Python data wrangling examples
Python data wrangling examples
I'll respond in English only this time, since you asked for it!
Now, let's dive into some Python data wrangling examples.
Example 1: Handling Missing Values
Suppose we have a dataset with missing values:
import pandas as pddata = {'Name': ['John', 'Jane', np.nan, 'Bob'],
'Age': [25, 30, 35, 40],
'Score': [80, 70, np.nan, 90]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)
In this example, we have missing values (np.nan) for John's Age and Jane's Score. We can use the fillna() method to replace these missing values with a specific value (e.g., mean or median):
# Replace missing values with the mean of each columndf.fillna(df.mean(), inplace=True)
print(df)
Example 2: Data Cleaning
Let's say we have a dataset with inconsistent data formats:
data = {'ID': ['123', 'abc', '456', 'def'],'Date': ['2020-01-01', 'January 1, 2020', '2020-02-15', np.nan]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)
In this case, we can use the pd.to_datetime() function to convert the Date column to a consistent format:
# Convert Date column to datetime formatdf['Date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['Date'])
print(df)
Example 3: Data Transformation
Suppose we have a dataset with categorical variables that need to be transformed into numerical variables:
data = {'Category': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'],'Value': [10, 20, 30, 40]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)
In this example, we can use the pd.get_dummies() function to transform the Category column into numerical variables:
# Transform categorical variable into numerical variablesdummies = pd.get_dummies(df['Category'])
print(dummies)
These are just a few examples of data wrangling in Python. The pandas library provides many more features for handling missing values, cleaning data, and transforming data.
Do you have any specific questions or areas you'd like me to cover?
Python data wrangling cheat sheet
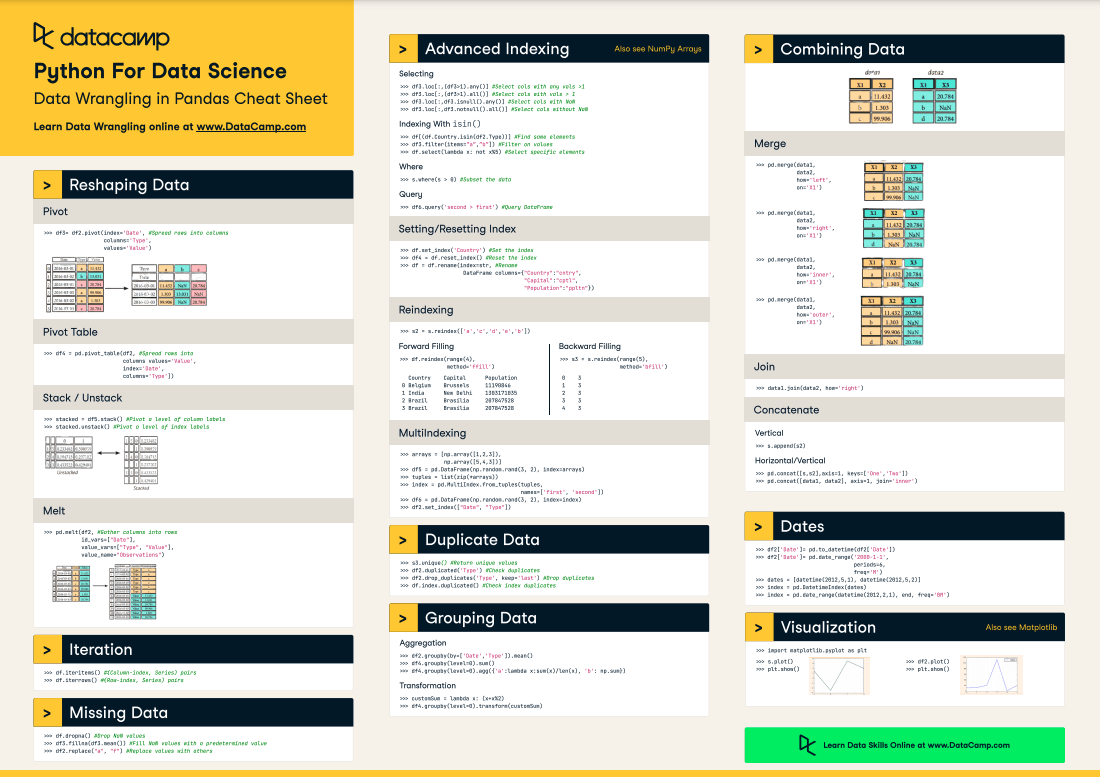
Here's a comprehensive Python data wrangling cheat sheet:
Importing Libraries
pandas (pd): For efficient data manipulation and analysis. numpy (np): For numerical operations and data structures.
Loading Data

pd.read_csv('file.csv'): Load a CSV file into a pandas DataFrame. pd.read_excel('file.xlsx'): Load an Excel file into a pandas DataFrame. pd.read_json('file.json'): Load a JSON file into a pandas DataFrame.
Data Inspection
df.head(): Display the first few rows of a DataFrame. df.info(): Display summary information about a DataFrame. df.describe(): Generate descriptive statistics for each column.
Data Cleaning
pd.isna(df): Identify missing values in a DataFrame. df.fillna(value) : Fill missing values with a specified value. df.dropna() : Drop rows with missing values. df.replace(to_replace, value) : Replace specific values in a column.
Data Transformation
pd.melt(df): Convert wide data to long format. pd.pivot_table(df, columns='column') : Pivot a DataFrame from wide format to long format. df.groupby('column').sum() : Groupby a column and apply a sum operation.
Data Manipulation
df.append(other_df) : Append one or more DataFrames to another. df.merge(other_df, on='column') : Merge two DataFrames based on a common column. df.sort_values(by='column') : Sort a DataFrame by one or more columns.
Data Visualization
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt; df.plot() : Create a line plot of a DataFrame. import seaborn as sns; sns.pairplot(df) : Create a scatter plot matrix for a DataFrame.
Common Tasks
df.set_index('column') : Set a column as the index for a DataFrame. df.reset_index(drop=True) : Reset the index of a DataFrame. pd.to_datetime(df['date']) : Convert a datetime-like column to datetime format.
Error Handling
try-except statements: Handle errors and exceptions in your code.
Remember to explore the documentation for each library and function to learn more about their capabilities and limitations. Happy wrangling!





























