Python array 2D
Python array 2D
I'm happy to help you with your request! Here's a detailed explanation of working with 2D arrays in Python:
What is a 2D Array?
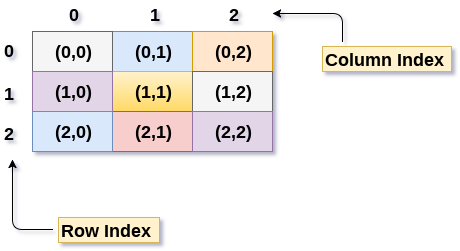
In programming, an array is a collection of items that can be accessed by their index or key. A 2D array, also known as a matrix, is a type of array that has two dimensions - rows and columns.
Think of it like a spreadsheet where each row represents a single "row" (or line) and each column represents a single "column". Each cell in the spreadsheet corresponds to an element in your 2D array, which can be accessed by its row and column index.
Creating a 2D Array in Python
There are several ways to create a 2D array in Python:
Using List Comprehension:my_2d_array = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
This creates a 2D array with three rows and three columns.
Using Numpy:The NumPy library in Python provides support for large, multi-dimensional arrays and matrices. You can create a 2D array using the numpy.array() function:
Using Python's Built-in List:import numpy as npmy_2d_array = np.array([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]])
my_2d_array = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
This creates a 2D array with three rows and three columns.
Accessing Elements in a 2D Array
To access an element in your 2D array, you need to specify the row index (0-based) and column index (0-based).
For example:
print(my_2d_array[1][1]) # prints 5
Here, my_2d_array[1][1] returns the element at the second row (index 1) and second column (index 1), which is equal to 5.
Manipulating a 2D Array
You can manipulate elements in your 2D array using standard Python list operations:
Append: Add new rows or columns:Insert: Insert a row or column at a specific position:my_2d_array.append([10, 11, 12])
Update: Modify elements:my_2d_array.insert(0, [1, 2, 3]) # adds a new first row
my_2d_array[1][1] = 10 # sets the second row and second column to 10
Benefits of Working with 2D Arrays in Python
Python's ability to handle 2D arrays (and higher dimensions) offers many benefits:
Efficient Data Storage: Store large amounts of data efficiently. Easy Data Manipulation: Perform complex operations on your data with ease. Scalability: Handle large datasets and perform operations quickly.Real-World Applications of 2D Arrays in Python
2D arrays have numerous real-world applications:
Data Analysis: Work with large datasets, such as financial transactions or sensor readings. Image Processing: Manipulate image data structures using 2D arrays. Scientific Computing: Perform numerical computations on large matrices.In conclusion, 2D arrays are a powerful feature in Python that can be used for various purposes. Understanding how to work with them will help you solve real-world problems efficiently and effectively.
What is array () Python?
I'm glad you asked!
In Python, array() is not a built-in function. However, the term "array" can refer to several concepts:
[] and add elements to it using the append() method. While lists are not strictly arrays in the mathematical sense, they share some similarities with NumPy arrays.
How array() differs from Python Lists
While both NumPy arrays and Python lists can store multiple values, there are key differences:
Type: NumPy arrays are designed specifically for numerical computations and have additional features for efficient processing. Python lists, on the other hand, are more general-purpose containers. Indexing: NumPy arrays use zero-based indexing (i.e., the first element is at index 0), whereas Python lists can also use negative indices to access elements from the end of the list. Operations: NumPy arrays support vectorized operations (e.g., matrix multiplication) and broadcasting, which enables efficient computation on large datasets. Python lists do not have these features.When to use array()
If you:
Need to perform numerical computations efficiently (e.g., scientific simulations, data analysis). Are working with large datasets or matrices. Require features like vectorized operations and broadcasting.In this case, NumPy arrays (numpy.array()) would be the better choice.
However, if your tasks don't require these specific features and you're just looking for a simple, flexible container to store data, Python lists (e.g., [] or list() ) might suffice.





























