How to use >= in Python?
How to use >= in Python?

I'm happy to help!
In Python, >= is an operator used for greater than or equal comparison. It's a fundamental part of the language and plays a crucial role in making decisions within your code.
Let's take a simple example to understand how it works:

a = 10
b = 15
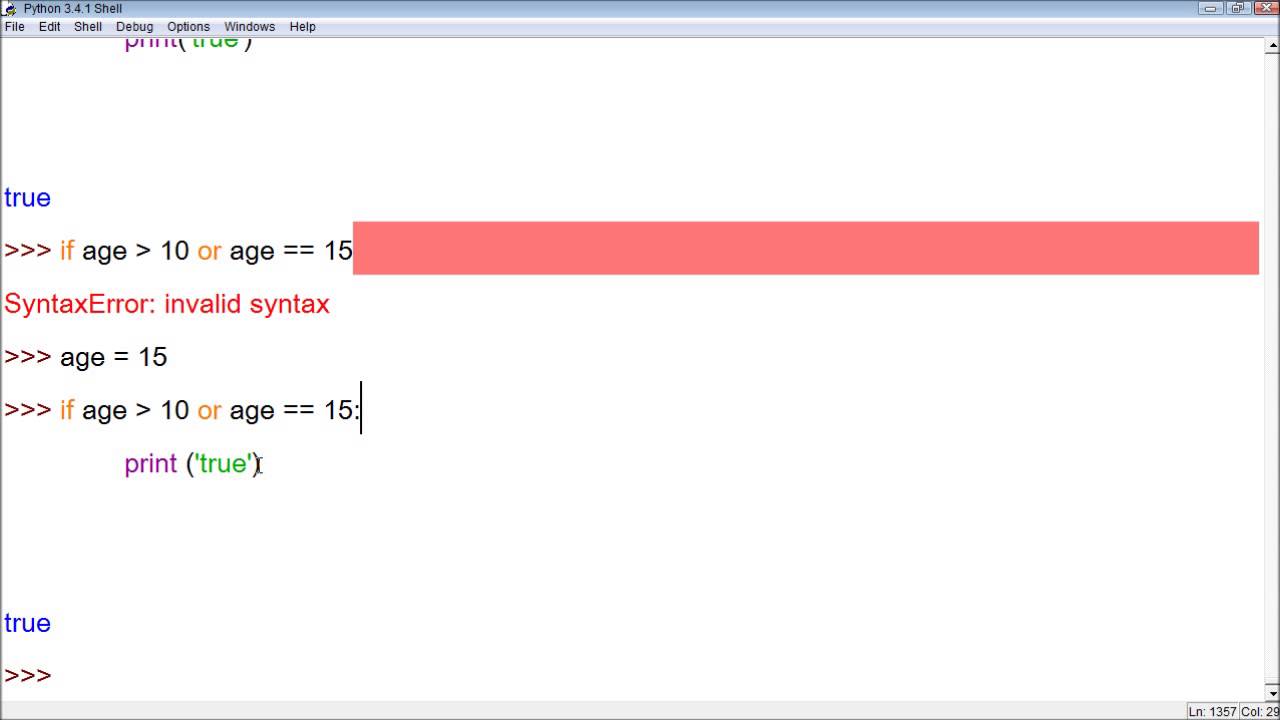
if b >= a:
print("This is true!")
else:
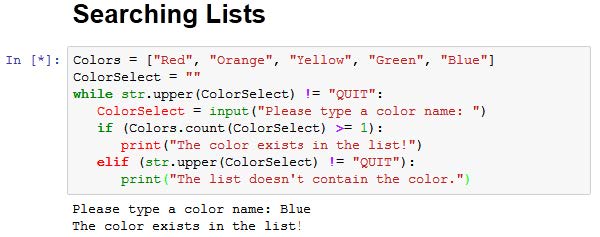
print("This is false!")
When you run this code, the output will be: "This is true!" because b (15) is indeed greater than or equal to a (10).
In real-world scenarios, using >= can be incredibly helpful. For instance, imagine you're developing a program that deals with user input, and you want to check if the entered age is at least 18.
age = int(input("Enter your age: "))
if age >= 18:
print("You are considered an adult!")
else:
print("Sorry, you're still a minor!")
In this case, >= allows you to compare the user's entered age to 18 and respond accordingly.
Another common application of >= is in range-checking. You can use it to ensure that a given number falls within a specific interval.
x = 25
if x >= 0 and x <= 100:
print("Your score is valid!")
else:
print("Invalid score, please try again!")
Here, >= helps you verify whether the input value lies between 0 and 100 (inclusive).
As you can see, >= is a versatile operator in Python that plays a vital role in conditional statements and range-checking. By mastering its usage, you'll be well-equipped to tackle various programming tasks!
Now, let's have some fun! Here's a short quiz to test your understanding:
In the following code, what willx equal when y = 20?
x = 10
if y >= x:
print("x is correct!")
else:
print("x is incorrect!")
age = 17?
age = int(input("Enter your age: "))
if age >= 18:
print("You're an adult now!")
else:
print("Sorry, kiddo! You're still a minor!")
x = 75
if x >= 1 and x <= 100:
print("Your score is valid!")
else:
print("Invalid score, please try again!")
Feel free to share your answers in the comments below!
Python comparison operators list
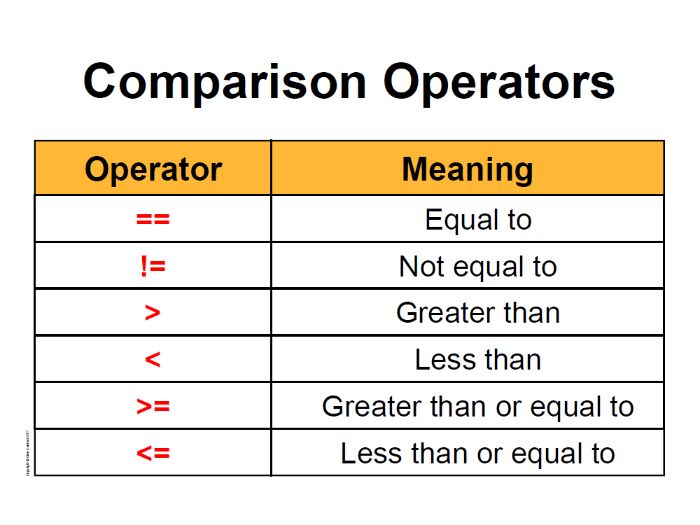
Here is the list of Python comparison operators:
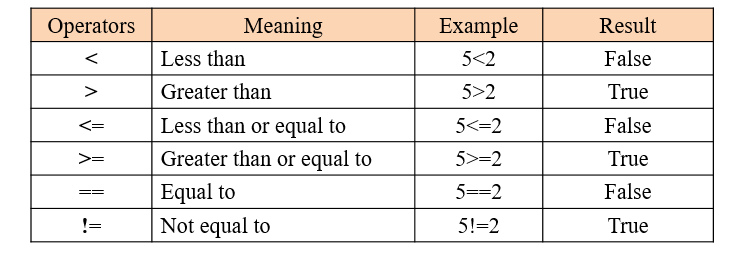
== Equal: Returns True if the values of two operands are equal.
Example:
a = 5
b = 5
print(a == b) # Output: True
!= Not Equal: Returns True if the values of two operands are not equal.
Example:
a = 5
b = 10
print(a != b) # Output: True
> Greater Than: Returns True if the value of the left operand is greater than the value of the right operand.
Example:
a = 5
b = 2
print(a > b) # Output: True
< Less Than: Returns True if the value of the left operand is less than the value of the right operand.
Example:
a = 5
b = 7
print(a < b) # Output: False
>= Greater Than or Equal to: Returns True if the value of the left operand is greater than or equal to the value of the right operand.
Example:
a = 5
b = 5
print(a >= b) # Output: True
<= Less Than or Equal to: Returns True if the value of the left operand is less than or equal to the value of the right operand.
Example:
a = 5
b = 3
print(a <= b) # Output: False
is Is (Identity): Checks whether two operands refer to the same object in memory.
Example:
a = [1, 2, 3]
b = a
print(a is b) # Output: True
is not Is Not (Not Identity): Checks whether two operands do not refer to the same object in memory.
Example:
a = [1, 2, 3]
b = [4, 5, 6]
print(a is not b) # Output: True
in In: Checks whether a value is present in a sequence (such as list, tuple, or string).
Example:
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
print('banana' in fruits) # Output: True
not in Not In: Checks whether a value is not present in a sequence.
Example:
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
print('pear' not in fruits) # Output: True
@ Matmul (Matrix Multiplication): Used to perform matrix multiplication on numpy arrays.
Example:
import numpy as np
a = np.array([[1, 2], [3, 4]])
b = np.array([[5, 6], [7, 8]])
print(np.matmul(a, b)) # Output: Matrix product
These comparison operators are used to compare values in Python and return a boolean result. They can be used in various contexts, such as control flow statements (if-else), logical operations, or data validation.