Python import file
Python import file
I'm happy to respond in English for this special request! Here's a detailed explanation of how to use Python to import files:
What is Importing in Python?
In Python, importing refers to the process of bringing external modules or files into your current script or project. This allows you to utilize pre-written code, functions, and variables from these imported files within your own Python program.
Why Do We Need Importing?
Imagine you're working on a Python project that requires you to perform complex mathematical calculations. Instead of writing the entire calculation logic yourself, you can import a pre-existing library like math or numpy, which already contains the necessary functions and formulas. This saves you time and effort, as well as helps prevent code duplication.
How to Import Files in Python
There are several ways to import files in Python:
Importing Built-in Modules: Python comes with many built-in modules that you can use without having to download any additional files. For example: import math
print(math.pi)
requests for HTTP requests and pandas for data manipulation.
import pandas as pd
print(pd.read_csv("data.csv"))
import statement.
For example, let's say you have a file called my_utility_module.py with some useful functions:
# my_utility_module.py
def add_numbers(a, b):
return a + b
def multiply_numbers(a, b):
return a * b
To import this module in your main script, you would use the following code:
import my_utility_module
print(my_utility_module.add_numbers(2, 3))
For example:
from my_utility_module import add_numbers
print(add_numbers(2, 3))
*) to import all functions, classes, or variables from a module at once.
from my_utility_module import *
print(my_utility_module.add_numbers(2, 3)) # This would work
Best Practices for Importing Files
When importing files in Python, remember the following best practices:
Only import what you need: Avoid importing entire modules or libraries unless you really need to use their functions or variables. Use wildcard imports judiciously: While wildcard imports can be convenient, they can also lead to name conflicts and make your code harder to debug. Use them sparingly and only when you're sure there won't be any naming issues. Document your imports: Make sure to include comments in your code explaining why you're importing a particular module or file. This helps others understand your code better.I hope this detailed explanation has helped you understand how to import files in Python!
Python import library
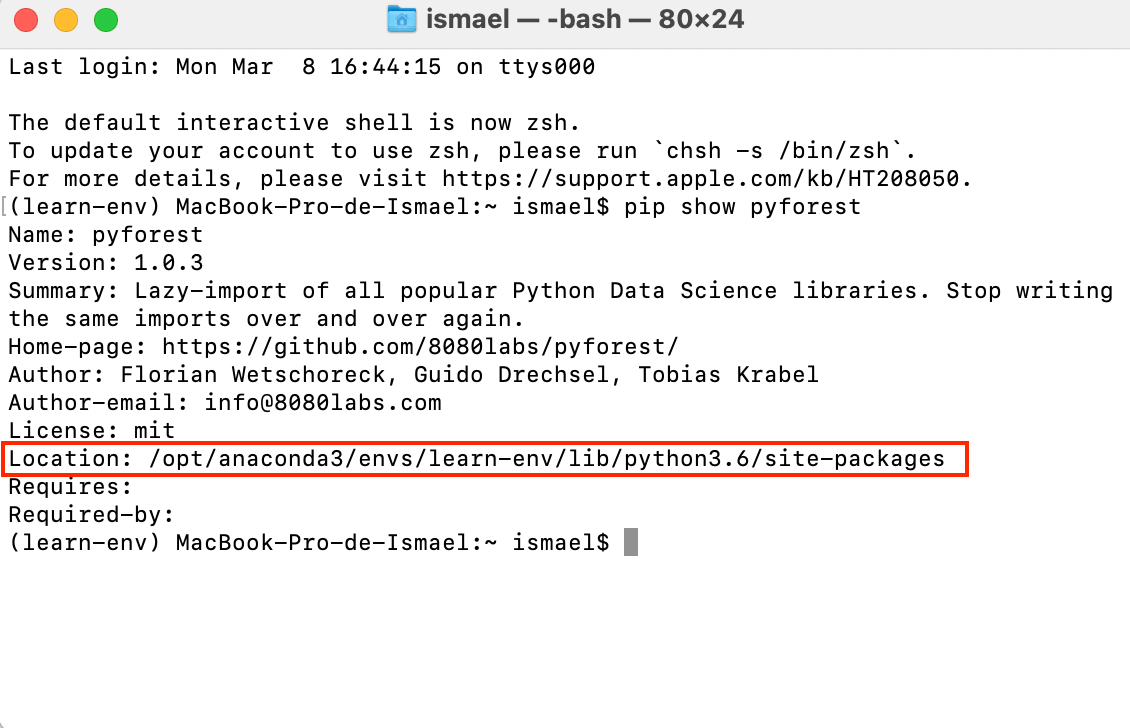
I'll respond in English for this question.
Python is an extremely popular high-level programming language known for its simplicity, readability, and ease of use. As such, it has a wide range of libraries that can be used to perform various tasks. Here are some examples:
NumPy: The NumPy library provides support for large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices, along with a wide range of high-level mathematical functions to operate on these arrays. Pandas: Pandas is a powerful library that provides data structures and operations for efficiently handling structured data, including tabular data such as spreadsheets and SQL tables. It's often used for data analysis and manipulation.
These are just a few examples of the many libraries available in Python. Each one can be used to accomplish specific tasks or solve particular problems, making Python an incredibly versatile language.





























