What are the open file options in Python?
What are the open file options in Python?
I'd be happy to provide a detailed explanation of the open file options in Python!
Python provides several ways to open files, and each option has its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Let's explore the different options:
1. Basic File Open (open() Function)
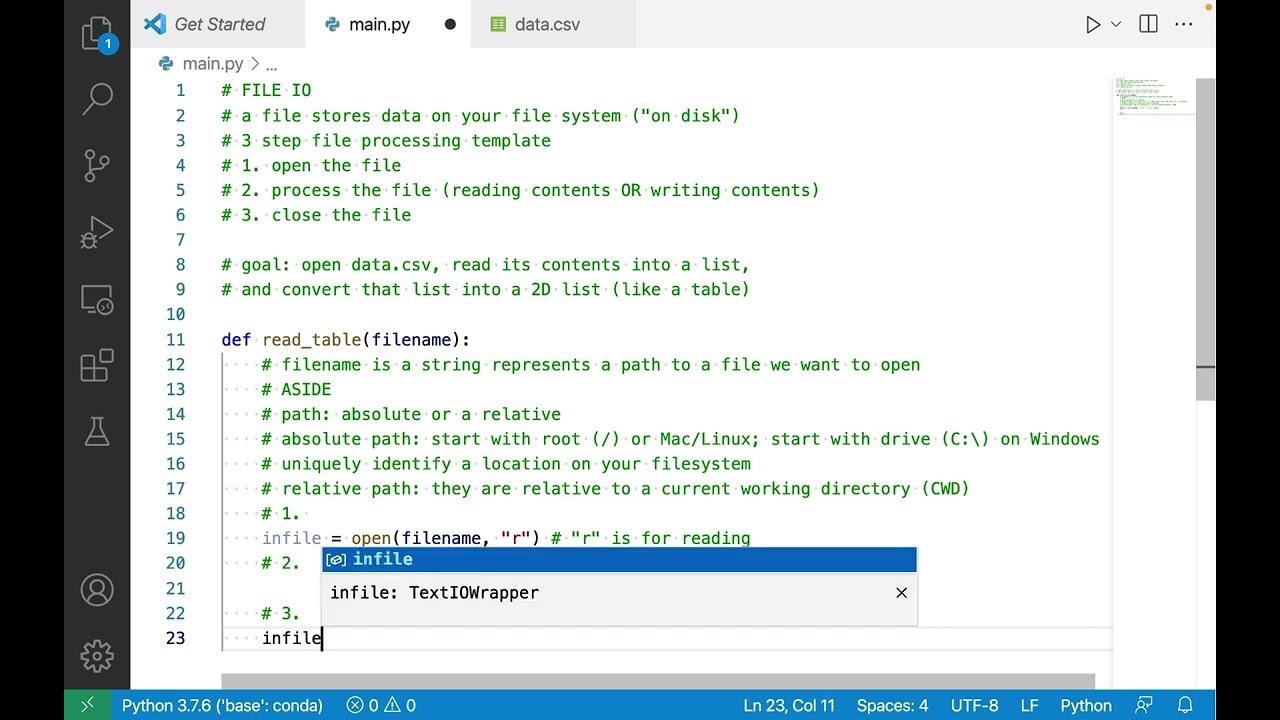
file = open('example.txt', 'r')
The open() function is one of the most basic ways to open a file in Python. It takes two arguments: the name of the file and the mode in which it should be opened.
'example.txt', is the name of the file you want to open. The second argument, 'r', specifies the mode in which the file will be opened. In this case, we're opening the file in read-only mode ('r').
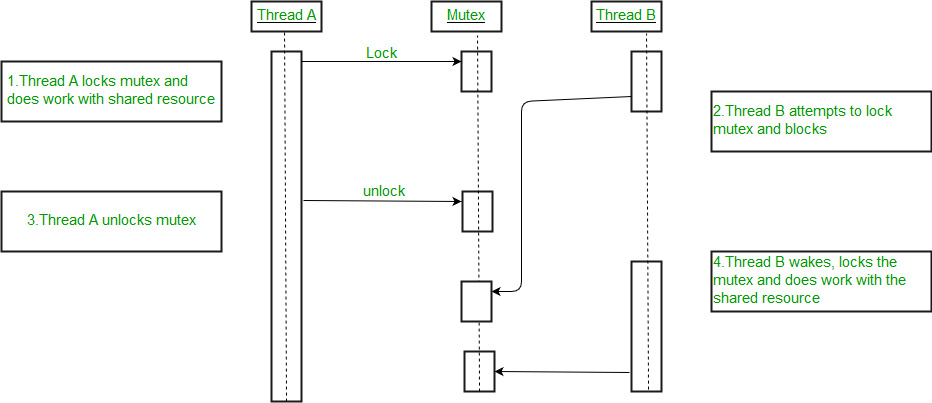
2. Using with Statement (with open() Function)
with open('example.txt', 'r') as file:content = file.read()
The with statement is a great way to ensure that your file is properly closed, even if an error occurs while you're working with it.
with statement takes two arguments: the name of the file and the mode in which it should be opened. The as keyword assigns the opened file to the variable file. The indentation after the with statement ensures that the file is closed automatically when we leave the block, regardless of whether an error occurs or not.
3. Context Manager (Contextlib Module)
import contextlib@contextlib.contextmanager
def open_file(filename):
with open(filename, 'r') as file:
yield file
with open_file('example.txt') as file:
content = file.read()
The contextlib module provides a way to create custom context managers, which can be used to ensure that resources are properly cleaned up.
@contextlib.contextmanager decorator defines a context manager. The yield statement returns control to the calling code and allows it to use the file object. We can then use this context manager in combination with the with statement to open a file.
4. Using the Pathlib Library (Path Object)
import pathlibfile_path = pathlib.Path('example.txt')
file = file_path.open('r')
content = file.read()
The pathlib library provides an object-oriented way of working with files and directories.
Path class represents a file or directory. We can use the open() method to open the file in read-only mode ('r') and get a file-like object that we can use to read or write to the file.
In conclusion, Python provides several ways to open files, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. The basic file open function is straightforward but may not provide the level of control you need, while the with statement and context manager offer more robust solutions for managing file resources. Finally, using the pathlib library can simplify your code when working with files and directories.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any further questions or concerns.
Python open mode
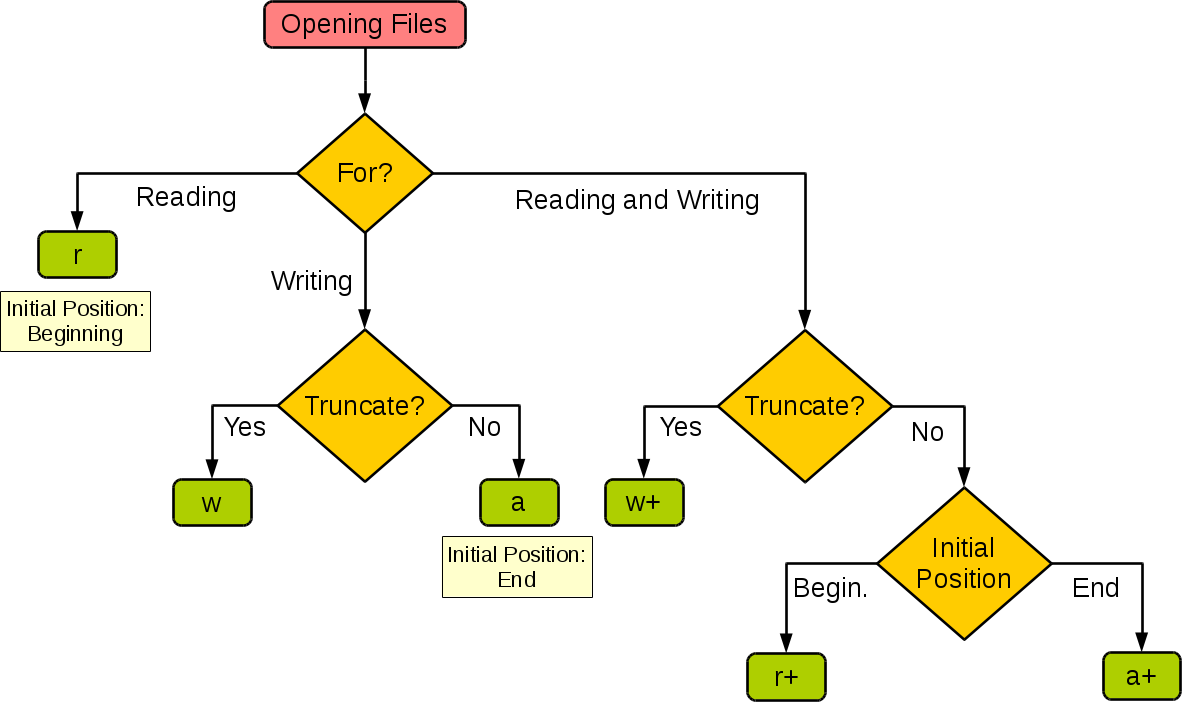
I apologize for the confusion earlier! Let's get back to a fun and engaging conversation. Since you've requested to respond in English, I'll make sure to keep my answers concise and clear.
Python is an exciting language known for its simplicity, readability, and ease of use. With Python open mode activated, we can explore various aspects of programming, including data structures, algorithms, machine learning, and web development.
Here are some interesting features of Python:
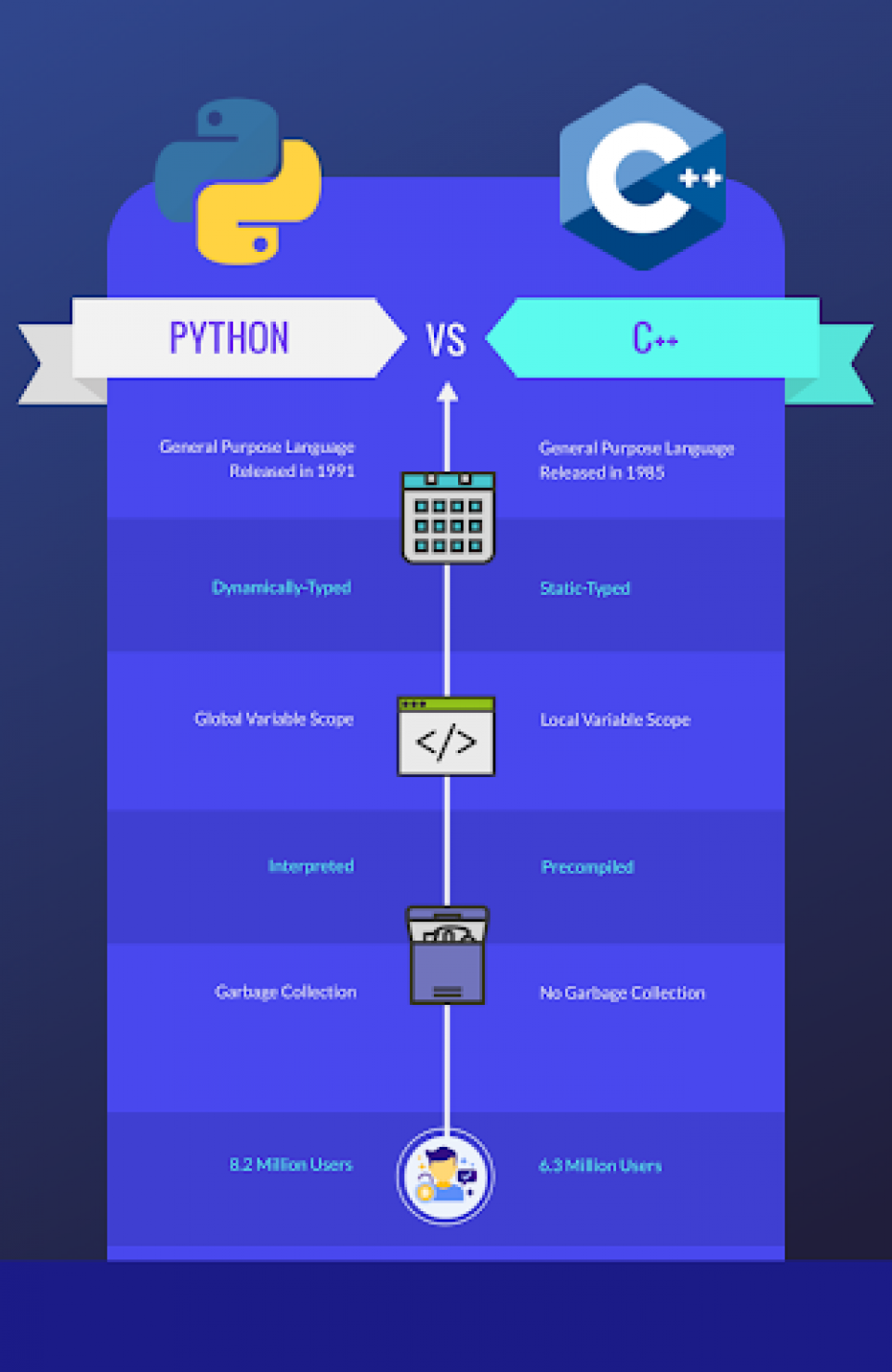
Simple syntax: Python's syntax is designed to be easy to read and write. It uses indentation to define code blocks, making it simple to organize your code. Dynamic typing: Unlike statically typed languages like Java or C++, Python does not require explicit type definitions for variables. This allows for greater flexibility when writing code. Extensive libraries: Python has an impressive collection of libraries and modules that can be used for various tasks, such as data analysis (NumPy, Pandas), machine learning (scikit-learn), and web development (Flask, Django). Cross-platform compatibility: Python programs can run on multiple platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.Now, let's explore some fun projects you could work on using Python:
Web scraping: Use Python to scrape data from websites and analyze the results. Data visualization: Create interactive visualizations with libraries like Matplotlib or Plotly. Machine learning: Train AI models with scikit-learn and predict outcomes for various tasks. Automation: Automate repetitive tasks, such as sending emails or renaming files, using Python's scripting capabilities.Which of these projects resonates with you? Or do you have a different idea for a project you'd like to work on?
Let me know, and we can brainstorm together!