has many more libraries and frameworks for various domains, including artificial intelligence, machine learning, data science, web development, automation, gaming, scientific computing, and more.
How python is used for in real life
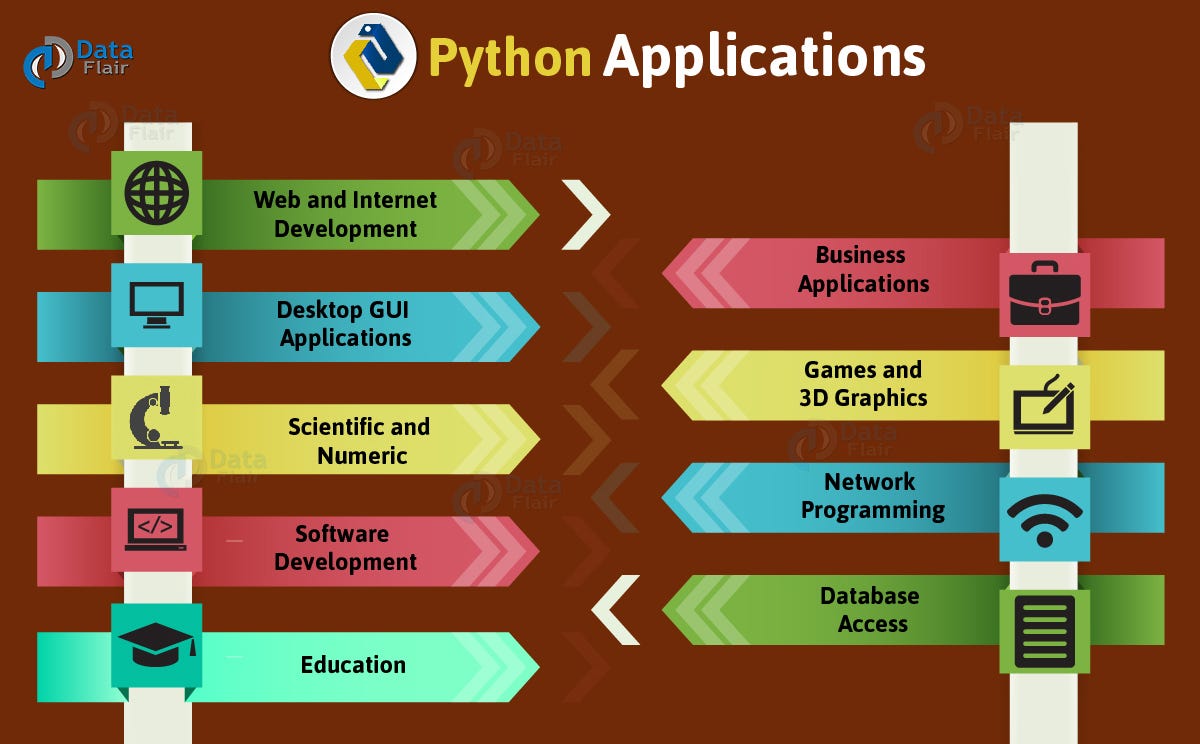
I'd be happy to respond in English!
Python has become an incredibly versatile and widely-used programming language, with its applications extending far beyond academia and research to real-life scenarios. Here are some ways Python is used in real life:
Web Development: Many popular websites and web apps rely on Python-based frameworks such as Django or Pyramid for building scalable and efficient backends. For instance, Pinterest's backend infrastructure is built using Python.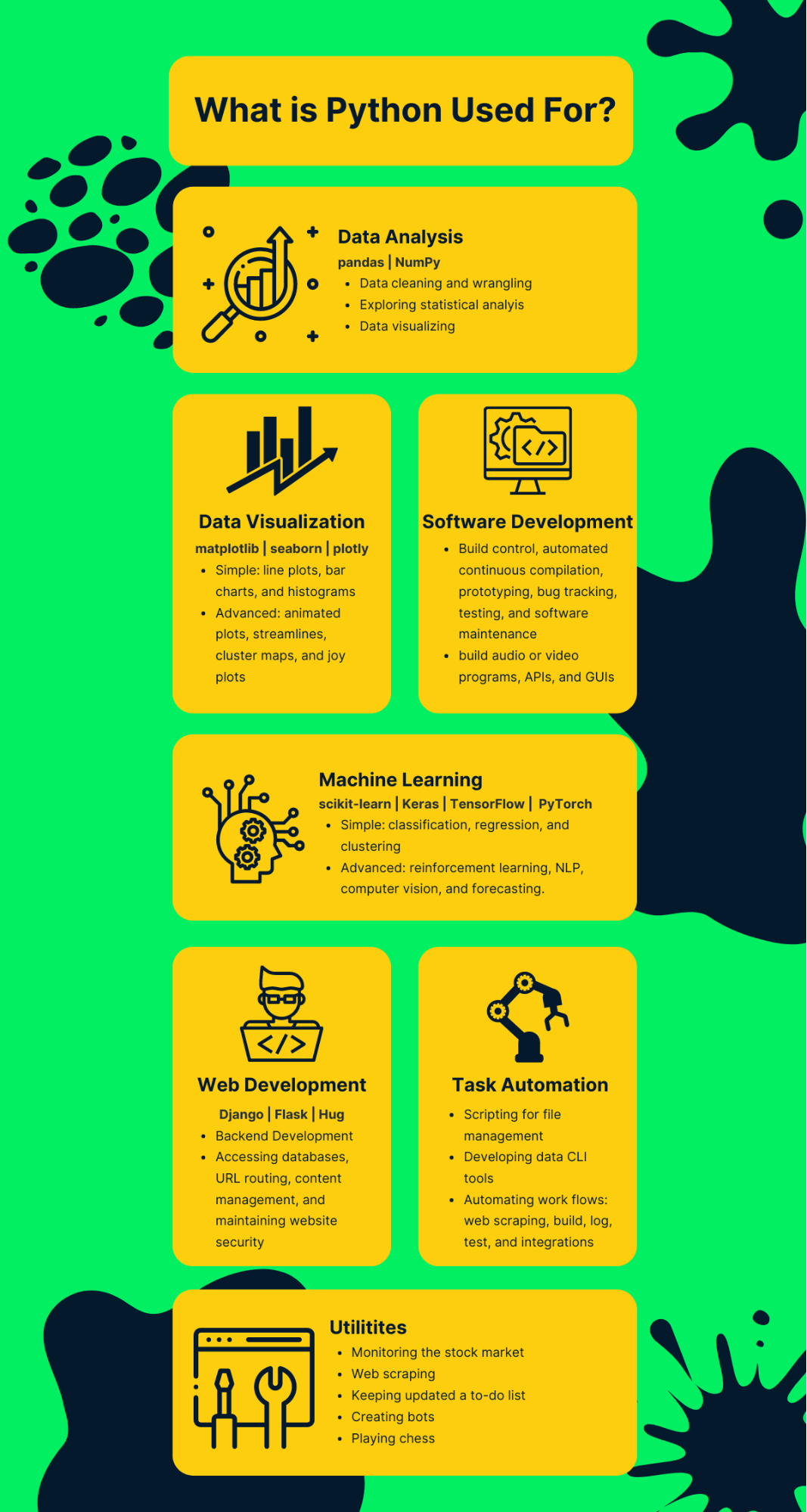
These examples demonstrate the versatility of Python in real-life scenarios, making it an essential tool for many industries and applications.





























