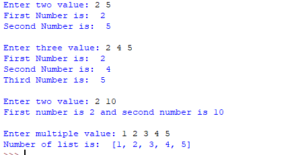
What is the list of logical operators in Python?
What is the list of logical operators in Python?
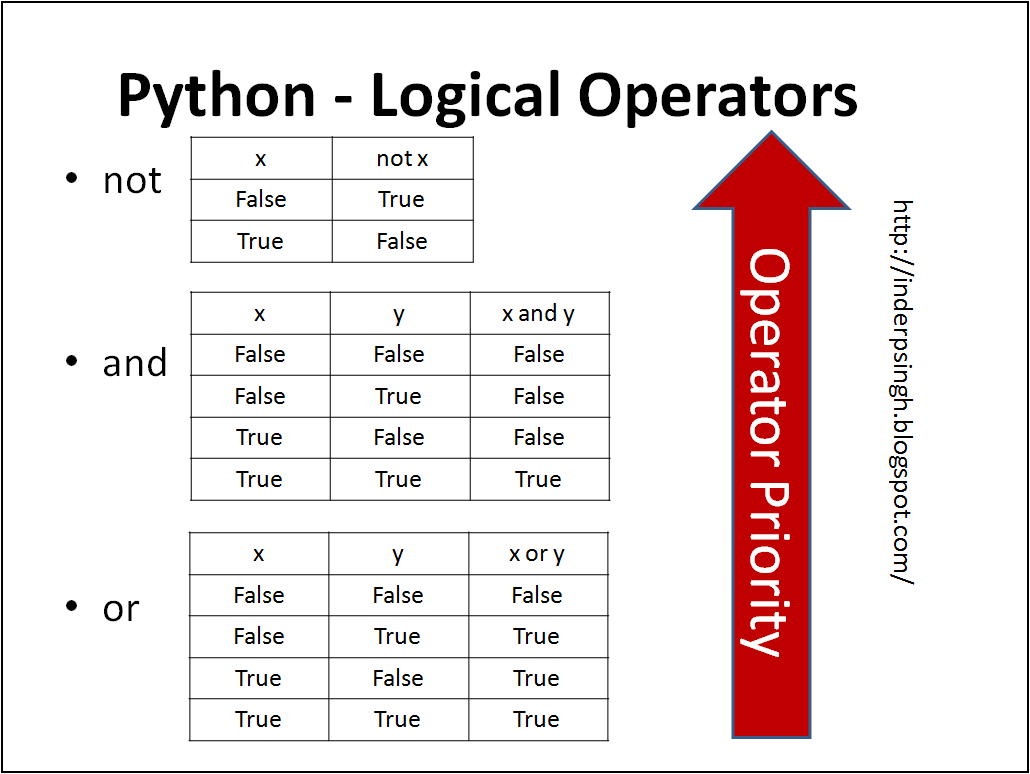
Here is the list of logical operators in Python:
and: Theand operator returns True if both operands are true, and False otherwise.
Example:
>>> True and True
True
True and False
False
False and True
False
False and False
False
or operator returns True if at least one operand is true, and False otherwise.
Example:
>>> True or True
True
True or False
True
False or True
True
False or False
False
not operator inverts the boolean value of its operand.
Example:
>>> not True
False
not False
True
in operator checks if a value is present in a sequence (such as a list or tuple), or in a dictionary, and returns True if it is, and False otherwise.
Example:
>>> 1 in [1, 2, 3]
True
'hello' in {'hello': 'world', 'goodbye': 'cruel world'}
True
4 in [1, 2, 3]
False
not in operator checks if a value is not present in a sequence (such as a list or tuple), or in a dictionary, and returns True if it is not, and False otherwise.
Example:
>>> 4 not in [1, 2, 3]
True
'goodbye' not in {'hello': 'world', 'goodbye': 'cruel world'}
True
1 not in [1, 2, 3]
False
Note that the in and not in operators only work on sequences (such as lists or tuples) and dictionaries.
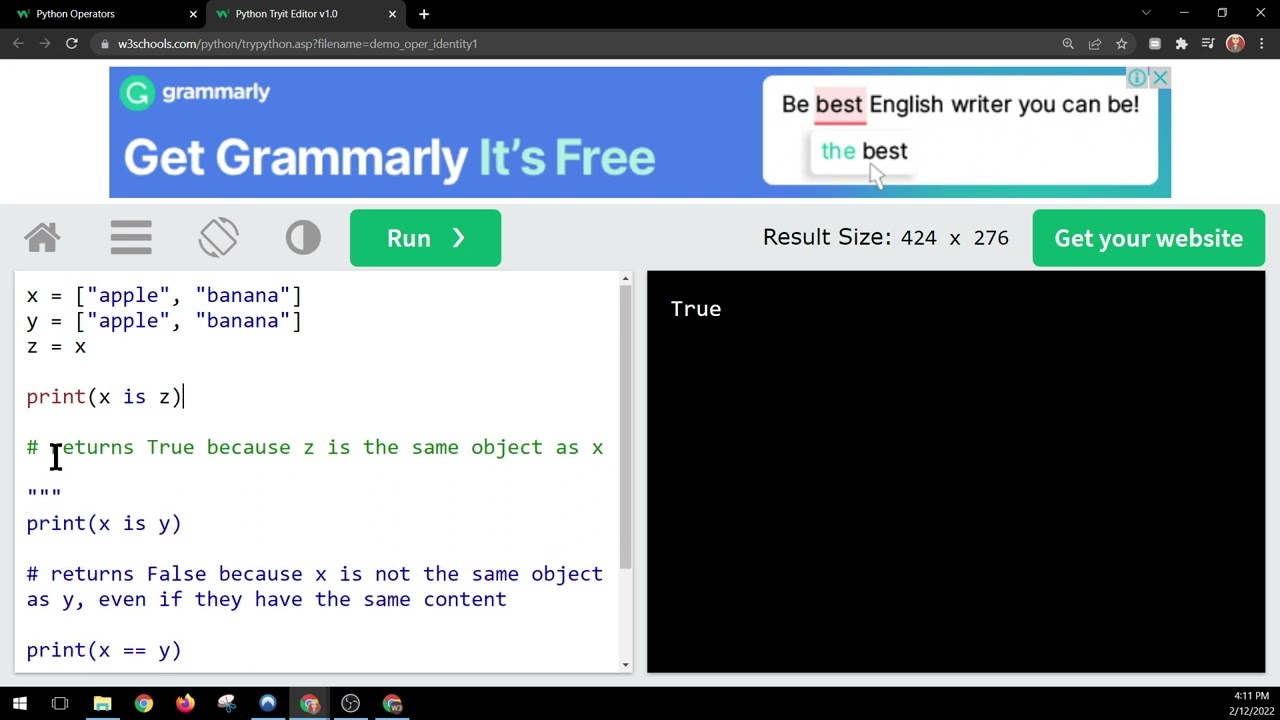
is operator checks if two objects are the same instance, and returns True if they are, and False otherwise.
Example:
>>> a = [1, 2, 3]; b = [1, 2, 3]; c = [4, 5, 6]
a is b
False
a is c
False
a == b
True
a is a
True
is not operator checks if two objects are not the same instance, and returns True if they are not, and False otherwise.
Example:
>>> a = [1, 2, 3]; b = [1, 2, 3]; c = [4, 5, 6]
a is not b
True
a is not c
True
a != b
True
a is not a
False
Note that the is and is not operators only work on instances (i.e., objects), and not on values or variables.
In summary, Python's logical operators include:
and: returns True if both operands are true, and False otherwise. or: returns True if at least one operand is true, and False otherwise. not: inverts the boolean value of its operand. in: checks if a value is present in a sequence or dictionary, and returns True if it is, and False otherwise. not in: checks if a value is not present in a sequence or dictionary, and returns True if it is not, and False otherwise. is: checks if two objects are the same instance, and returns True if they are, and False otherwise. is not: checks if two objects are not the same instance, and returns True if they are not, and False otherwise.What are operators in Python W3schools?
I'm happy to respond in English!
According to W3Schools, in Python, an operator is a symbol used to perform operations on values and expressions. In other words, operators are used to manipulate data and variables in your code.
Python provides various types of operators, including:
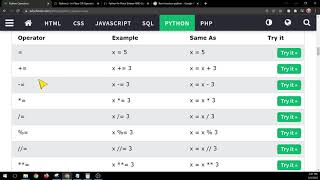
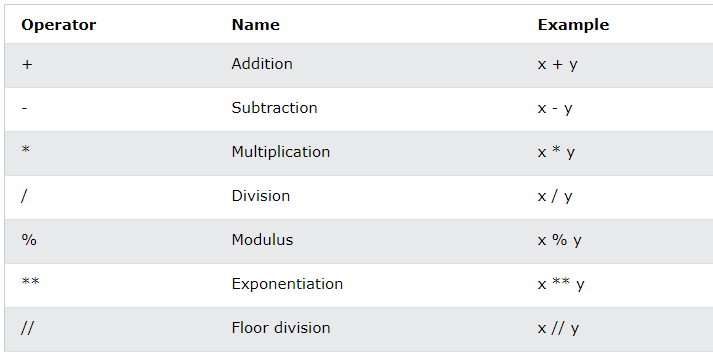
Arithmetic Operators: These operators are used for mathematical calculations, such as addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), division (/ or // for integer division), modulus (%), exponentiation (**).Example: x = 5; y = 3; print(x + y) (output: 8)
Example: x = 5; y = 3; print(x > y) (output: True)
Example: x = 5; y = 3; print(x > y and x != 0) (output: False)
Example: x = 5; x += 3; print(x) (output: 8)
Example: x = 5; y = 3; print(x & y) (output: 1)
Example: fruits = ['apple', 'banana']; print('apple' in fruits) (output: True)
Example: x = 5; y = 3; print(x is y) (output: False)
Example: print(2 ** 3) (output: 8)
In Python, these operators can be used in various combinations to create complex expressions and calculations. For example, you can use parentheses to group operations or use the precedence rules for each operator type.
Overall, understanding the different types of operators in Python is crucial for writing efficient, readable, and effective code!