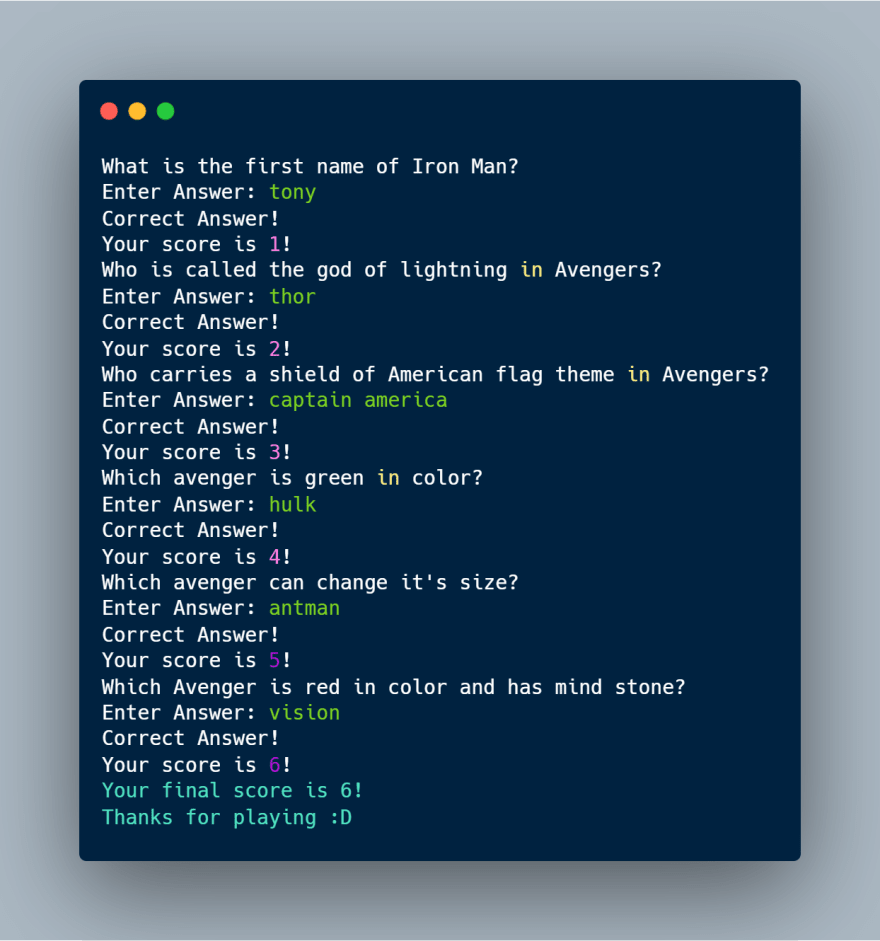
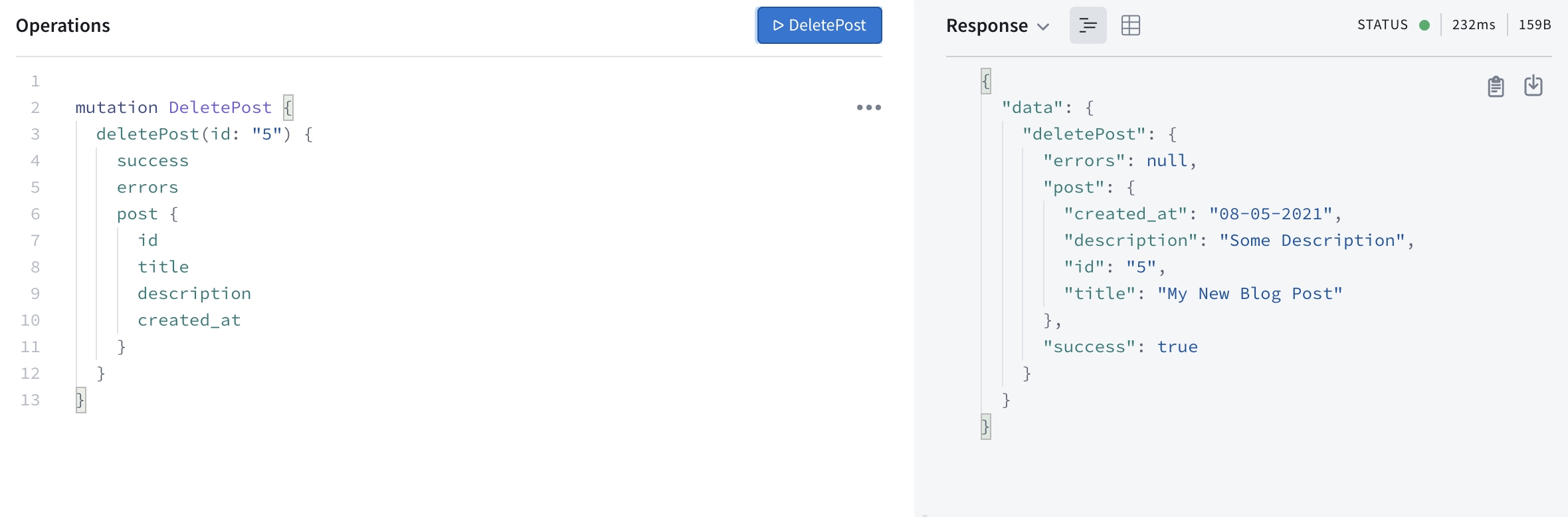
List and tuple in python example w3schools
List and tuple in python example w3schools
I'm happy to help!
W3Schools is a website that provides tutorials, references, and examples on web development topics such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and Python. One of the resources they offer is examples on using lists and tuples in Python.
Here are some examples from W3Schools:
Lists Example:
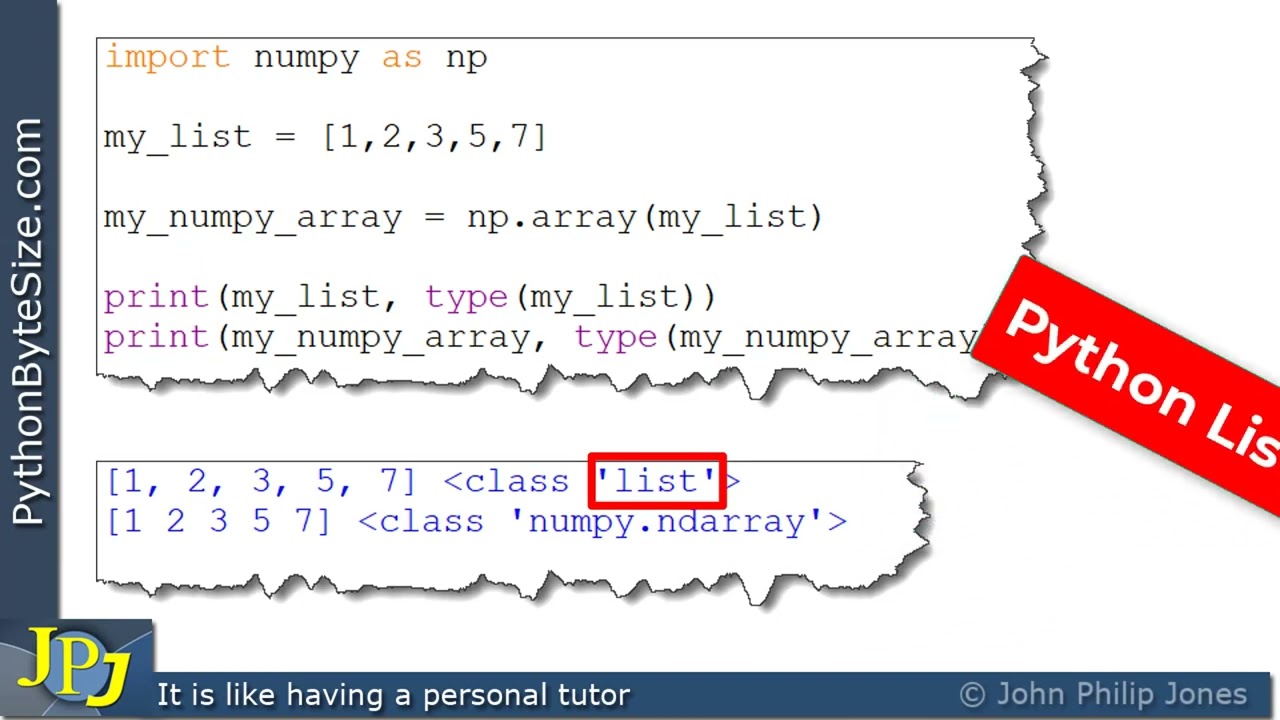
# Create a list
my_list = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"]
print(my_list)
Access an element by index
print(my_list[0]) # Output: apple
Change an element
my_list[1] = "mango"
print(my_list) # Output: ["apple", "mango", "cherry"]
Add an element to the list
my_list.append("orange")
print(my_list) # Output: ["apple", "mango", "cherry", "orange"]
Remove an element from the list
my_list.remove("cherry")
print(my_list) # Output: ["apple", "mango", "orange"]
Tuples Example:
# Create a tuple
my_tuple = ("apple", "banana", "cherry")
print(my_tuple)
Access an element by index
print(my_tuple[0]) # Output: apple
Try to change an element (this will raise an error)
my_tuple[1] = "mango" # TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
Create a new tuple with some elements from the original tuple
new_tuple = my_tuple[:2] + ("mango",)
print(new_tuple) # Output: ("apple", "banana")
Convert the tuple to a list and make changes (this will allow you to change the element)
my_list = list(my_tuple)
my_list[1] = "mango"
print(my_list) # Output: ["apple", "mango"]
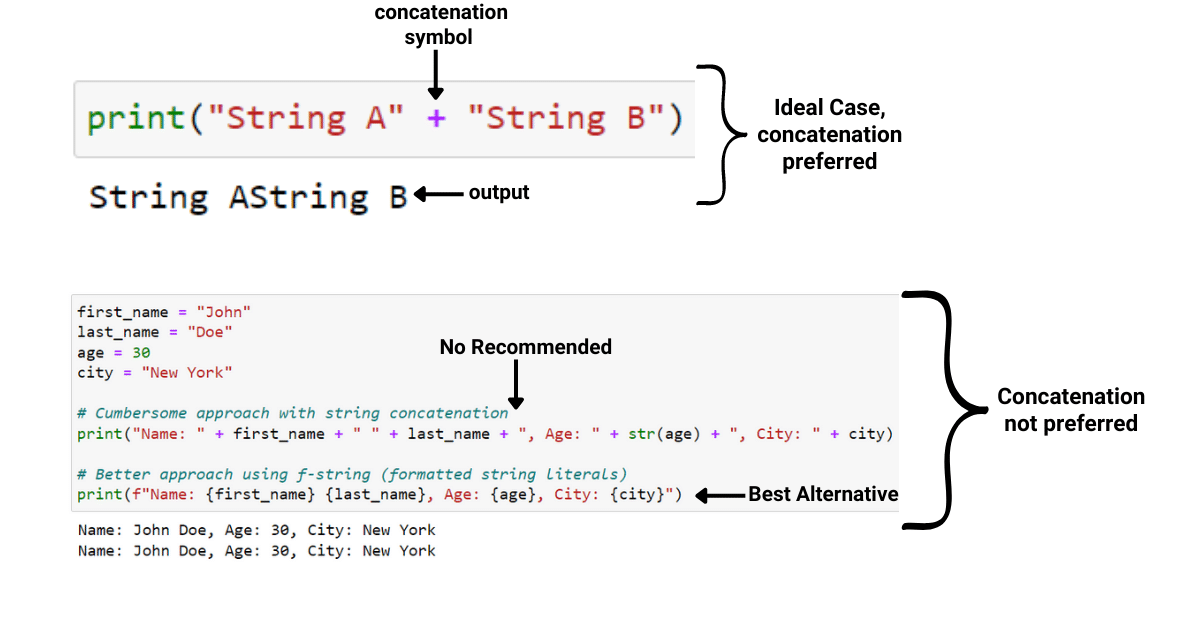
These examples demonstrate how to create, access, modify, add, remove, and convert lists and tuples in Python. Lists are mutable (can be changed), while tuples are immutable (cannot be changed once created). Tuples can be thought of as an ordered collection of items.
Note that W3Schools has many more examples and tutorials on using lists and tuples, including more advanced topics like nested lists and dictionaries. If you're interested in learning more, I encourage you to check out their website!
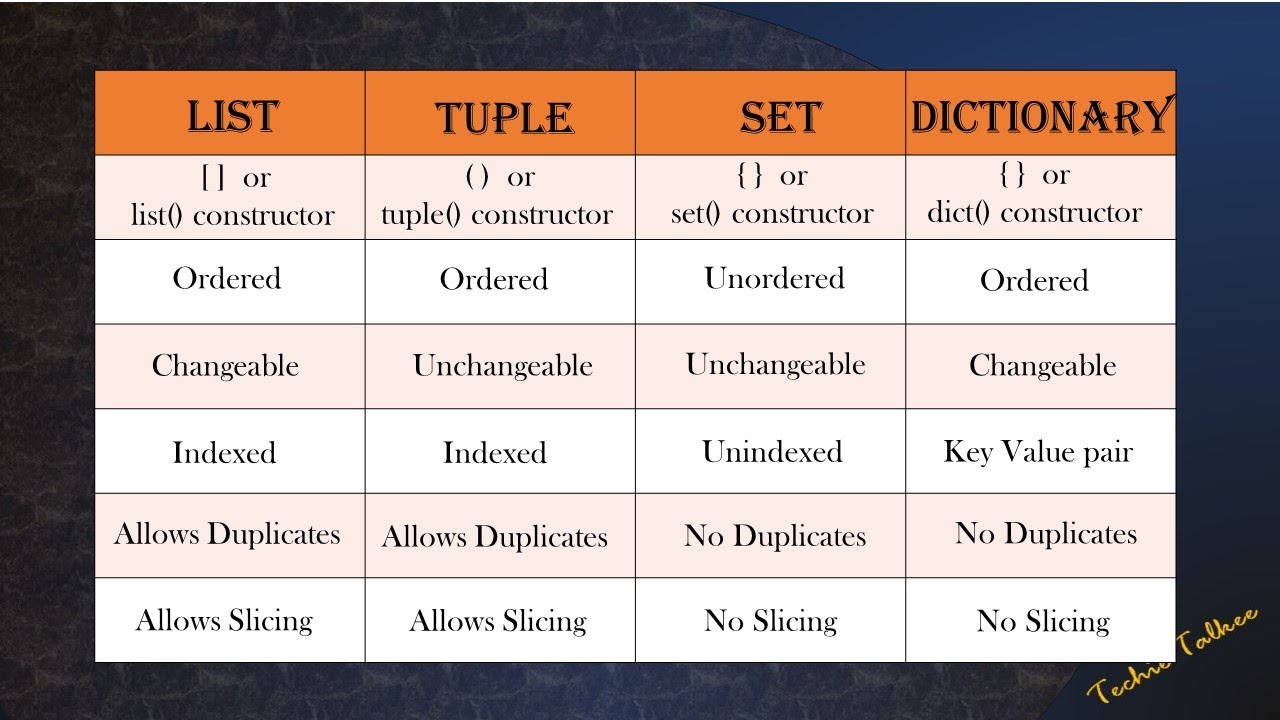
What is the difference between list set and tuple in Python?
I'll respond in English only as requested.
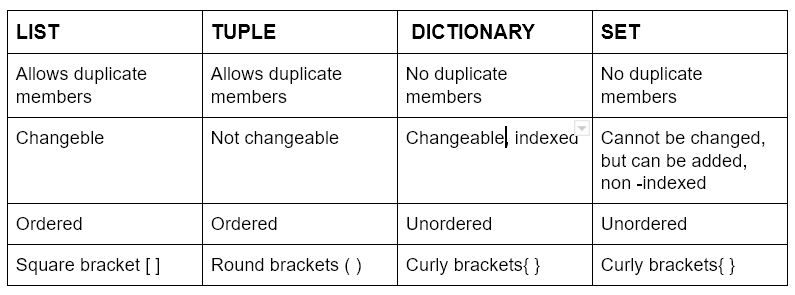
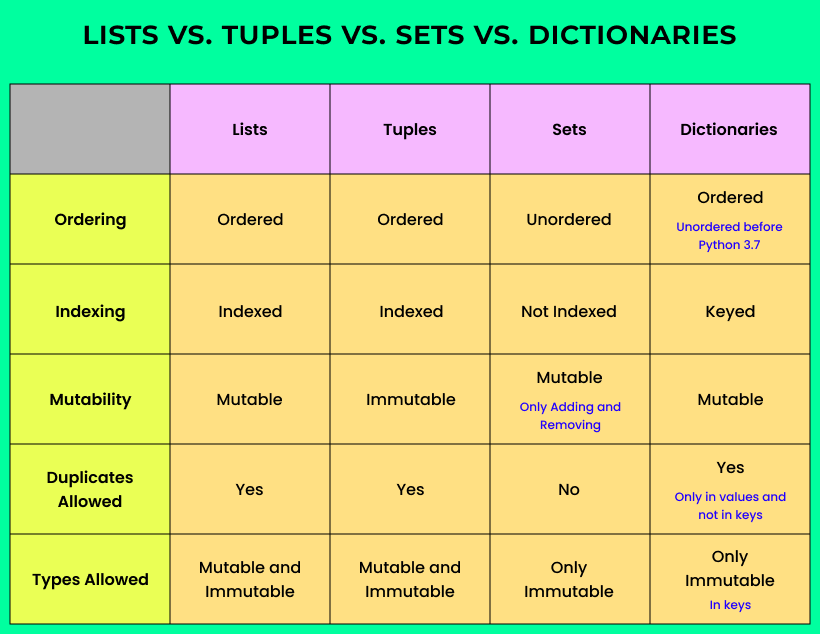
In Python, list, set, and tuple are three fundamental data structures that serve distinct purposes. Understanding their differences is crucial for efficient coding and effective problem-solving.
List (Mutable)
A list is a dynamic, ordered collection of items that can be modified after creation. You can think of it as a array with growable size. Lists are denoted by square brackets [] and elements are separated by commas.
Here's an example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3]
my_list.append(4) # Output: [1, 2, 3, 4]
In this case, the list is initialized with three integers. You can append (add at the end), extend (insert multiple elements), or modify individual elements.
Set (Immutable)
A set is an unordered, unindexed collection of unique elements. It's a bag that only allows distinct items. Sets are denoted by curly braces {} and elements are separated by commas.
Here's an example:
my_set = {1, 2, 3}
print(my_set) # Output: {1, 2, 3}
You can't modify a set after creation
try:
my_set.add(4)
except AttributeError:
print("Can't add to an immutable set")
Sets are useful when you need to store unique elements and perform operations like union, intersection, or difference.
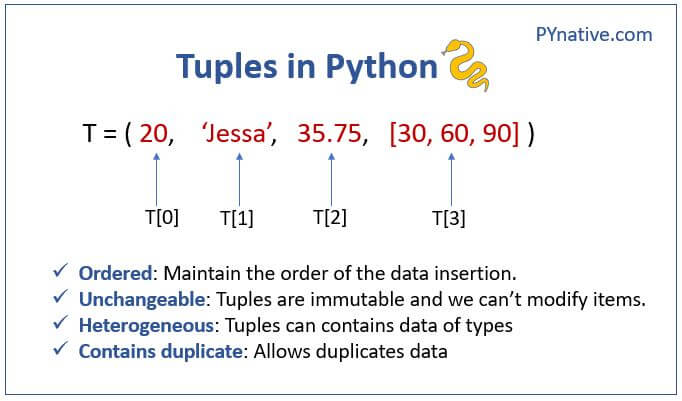
Tuple (Immutable)
A tuple is a fixed-size, ordered collection of items that cannot be modified after creation. You can think of it as an array with a fixed size. Tuples are denoted by parentheses () and elements are separated by commas.
Here's an example:
my_tuple = (1, 2, 3)
print(my_tuple) # Output: (1, 2, 3)
You can't modify a tuple after creation
try:
my_tuple.append(4)
except AttributeError:
print("Can't add to an immutable tuple")
Tuples are useful when you need a collection that cannot be modified and requires efficient lookup or iteration.
Key Differences
Here's a summary of the key differences between list, set, and tuple:
In conclusion, list is suitable for dynamic collections that need to grow or shrink, set is ideal for storing unique, unordered elements, and tuple is perfect for immutable, ordered collections that do not require modification. By choosing the right data structure, you can write more efficient, effective, and maintainable code in Python.