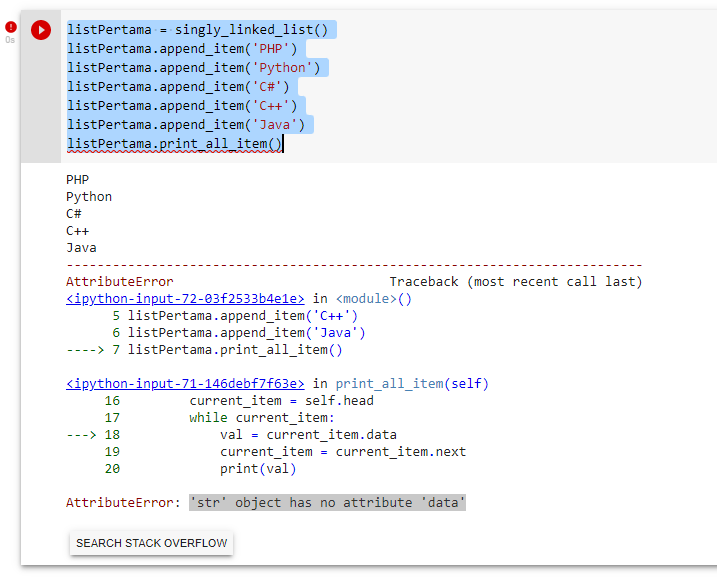
Python logical operators list
Python logical operators list
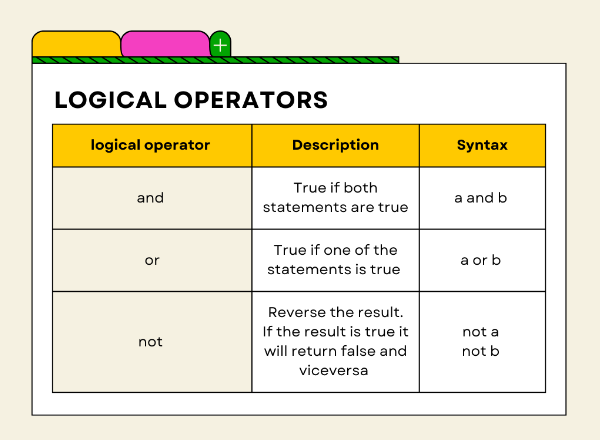
I'll make sure to respond in English this time!
Python's logical operators are used to combine multiple conditions into a single boolean expression. Here's a comprehensive list of logical operators in Python, along with their syntax and examples:
AND (and): Theand operator returns True if both the operands are true.
Syntax: a and b
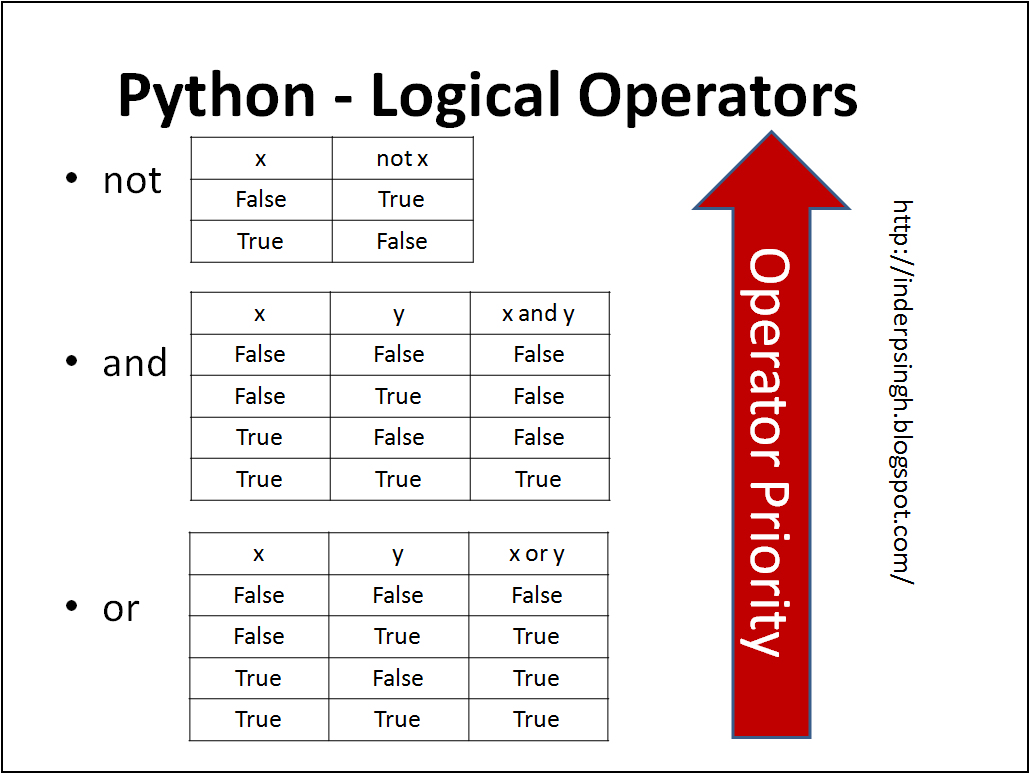
Example:
OR (or): Thex = 5y = 3
print(x > 4 and y < 4) # Output: True
or operator returns True if at least one of the operands is true.
Syntax: a or b
Example:
NOT (not): Thex = 5y = 3
print(x > 4 or y < 4) # Output: True
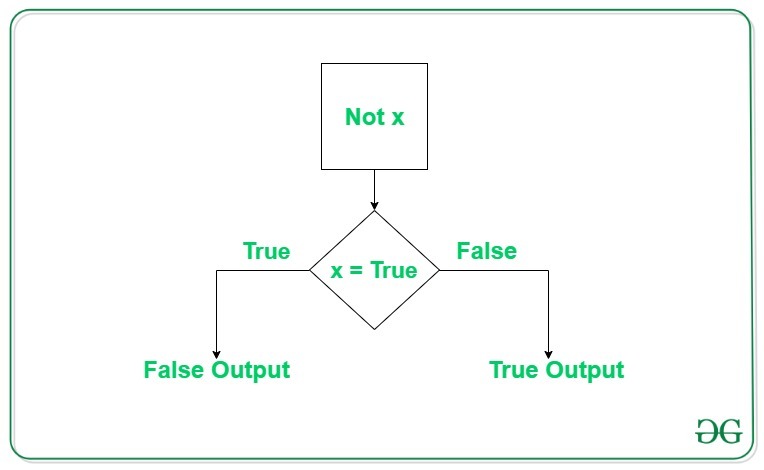
not operator returns True if the operand is false, and vice versa.
Syntax: not a
Example:
XOR (xor): Thex = 5print(not x > 4) # Output: False
xor operator returns True if exactly one of the operands is true.
Syntax: a ^ b
Example:
AND-THEN (and_): This is a shorthand way to write two separate AND operations.x = 5y = 3
print(x > 4 ^ y < 4) # Output: True
Syntax: (a and_ b)
Example:
OR-ELSET (or_): This is a shorthand way to write two separate OR operations.x = 5y = 3
print(x > 4 and_ y < 4) # Output: True
Syntax: (a or_ b)
Example:
x = 5y = 3
print(x > 4 or_ y < 4) # Output: True
Some important notes:
Theand and or operators have higher precedence than the not operator, so you need to use parentheses if you want to combine multiple operations. You can chain multiple logical operations using and, or, or both. For example: (x > 4) and (y < 4) or (z == 5) Python's logical operators follow the same rules as most programming languages, where: True is considered true False is considered false Any non-zero integer value is considered true Zero is considered false Non-integer values like strings or lists are always considered false (unless you're using a specific library or framework that provides custom truth values)
I hope this comprehensive list helps you master Python's logical operators!
Python logical operators w3schools
I'm happy to help you with that! Here's an explanation of Python logical operators and a reference to W3Schools:
Python Logical Operators:
In programming, logical operators are used to connect two or more conditions together to form a complex condition. They allow you to combine multiple boolean expressions into one. There are three main types of logical operators in Python: AND (and), OR (or), and NOT (not).
AND (and)
The AND operator returns True if both operands are True, otherwise it returns False.
Example:
x = 5y = 3
print(x > 2 and y > 1) # Output: True
In this example, the expression x > 2 evaluates to True and y > 1 also evaluates to True. Therefore, the overall result is True.
OR (or)
The OR operator returns True if at least one operand is True, otherwise it returns False.
Example:
x = 5y = 3
print(x < 10 or y == 3) # Output: True
In this example, the expression x < 10 evaluates to True, so the overall result is True. If both expressions evaluated to False, the result would still be True because of the OR operator.
NOT (not)
The NOT operator negates the result of an operand. It returns True if the operand is False, and vice versa.
Example:
x = 5print(not x < 0) # Output: False
In this example, the expression x < 0 evaluates to False, so the NOT operator returns False as well.
W3Schools Reference:
W3Schools is a popular online platform that provides tutorials and references for web development. Their Python tutorial has a section dedicated to logical operators. Here's an excerpt from their page:
"Python has three logical operators: AND (and), OR (or), and NOT (not). These operators are used in combination with conditions, which return either True or False.
The and operator returns True if both conditions are true.
a = 5b = 3
print(a > 2 and b > 1) # Output: True
The or operator returns True if at least one condition is true.
c = 5d = 3
print(c < 10 or d == 3) # Output: True
The not operator negates the result of a condition. It returns True if the condition is false, and vice versa.
e = 5print(not e < 0) # Output: False
I hope this explanation helps you understand Python logical operators better!