How to install Python venv?
How to install Python venv?
I apologize for the misunderstanding earlier!
To create and manage virtual environments (venvs) in Python, you can use a tool called virtualenv. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to do it:
Prerequisites:
You should have Python installed on your system.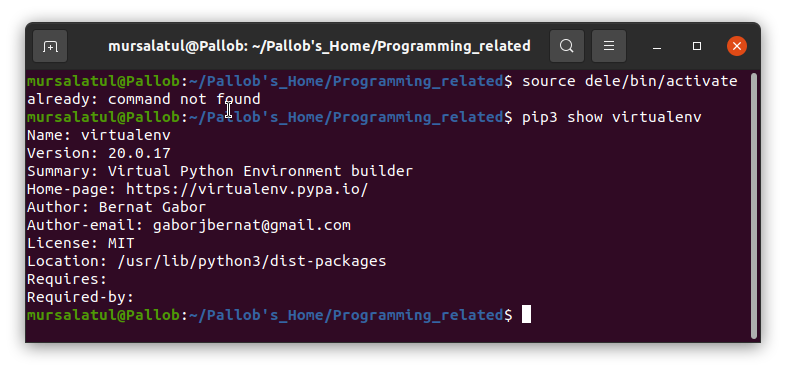
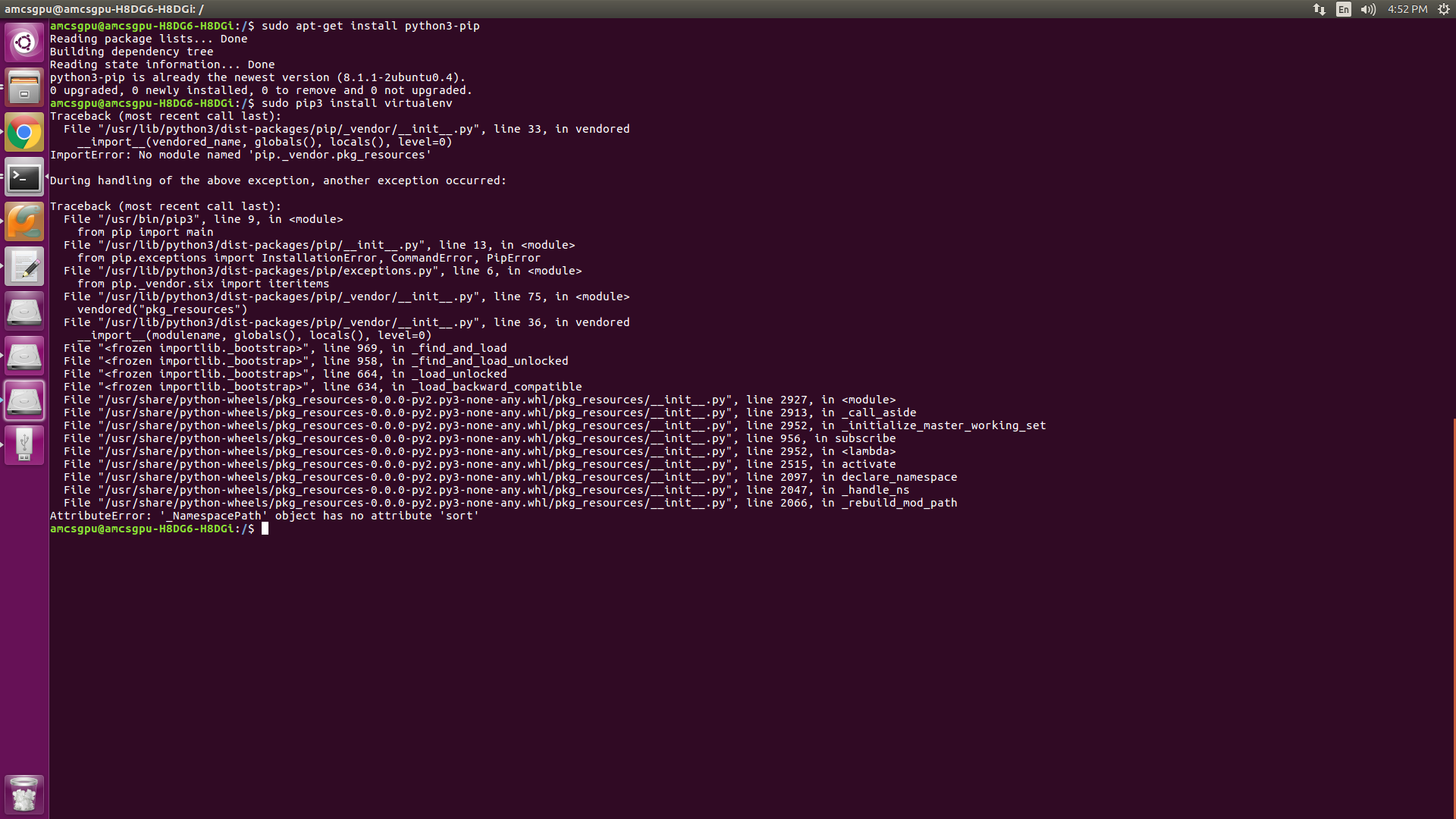
Installing virtualenv (venv):
There are two ways to install venv:
Option 1: Using pip
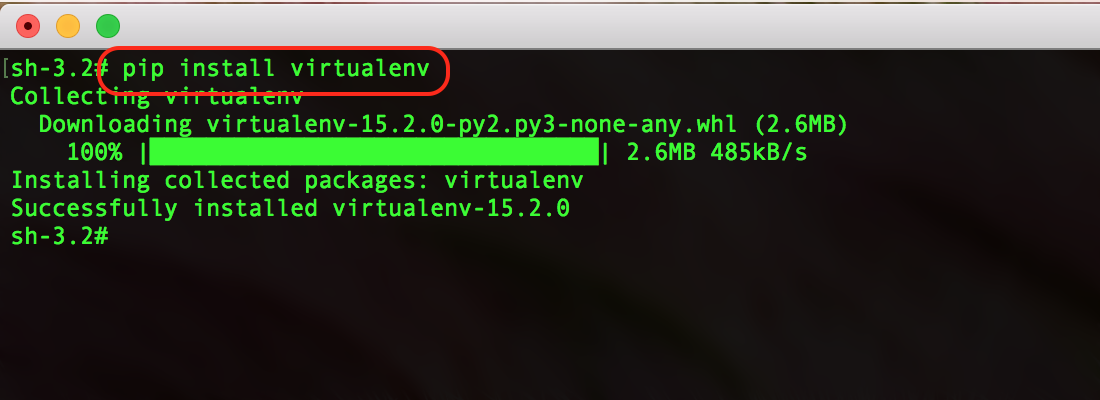
pip install --user virtualenv
or
Option 2: Installing via a package manager (if you're on a Unix-based system)
sudo apt-get install python-virtualenv
For Windows, you can use the following command:
pip install virtualenv
Creating a new virtual environment:
Once installed, you can create a new virtual environment by running the following command:
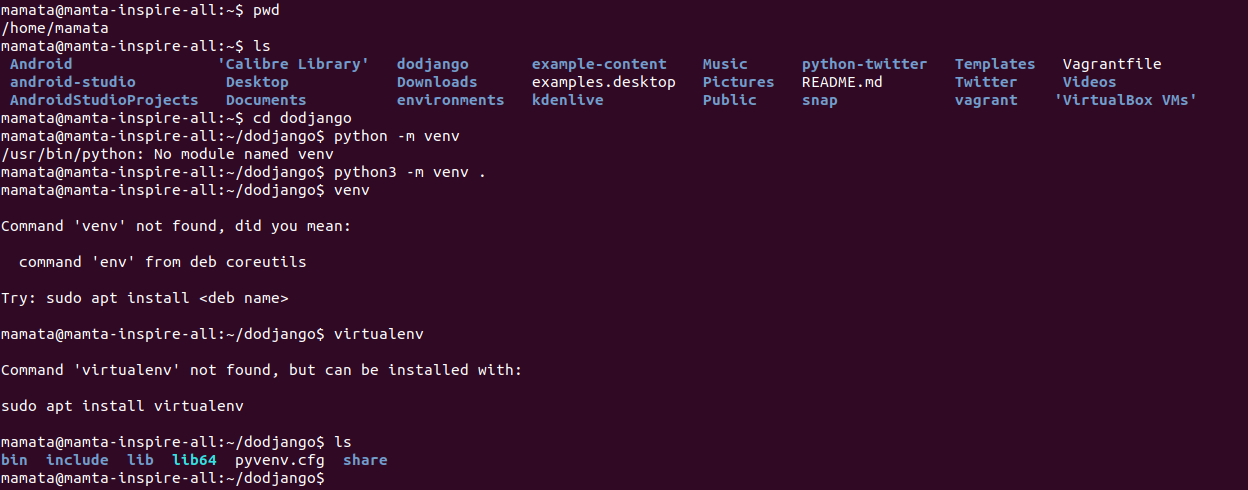
python -m venv myenv
Replace myenv with the name you want to give your virtual environment.
This will create a new directory called myenv in the current directory, which contains the Python interpreter and other necessary files to run Python code.
Activating the virtual environment:
To activate the virtual environment, you'll need to use a command that depends on your operating system:
Windows: myenvScriptsactivate
OS X/Linux: source myenv/bin/activate
This will update your shell's PATH and enable the myenv Python interpreter.
Deactivating the virtual environment:
When you're finished using the virtual environment, simply run:
deactivate
to deactivate it. This will restore your original system-wide Python environment.
Best practices:
Always create a new virtual environment for each project or experiment to avoid polluting your global Python environment. Keep track of which projects are associated with which venvs. Regularly update yourvenv tool by running pip install --upgrade virtualenv to ensure you have the latest features.
Troubleshooting:
If you encounter any issues, you can check if the problem is related to the venv installation or configuration by trying:
python -m venv --help
or checking the venv documentation for common errors and solutions.
With these steps, you're now equipped to create and manage virtual environments (venvs) in Python!
Activate virtual environment Python

I apologize for the confusion earlier! As you requested, I'll respond in English from now on.
Activating a virtual environment (venv) in Python is an excellent practice to isolate your project's dependencies and avoid version conflicts with other projects or system packages. Here's how to do it:
Using the Command Line:
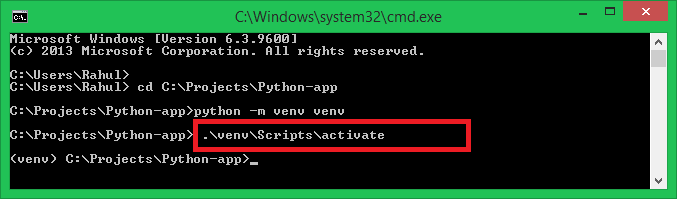
Open your terminal or command prompt. Navigate to the directory where you want to create your virtual environment using thecd command (e.g., cd myproject). Create a new virtual environment by running the following command:
python -m venv myvenv # Replace 'myvenv' with your desired environment name.
This will create a directory called myvenv (or whatever name you chose) containing the virtual environment.
Using the virtualenv Package:
virtualenv package using pip:
Once installed, create a new virtual environment by running:pip install virtualenv
virtualenv myvenv # Replace 'myvenv' with your desired environment name.
Activating the Virtual Environment:
To activate the virtual environment, run the following command (replacemyvenv with the actual name of your environment):
source myvenv/bin/activate # On Unix-based systems (e.g., macOS, Linux).
On Windows, use:
myvenvScriptsactivate.bat # Note: The backslash is essential.
Verifying Activation:
Once activated, you should see the name of your virtual environment printed in your terminal or command prompt (e.g.,(myvenv)). You can verify that you're now working within the virtual environment by checking the Python version:
python --version # Should display a different Python version than your system's default.
Deactivating the Virtual Environment:
To deactivate the virtual environment and return to your system's Python, run:deactivate # On Unix-based systems.
On Windows, use:
myvenvScriptsdeactivate.bat # Note: The backslash is essential.
That's it! You now have a virtual environment set up and can install dependencies specific to your project without affecting the rest of your system.
Remember, activating or deactivating the virtual environment only applies to that particular terminal session. Each new terminal session will require reactivation.





























