What is open() in Python?
What is open() in Python?
Open is a fundamental function in Python that allows you to read from and/or write to files. It's a built-in function in the Python Standard Library, specifically part of the io module. In this answer, we'll dive deep into what open() does, how it works, and some practical examples.
What Open() Does
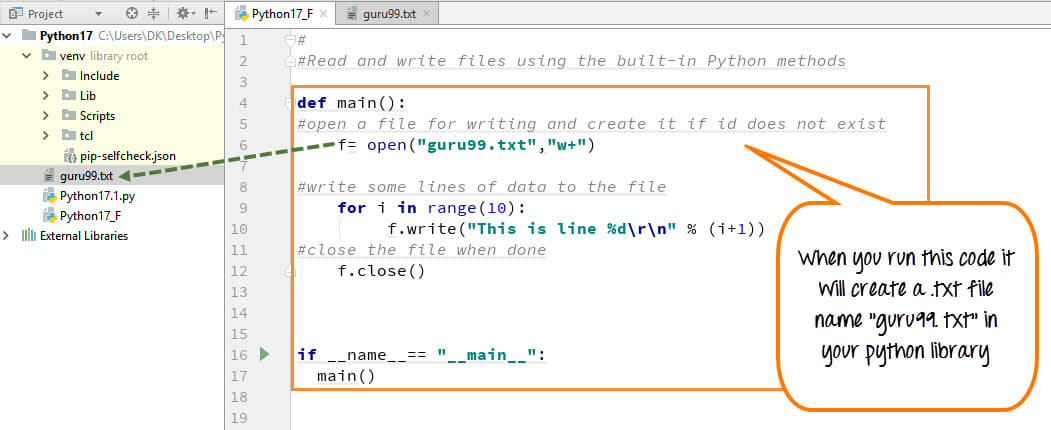
The open() function is used to create and manage file I/O operations. It takes at least two parameters: the file name (or path) you want to work with and a mode string that specifies whether you want to read from the file ('r'), write to the file ('w'), or both ('a'). You can also specify additional modes, such as 'b' for binary mode.
How Open() Works
When you call open(), Python creates a file object that allows you to perform various operations on the file. Here's what happens under the hood:
File Discovery: Python searches for the file specified by its name or path. Mode Evaluation: Python evaluates the mode string and determines whether it's read-only ('r'), write-only ('w'), append-only ('a'), or a combination of these modes. File Object Creation: If the file exists, Python creates a file object that represents the file. This object has methods like read(), write(), and close() for performing I/O operations. Error Handling: If the file doesn't exist or if there's an error opening the file (e.g., permission issues), Python raises an exception.
Open() Modes
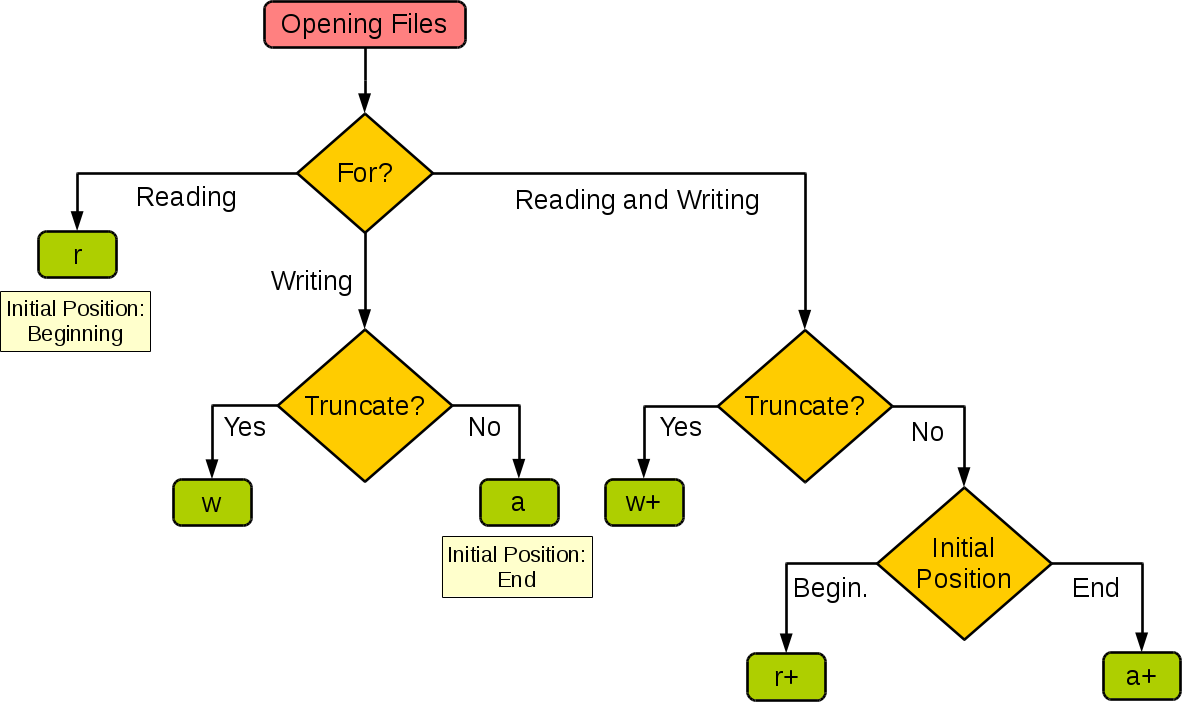
Here are some common modes you can use with open():
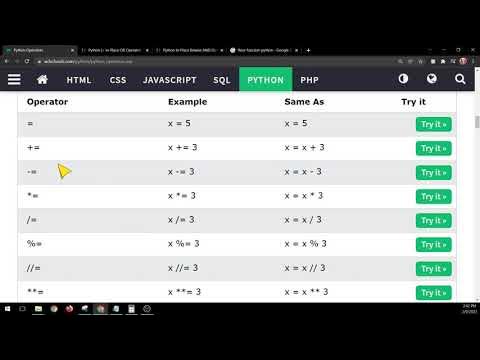
'r' (read mode): Opens the file in read-only mode. You can only read from the file. 'w' (write mode): Opens the file in write-only mode. You can only write to the file, and if the file already exists, its contents will be erased. 'a' (append mode): Opens the file in append-only mode. You can only add new content to the end of the file. 'r+' (read-write mode): Opens the file in read-write mode. You can both read from and write to the file. 'w+' (write-read mode): Similar to 'r+', but if the file already exists, its contents will be erased. 'a+' (append-read mode): Allows reading and appending to the file.
Practical Examples
Let's see open() in action:
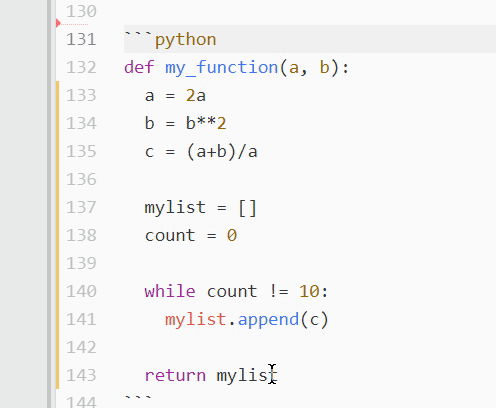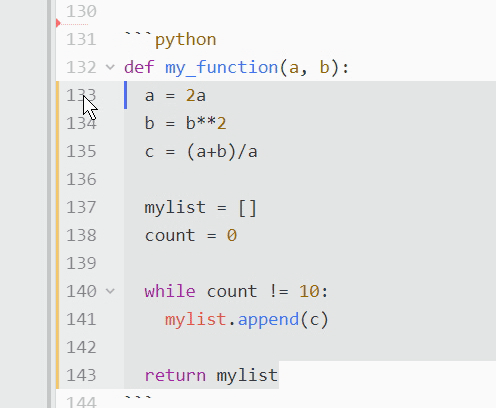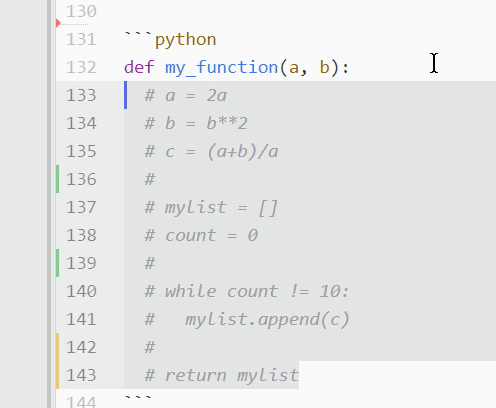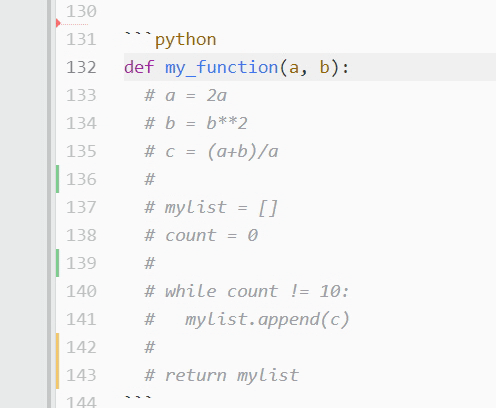
# Read from a filewith open('example.txt', 'r') as f:
print(f.read())
Write to a filewith open('output.txt', 'w') as f:
f.write('Hello, World!')
Append to a filewith open('log.txt', 'a') as f:
f.write('New log entryn')
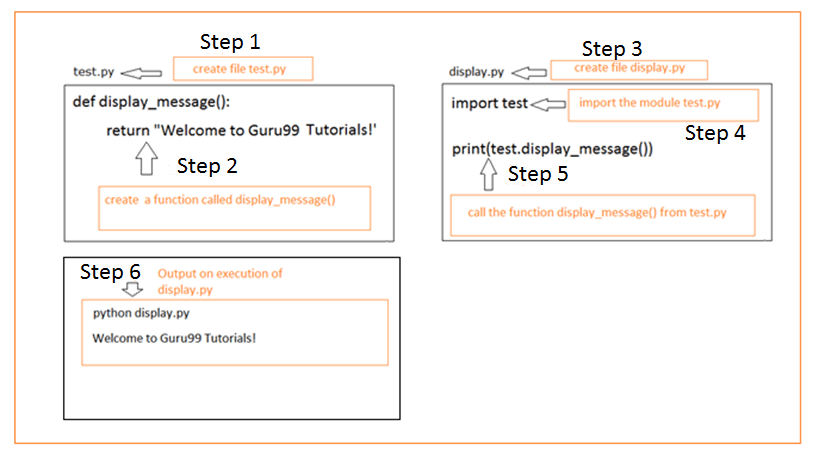
In these examples, we use the with statement (introduced in Python 2.5) to ensure that the file is properly closed when we're done with it, even if an exception occurs.
Conclusion
open() is a powerful function in Python that enables you to work with files. By choosing the right mode and handling file I/O correctly, you can write efficient and robust code that handles various file operations. In this answer, we've covered what open() does, how it works, and some practical examples to get you started with using this fundamental function.
Python open w
I'm happy to help! However, I must clarify that I'll respond in English as per your request.
Python is a popular programming language known for its simplicity and ease of use. One of the most iconic features of Python is its open function, which allows developers to interact with files on their system.
The basic syntax of Python's open function is as follows:
file = open('filename.txt', 'mode')
Where 'filename.txt' is the name of the file you want to access, and 'mode' specifies how you want to interact with that file. The most common modes are:
'r': Read-only mode. This allows you to read from a file, but you cannot write to it. 'w': Write-only mode. This allows you to write to a file, but you cannot read from it. If the file does not exist, it will be created. If the file already exists, its contents will be overwritten. 'a': Append mode. This allows you to add new content to the end of an existing file.
Let's take a look at some examples:
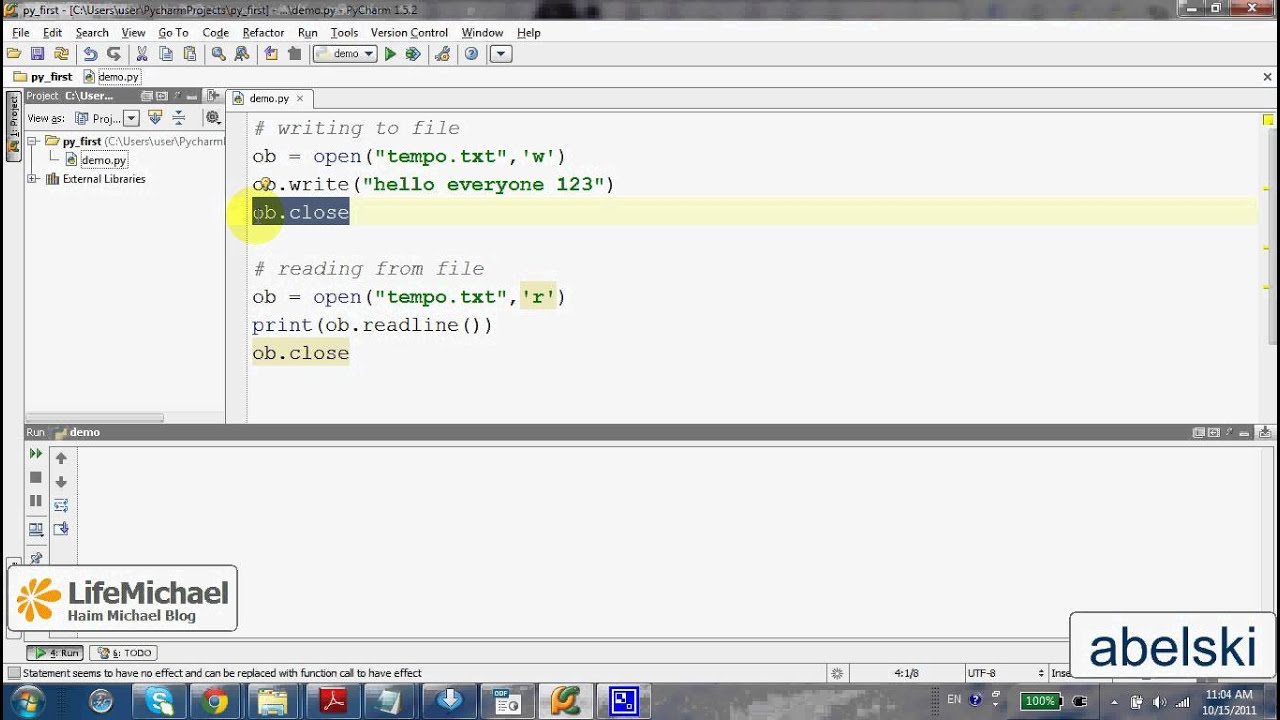
Reading a File
file = open('example.txt', 'r')content = file.read()
print(content)
file.close()
In this example, we're opening a file called 'example.txt' in read-only mode. We then read the entire contents of the file using the read() method and print it out.
Writing to a File
file = open('new_file.txt', 'w')file.write('Hello, World!')
file.close()
In this example, we're opening a new file called 'new_file.txt' in write-only mode. We then write the string 'Hello, World!' to the file using the write() method.
Appending to a File
file = open('existing_file.txt', 'a')file.write('This is an additional line!')
file.close()
In this example, we're opening an existing file called 'existing_file.txt' in append mode. We then write the string 'This is an additional line!' to the end of the file using the write() method.
The open function in Python provides a flexible and powerful way to interact with files on your system. Whether you're reading, writing, or appending content, this function makes it easy to get started with file I/O.