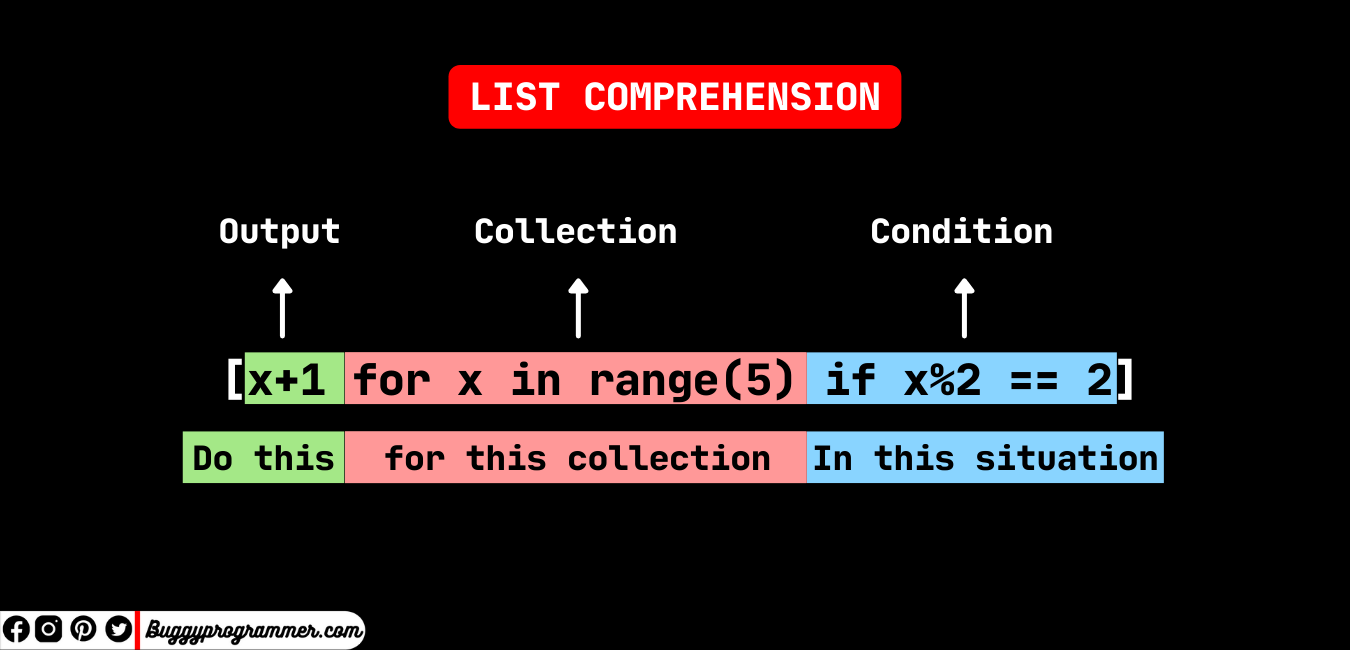
With keyword Python
With keyword Python
I'm happy to help!
Python: A Powerful Programming Language
Python is an interpreted high-level programming language that has become widely popular in recent years, particularly among beginners and experienced developers alike. Developed by Guido van Rossum and first released in 1991, Python is known for its simplicity, ease of use, and flexibility.
Key Features of Python:
Easy to Learn: Python has a syntax that is designed to be easy to read and write, making it an ideal language for beginners. It has fewer syntactical constructs than other languages, which reduces the amount of code you need to write. High-Level Abstraction: Python's high-level abstraction means that you can focus on solving problems without worrying about low-level details, such as memory management or pointer arithmetic. Dynamic Typing: Python is dynamically typed, which allows you to declare variables and assign them values without specifying the data type beforehand. Cross-Platform Compatibility: Python programs can run seamlessly across different platforms, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and mobile devices. Extensive Libraries: Python has a vast array of libraries and modules that make it easy to perform tasks such as file I/O, networking, web development, scientific computing, data analysis, machine learning, and more.Real-World Applications of Python:
Web Development: Python is used extensively for web development with frameworks like Django, Flask, Pyramid, and others. Data Science and Machine Learning: Python has become a popular choice for data science and machine learning due to libraries like NumPy, pandas, scikit-learn, TensorFlow, Keras, and more. Automation: Python is widely used for automating tasks such as data entry, file management, and system administration. Scientific Computing: Python is a popular choice for scientific computing, particularly in fields like astronomy, physics, biology, and chemistry. Education: Python is often taught in introductory programming courses due to its simplicity and ease of use.Why Choose Python:
Rapid Development: Python's syntax and nature make it ideal for rapid prototyping and development. Flexibility: Python can be used for a wide range of applications, from data analysis to web development to machine learning. Large Community: Python has a massive and supportive community, with numerous online resources, forums, and documentation available. Extensive Libraries: Python's extensive library ecosystem makes it easy to find the right tool for the job.In conclusion, Python is an incredibly powerful and versatile programming language that offers many advantages, making it an ideal choice for beginners and experienced developers alike. Its ease of use, flexibility, and large community make it an excellent option for a wide range of applications.
Python with statement example
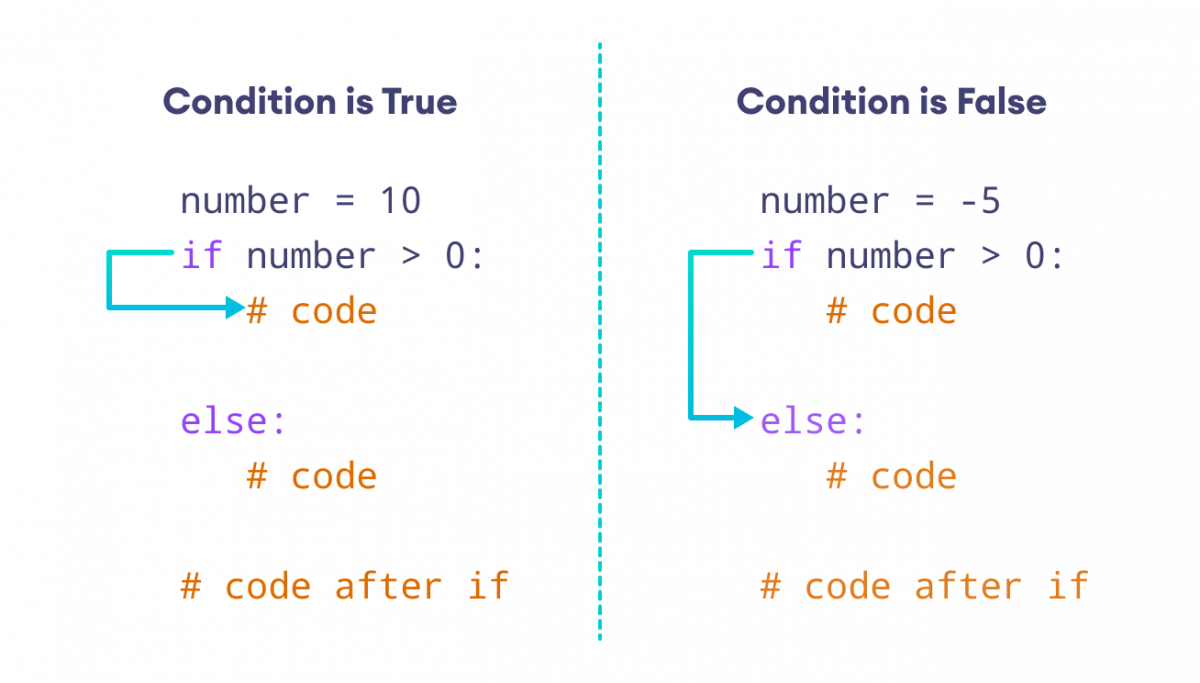
I'd be happy to explain the with statement in Python!
In Python, the with statement is used to define a block of code that needs to release resources (e.g., files, network connections) after execution. This statement ensures that the resource is properly cleaned up regardless of whether an exception was thrown or not.
Here's a simple example:
def read_file(filename):try:
with open(filename, 'r') as file:
print(file.read())
except FileNotFoundError:
print(f"File {filename} not found!")
In this example, the with statement is used to open and read a file. The code inside the block will be executed, and then the file object will automatically be closed when you exit the block.
Here are some key benefits of using the with statement:
try-finally or try-except blocks to release resources. Improved code readability: The code within the block is focused on performing the task without worrying about resource cleanup.
Here's another example with a context manager that uses the with statement:
class Timer:def init(self):
self.start_time = None
def start(self):
self.start_time = time.time()
def stop(self):
if not self.start_time:
return
print(f"Time taken: {time.time() - self.start_time:.2f} seconds")
self.start_time = None
def main():
timer = Timer()
try:
with timer:
do some workpass
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
if name == "main":
main()
In this example, the Timer class is a context manager that tracks the start and stop times. When you use it with the with statement, the start() method is called when entering the block, and the stop() method is called when exiting the block.
Python's with statement makes working with resources like files and network connections much more straightforward and exception-safe. By using a context manager to manage these resources, you can write cleaner and more robust code!