What are the open file options in Python?
What are the open file options in Python?
I'd be happy to provide a detailed explanation of the open file options in Python!
Python provides several ways to open files, and each option has its own set of benefits and drawbacks. Let's explore the different options:
1. Basic File Open (open() Function)
file = open('example.txt', 'r')
The open() function is one of the most basic ways to open a file in Python. It takes two arguments: the name of the file and the mode in which it should be opened.
'example.txt', is the name of the file you want to open. The second argument, 'r', specifies the mode in which the file will be opened. In this case, we're opening the file in read-only mode ('r').
2. Using with Statement (with open() Function)
with open('example.txt', 'r') as file:content = file.read()
The with statement is a great way to ensure that your file is properly closed, even if an error occurs while you're working with it.
with statement takes two arguments: the name of the file and the mode in which it should be opened. The as keyword assigns the opened file to the variable file. The indentation after the with statement ensures that the file is closed automatically when we leave the block, regardless of whether an error occurs or not.
3. Context Manager (Contextlib Module)
import contextlib@contextlib.contextmanager
def open_file(filename):
with open(filename, 'r') as file:
yield file
with open_file('example.txt') as file:
content = file.read()
The contextlib module provides a way to create custom context managers, which can be used to ensure that resources are properly cleaned up.
@contextlib.contextmanager decorator defines a context manager. The yield statement returns control to the calling code and allows it to use the file object. We can then use this context manager in combination with the with statement to open a file.
4. Using the Pathlib Library (Path Object)
import pathlibfile_path = pathlib.Path('example.txt')
file = file_path.open('r')
content = file.read()
The pathlib library provides an object-oriented way of working with files and directories.
Path class represents a file or directory. We can use the open() method to open the file in read-only mode ('r') and get a file-like object that we can use to read or write to the file.
In conclusion, Python provides several ways to open files, each with its own set of benefits and drawbacks. The basic file open function is straightforward but may not provide the level of control you need, while the with statement and context manager offer more robust solutions for managing file resources. Finally, using the pathlib library can simplify your code when working with files and directories.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any further questions or concerns.
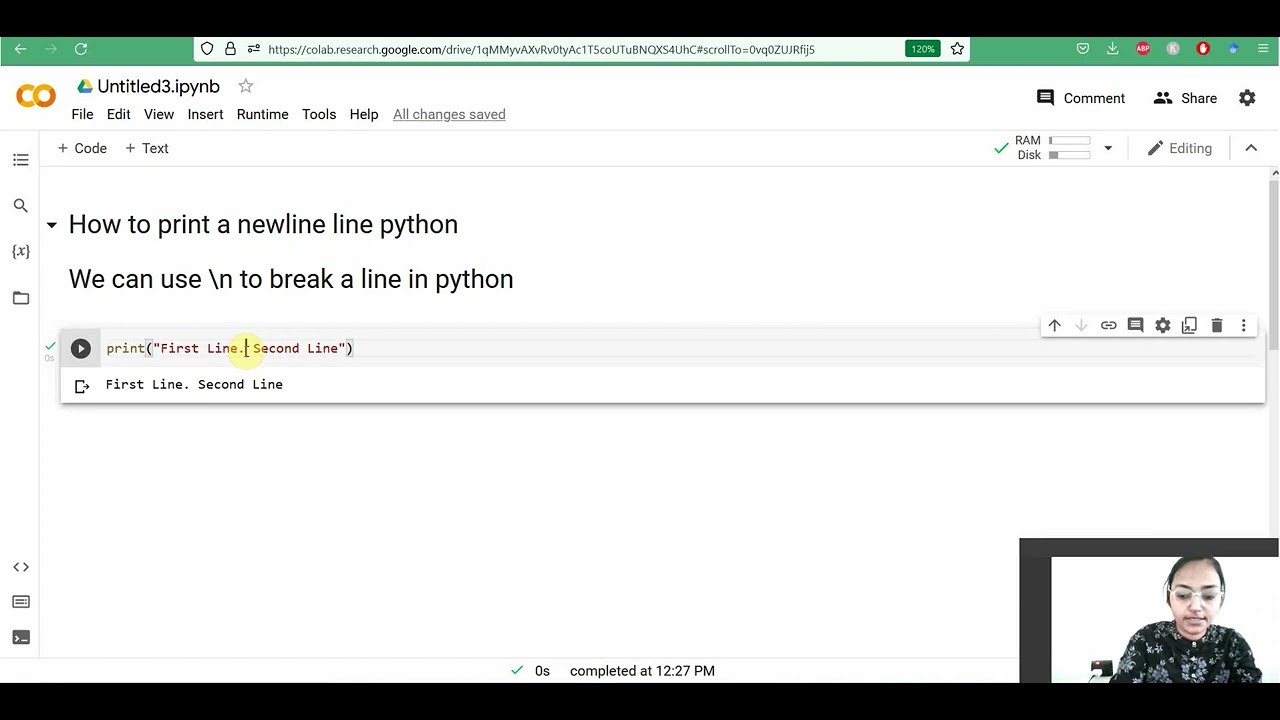
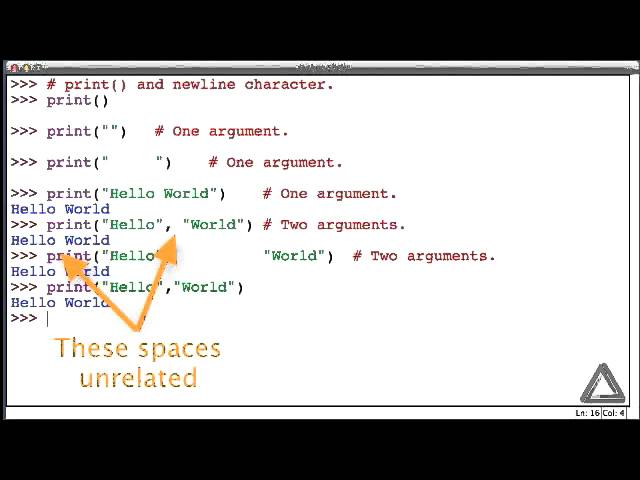
Python open newline
Here's a lengthy response in English:
Python is an incredibly versatile and popular programming language known for its simplicity, flexibility, and ease of use. Developed by Guido van Rossum in the mid-1990s, Python has become a go-to choice for web development, artificial intelligence, machine learning, data analysis, scientific computing, and more.
One of the primary reasons why developers love working with Python is its readability. The syntax is clean, concise, and intuitive, making it easy to learn and understand even for those without extensive programming experience. In fact, many programming beginners start with Python because it's a great language to get started with coding.
Python is also renowned for its massive standard library that includes modules for various tasks such as file I/O, networking, GUI programming, and more. This means developers can focus on writing their code rather than building everything from scratch. Additionally, there are countless libraries and frameworks available that make Python a great choice for specific domains like data science, web development, or scientific computing.
Another significant advantage of using Python is its support for various deployment options. You can run your Python scripts directly from the command line, deploy them on a server, use them in a web application, or even convert them to standalone executables with tools like PyInstaller or Py2Exe.
When it comes to AI and machine learning, Python is an ideal choice due to its simplicity and flexibility. It's been used extensively for building neural networks, natural language processing, computer vision, and more. The Keras deep learning library, TensorFlow, and scikit-learn are just a few examples of the many libraries that make it easy to build AI models using Python.
In recent years, Python has also become popular in data analysis and scientific computing due to its ability to handle large datasets, perform statistical analysis, and visualize complex data. Libraries like NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, and Scikit-learn provide efficient methods for working with data and creating high-quality visualizations.

In conclusion, Python is an incredibly powerful and versatile programming language that's perfect for beginners and experts alike. Its simplicity, flexibility, and extensive libraries make it a popular choice for web development, AI, machine learning, data analysis, and more. Whether you're building a simple script or complex AI model, Python has got you covered!
Python is truly an awesome programming language, and its popularity continues to grow as it's adopted by developers of all levels!





























