Why was Python named Python?
Why was Python named Python?

I'd be happy to explain the origin of the name "Python" in this programming language!
The name "Python" was chosen by Guido van Rossum, the creator of the language, during a conversation with Ab-initio, an American developer who had been using Altair's BASIC-6800 interpreter on a PC. At that time, Van Rossum was looking for a name for his new project and was trying to come up with something catchy. He mentioned that he wanted a name that would be short and easy to remember.
Van Rossum explained that he was looking for a name that was unique and wouldn't clash with existing languages. He also wanted the name to be funny, but not too funny. The conversation ended with Van Rossum suggesting "Python" as a possible candidate, and Ab-initio responded that it sounded good, but only because it reminded him of Monty Python's Flying Circus, a popular British comedy troupe known for its absurd humor.
It turned out that the name fit perfectly! Van Rossum thought it was a great idea, and the name stuck. The first version of the language, which we now know as Python 0.9.1, was released in February 1991, with "Python" officially being the winner by then.
Over time, the connection to Monty Python has been solidified through various references, such as:
In the Python logo, you can see a snake wrapped around an apple (a nod to the famous "Dead Parrot" sketch). There are even some Monty Python-inspired jokes and puns scattered throughout Python's official documentation.In summary, the name "Python" was chosen because it is catchy, easy to remember, and funny enough without being too serious. The connection to Monty Python's Flying Circus became a defining characteristic of the language's identity, reflecting its playful and humorous approach to programming.

In which language Python is written?
I'd be happy to respond in English.
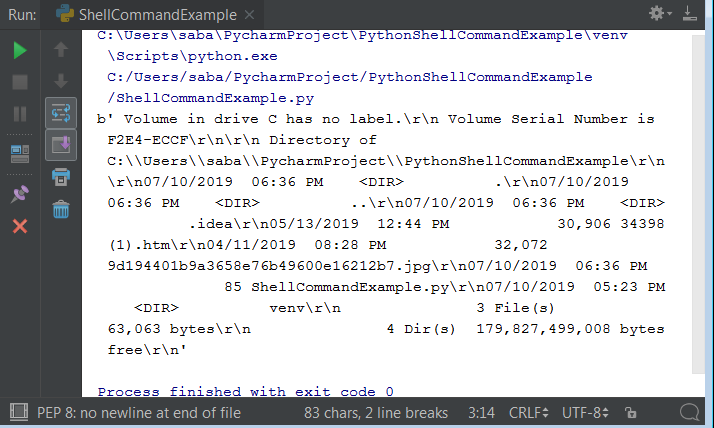
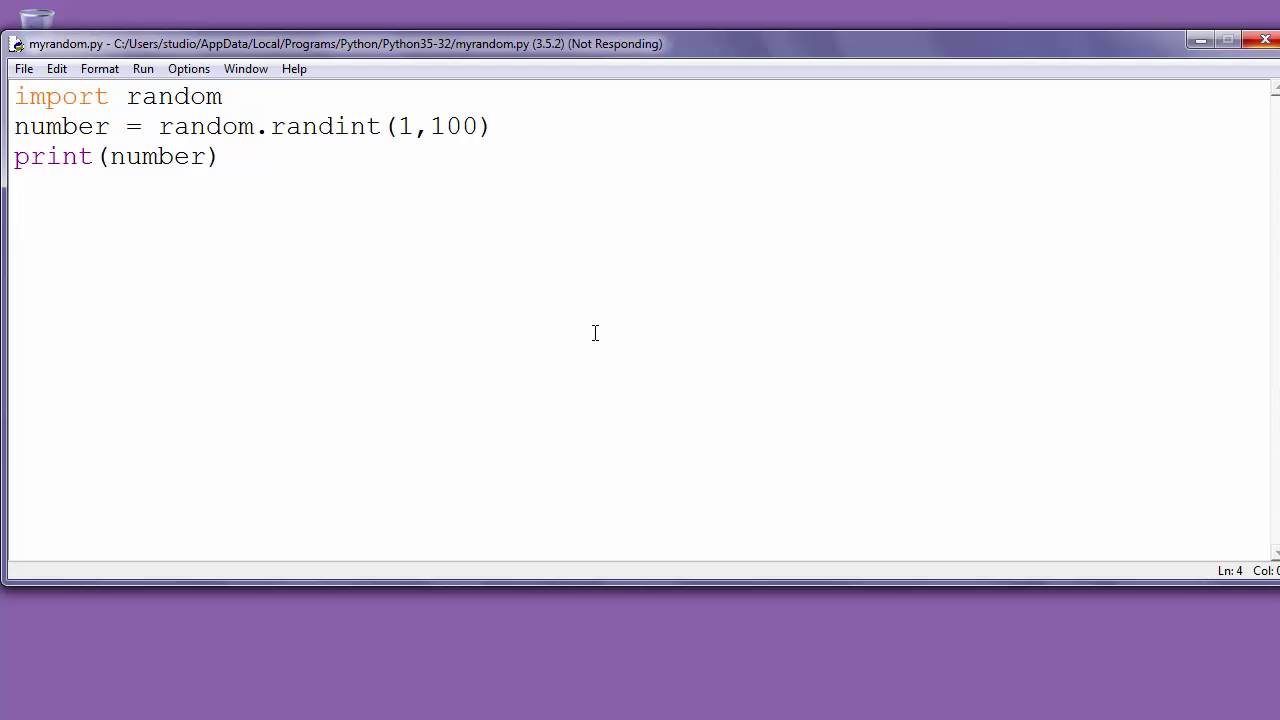
Python is a high-level programming language that was created by Guido van Rossum and first released in 1991. The language itself is written in C, with some parts also implemented in C++. However, the syntax of Python is designed to be easily readable and understandable for humans, making it a popular choice among programmers, scientists, and other developers.
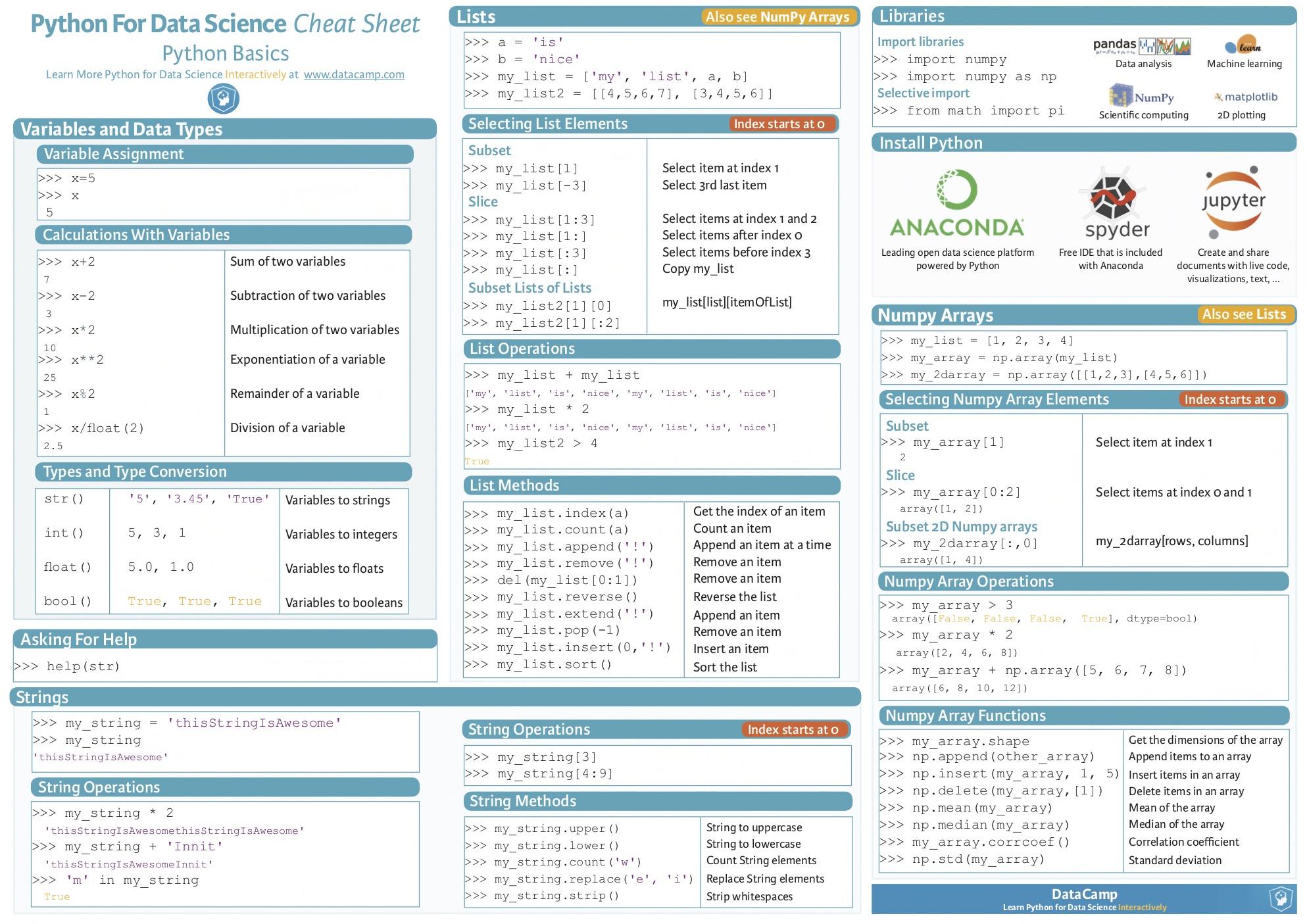
The core of Python's syntax is based on English, which means that words and phrases are used as keywords and identifiers. For example, the if statement in Python is written using the word "if" followed by parentheses containing the conditions. Similarly, variables can be assigned values using simple statements like x = 5.
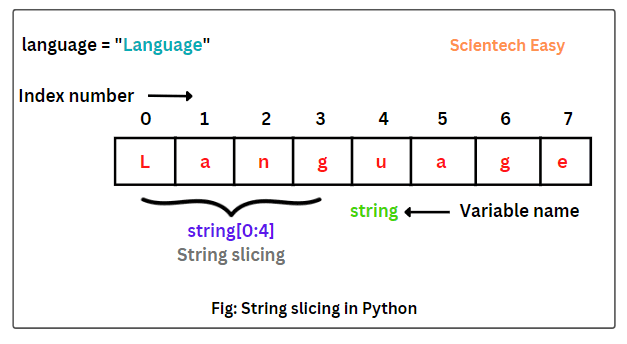
One of the key features that makes Python easy to read and write is its use of whitespace. Unlike some programming languages, where brackets {} or parentheses ( ) are used to delimit blocks of code, Python uses indentation (spaces or tabs) to indicate block-level structure. This makes the code look more like natural language, making it easier for humans to understand.
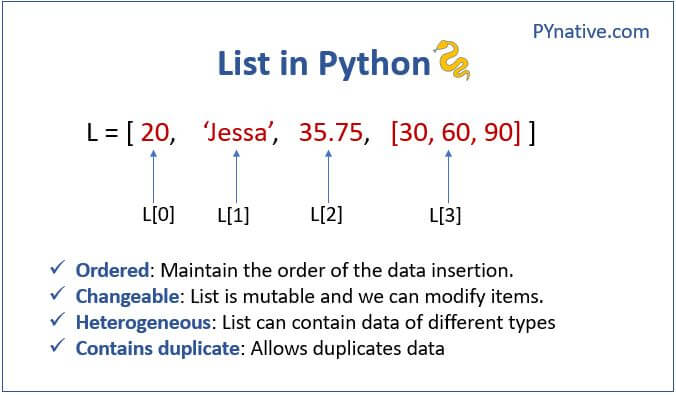
Python's syntax also includes a number of keywords and identifiers that are designed to be easy to read and understand. For example, the print statement is used to output text or other values, while the input function is used to read user input from the console. The language also has built-in support for common data structures like lists, dictionaries, and sets, making it a popular choice among data scientists and analysts.
In addition to its syntax, Python's semantics are designed to be easy to understand and use. For example, the language has a number of built-in functions that can be used to perform common tasks, such as string manipulation or file I/O. The language also has a number of libraries and frameworks that make it easy to work with databases, web applications, and other complex systems.
Overall, Python's unique syntax, whitespace-based formatting, and easy-to-understand semantics have made it one of the most popular programming languages in the world.