What are the different types of HTTP requests in Python?
What are the different types of HTTP requests in Python?
I'm happy to help you with that!
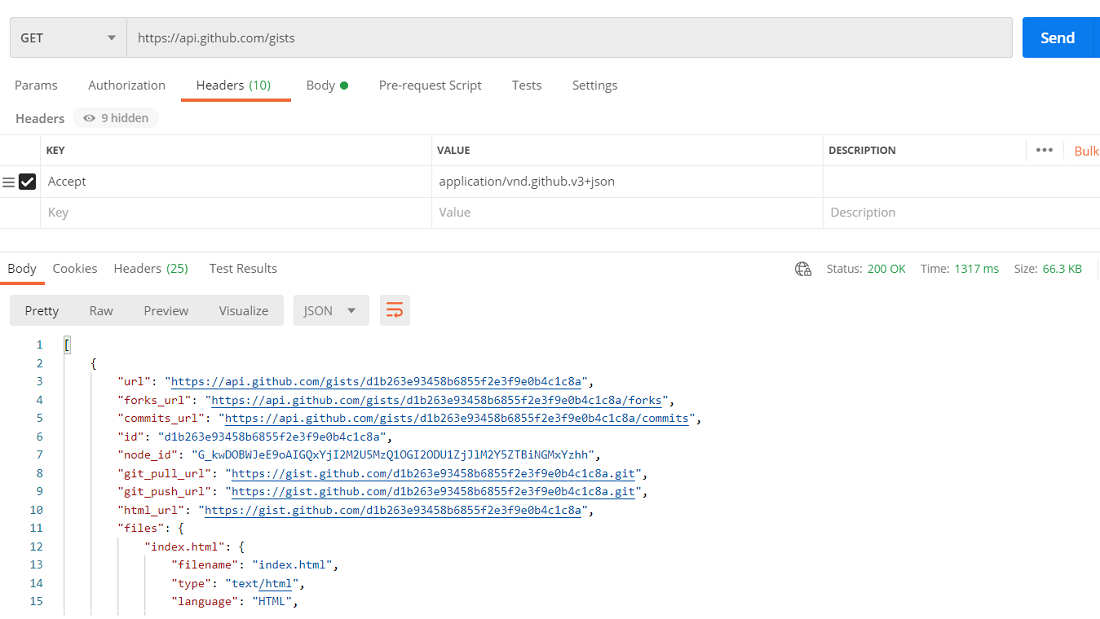
In Python, there are several types of HTTP requests that can be made using libraries such as requests or urllib. Here's a rundown of some common ones:
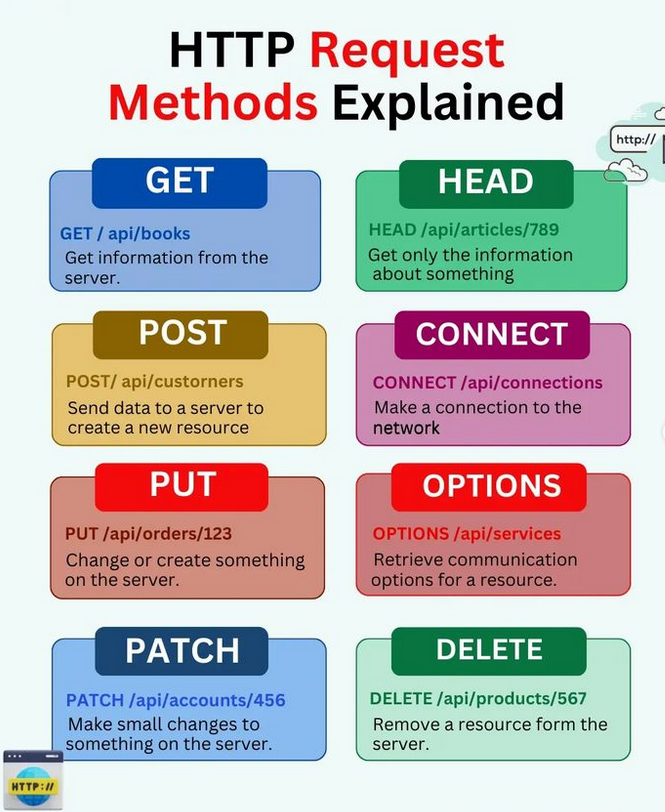
Example: requests.get('https://www.example.com/')
Example: requests.post('https://www.example.com/api/data', json={'key': 'value'})
Example: requests.put('https://www.example.com/api/data', json={'new_key': 'new_value'})
Example: requests.delete('https://www.example.com/api/data')
Example: requests.head('https://www.example.com/')
Example: requests.options('https://www.example.com/api/data')
Example: requests.patch('https://www.example.com/api/data', json={'partial_update': 'data'})
These are some of the most common types of HTTP requests in Python. Each has its own use case and is used to interact with servers in different ways.
Remember, when working with HTTP requests, it's important to consider factors like authentication, rate limiting, and error handling to ensure your code is robust and reliable.
Hope this helps!
How to send HTTP request using Python?
I'm happy to help!
Sending an HTTP request using Python is a fundamental task that can be achieved through various libraries and modules. In this answer, I will cover the most popular methods.
Method 1: Using Requests Library
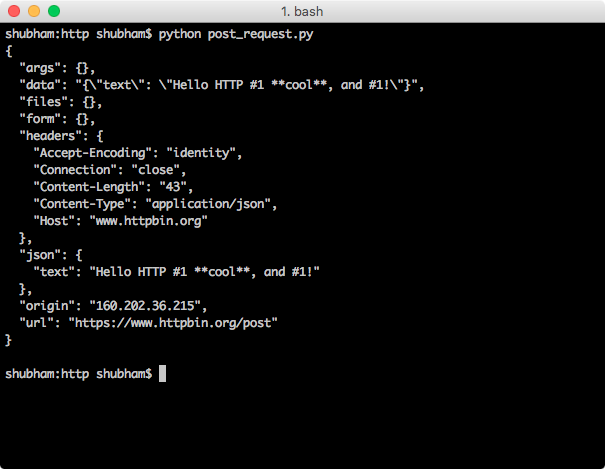
The requests library is one of the most popular and widely-used libraries for making HTTP requests in Python. It provides a simple and intuitive way to send requests, handle responses, and interact with web servers.
To install the requests library, run the following command:
pip install requests
Once installed, you can use the library as follows:
import requests
Define the URL and HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
url = "https://api.example.com/resource"
method = "GET"
try:
Send the request
response = requests.request(method, url)
Check if the request was successful
if response.status_code == 200:
print("Request Successful!")
print(response.text) # Print the response text
else:
print(f"Request Failed: {response.status_code}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
Method 2: Using urllib Library
The urllib library is another built-in Python library that provides support for working with URLs. It can be used to send HTTP requests and interact with web servers.
To use the urllib library, you can follow these steps:
import urllib.request
Define the URL and HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
url = "https://api.example.com/resource"
method = "GET"
try:
Create a request object
request = urllib.request.Request(url, data=None, method=method)
Send the request and get the response
response = urllib.request.urlopen(request)
Check if the request was successful
if response.getcode() == 200:
print("Request Successful!")
print(response.read().decode()) # Print the response text
else:
print(f"Request Failed: {response.getcode()}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
Method 3: Using Python's built-in http.client Library
Python's http.client module is a built-in library that provides support for sending HTTP requests and interacting with web servers. It can be used to send requests using the HTTPConnection or HTTPSConnection classes.
To use the http.client library, you can follow these steps:
import http.client
Define the URL and HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE)
url = "https://api.example.com/resource"
method = "GET"
try:
Create an HTTP connection object
conn = http.client.HTTPConnection("example.com")
Send the request
conn.request(method=method, url=url)
Get the response
response = conn.getresponse()
Check if the request was successful
if response.status == 200:
print("Request Successful!")
print(response.read().decode()) # Print the response text
else:
print(f"Request Failed: {response.status}")
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
In summary, Python provides several libraries and modules for sending HTTP requests. The requests library is one of the most popular and widely-used options, but the urllib and http.client libraries can also be used for specific purposes. Each method has its own strengths and weaknesses, and choosing the right one depends on your specific needs and requirements.





























