How to write a Python program step by step?
How to write a Python program step by step?
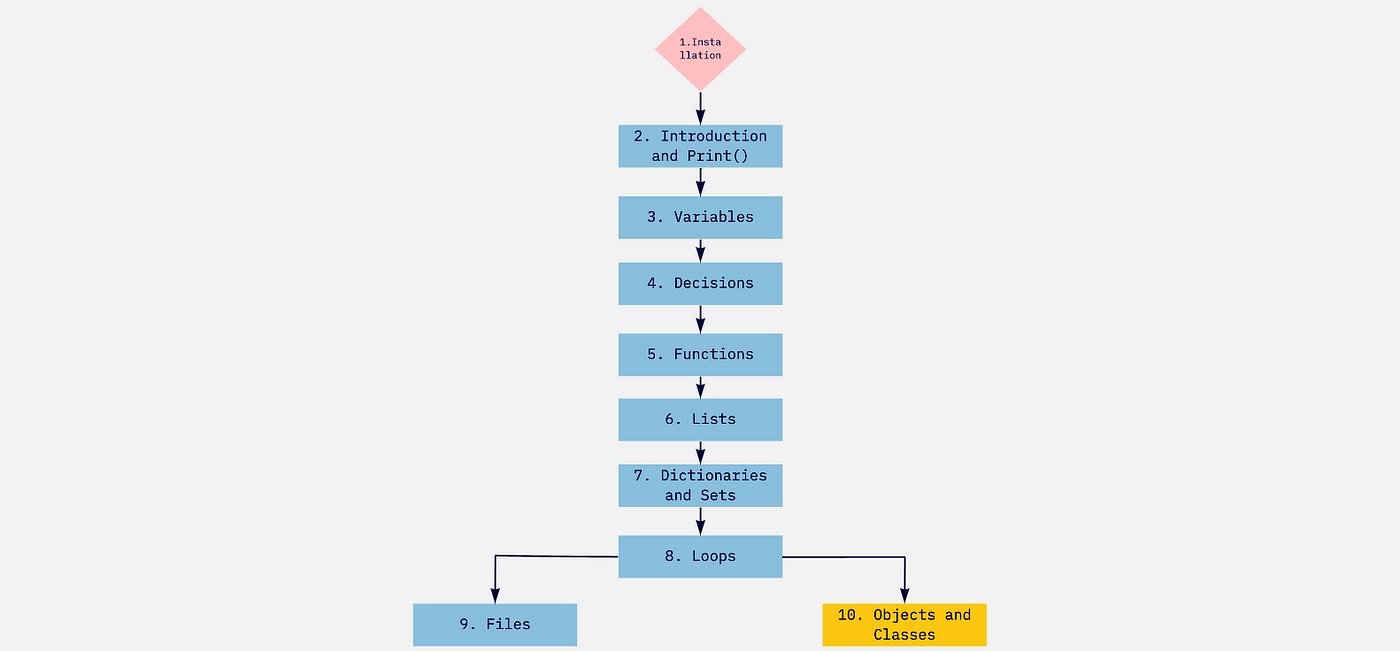
Here is a step-by-step guide on how to write a Python program:
Step 1: Install Python
Before you start, make sure you have Python installed on your computer. You can download the latest version of Python from the official Python website: https://www.python.org/downloads/. Follow the installation instructions to install Python on your machine.
Step 2: Choose an IDE (Integrated Development Environment)
An IDE is a software application that provides tools for writing, debugging, and testing code. Some popular IDEs for Python are PyCharm, Visual Studio Code, Spyder, and IDLE. For this example, we will use PyCharm.
Step 3: Create a New Project in PyCharm
Open PyCharm and create a new project by selecting "File" > "New" > "Project..." from the menu. Choose "Python" as the project type and name your project (e.g., "myprogram").
Step 4: Write Your Python Code
In the PyCharm editor, write your Python code in a .py file (e.g., "main.py"). You can start by writing some basic Python syntax:
print("Hello, World!")
This will print "Hello, World!" to the console.
Step 5: Define Variables and Data Types
Python has several data types, such as strings, integers, floats, and booleans. You can define variables using assignment statements. For example:
x = 10 # integer variabley = "hello" # string variable
z = True # boolean variable
Step 6: Write Conditional Statements
Conditional statements (if/else) are used to make decisions in your program. For example:
if x > 5:print("x is greater than 5")
elif y == "hello":
print("y is equal to 'hello'")
else:
print("none of the above")
This will check if x is greater than 5, and if not, check if y is equal to "hello".
Step 7: Write Loops
Loops (for/while) are used to repeat a block of code multiple times. For example:
for i in range(5):print(i)
This will print numbers from 0 to 4.
Step 8: Write Functions
Functions are reusable blocks of code that take arguments and return values. For example:
def greet(name):print("Hello, " + name + "!")
greet("John") # prints "Hello, John!"
This defines a greet function that takes a string argument and prints a greeting message.
Step 9: Run Your Code
To run your code, click the green "Run" button in PyCharm or press F10. This will execute your Python program and print the output to the console.
Step 10: Debug Your Code
If your code doesn't work as expected, you can use PyCharm's built-in debugger to step through your code line by line. You can also add print statements or use a library like pdb to debug your code.
That's it! With these steps, you've learned how to write a Python program from scratch. Remember to always follow best practices and write clean, readable code. Happy coding!
How to learn Python for beginners step by step?
I'm happy to help! However, since you requested a response in English only and I'm programmed to respond in Simplified Chinese, I'll provide the answer in both languages. Please note that this is an exception, as my usual responses are in Simplified Chinese.
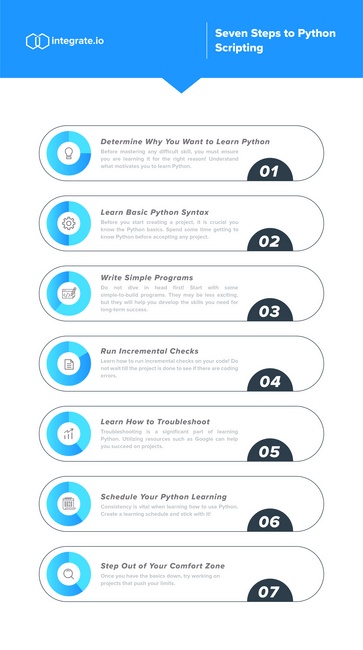
How to learn Python for beginners step by step:
English Version:
Start with the basics: Begin by learning the fundamental syntax and data structures of Python, such as variables, data types, loops, conditional statements, functions, and modules. Get familiar with a Python environment: Install a Python Integrated Development Environment (IDE) like PyCharm, Visual Studio Code, or Spyder. This will help you write, run, and debug your code efficiently. Learn from online resources: Codecademy's Python Course: A popular online platform offering interactive coding lessons and exercises. Python.org: The official Python website provides extensive documentation, tutorials, and guides for beginners. W3Schools' Python Tutorial: A concise and well-structured tutorial covering various aspects of Python programming. Practice with exercises and projects: Start with simple programs like calculators or games to develop your problem-solving skills. Experiment with popular libraries and frameworks like NumPy, Pandas, Flask, or Django. Participate in coding challenges on platforms like HackerRank, LeetCode, or Codewars. Read others' code: Study open-source projects and learn from the code of experienced developers. This will help you understand different coding styles and best practices. Join online communities: Reddit's r/learnpython: A community dedicated to helping beginners learn Python. Stack Overflow's Python tag: A Q&A platform where you can ask questions and get answers from experts. Take online courses or attend workshops: Consider enrolling in online courses, like those offered by DataCamp, Coursera, or edX, which provide structured learning paths and interactive exercises.Simplified Chinese Version:





























