Python xml tutorial
Python xml tutorial
Here is a detailed tutorial on using Python with XML:
Introduction
XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a markup language used to store and transport data between systems. Python provides several modules for parsing and creating XML files, including xml.etree.ElementTree and xml.dom.minidom. In this tutorial, we will cover the basics of using these modules to work with XML in Python.
Parsing XML Files
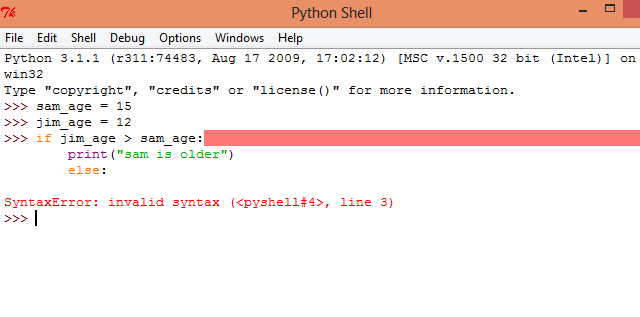
The most common way to use XML in Python is to parse an existing XML file. This involves opening the file, parsing its contents, and then extracting the desired data. Here's a basic example:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ETdef parse_xml(file_name):
tree = ET.parse('file.xml')
root = tree.getroot()
for elem in root:
print(elem.tag, elem.text)
parse_xml('example.xml')
This code will open the example.xml file, parse its contents, and then extract the text from each element. The ET.parse() function returns an ElementTree object, which we can use to traverse the XML document. We then get the root element of the tree with tree.getroot(). Finally, we loop through all elements in the XML document using a for loop.
Creating XML Files
To create a new XML file, you can use the ElementTree module. Here's how:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ETdef create_xml():
root = ET.Element('root')
for i in range(5):
elem = ET.SubElement(root, 'child')
elem.text = str(i)
tree = ET.ElementTree(root)
tree.write('example.xml')
create_xml()
This code creates a new XML file with the following structure:
0
1
2
3
4
Manipulating XML Files
The ElementTree module also provides methods for manipulating the XML structure. For example, you can add or remove elements using the SubElement() and remove() functions:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ETdef manipulate_xml():
tree = ET.parse('example.xml')
root = tree.getroot()
Add a new child elementelem = ET.SubElement(root, 'child')
elem.text = '5'
Remove the third child elementfor child in root.findall('.//child'):
if int(child.text) == 2:
child.remove(child)
Save changes to the XML filetree.write('example.xml')
manipulate_xml()
This code adds a new child element and then removes the third child element from the original XML file.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we have learned how to use Python with XML. We started by parsing an existing XML file using the xml.etree.ElementTree module. Then, we learned how to create a new XML file using the same module. Finally, we covered some basic manipulation techniques for modifying the XML structure.
I hope you enjoyed this tutorial and that it has helped you understand how to work with XML in Python.
How to parse XML file in Python?
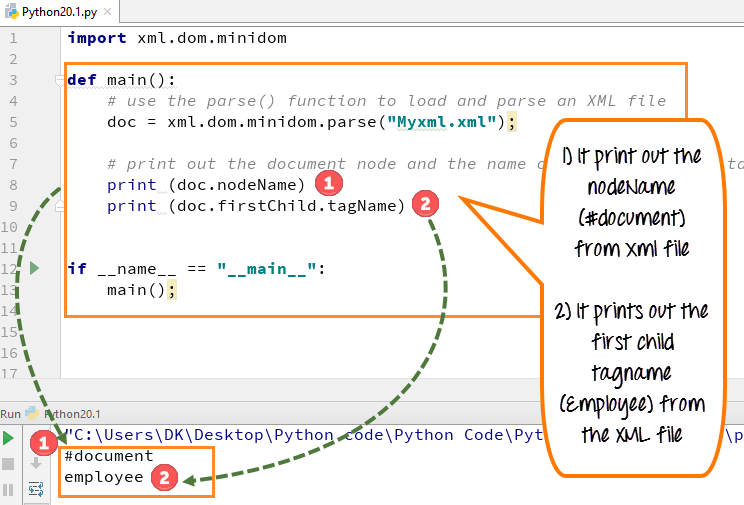
Parsing an XML (Extensible Markup Language) file in Python can be achieved using various libraries and tools. Here, we'll explore the popular xml.etree.ElementTree library that comes bundled with Python's standard library.
Why Parse XML files?
XML files are used to store and transport data between systems. They contain structured data in the form of elements, attributes, and text. Parsing an XML file involves reading and processing this data in a programming language like Python. This is useful when you need to:
Extract specific data from the XML file. Transform or convert the XML data into another format. Validate the structure and content of the XML file.Parsing XML files with xml.etree.ElementTree
The xml.etree.ElementTree library provides an easy-to-use API for parsing XML files. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Open the XML file: Use theimport xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
ET.parse() function to open and parse the XML file:
xml_file = 'example.xml' # Replace with your XML file nameroot_element = ET.parse(xml_file).getroot()
The parse() function returns an ElementTree object, which is then used to get the root element of the XML file using the getroot() method.
find() or findall() methods to traverse the XML elements:
# Find all elementspersons = root_element.findall('.//person')
Iterate over the persons and extract datafor person in persons:
name = person.find('.//name').text
age = person.find('.//age').text
print(f"Name: {name}, Age: {age}")
In this example, we find all <person> elements using the findall() method. Then, we iterate over each person and extract their name and age by finding and accessing the corresponding child elements.
text attribute to extract text values from XML elements:
# Find the element and extract its value </p>title = root_element.find('.//title').text
print(f"Title: {title}")
In this example, we find the <title> element and extract its text value using the text attribute.
Additional Tips
You can use XSLT (Extensible Stylesheet Language Transformations) to transform or convert XML data into another format. Thexml.etree.ElementTree library also provides methods for creating new XML elements, attributes, and texts. Check out the official documentation for more information. Python's standard library includes other XML-related libraries like xml.dom.minidom and xml.sax. These libraries provide more advanced features for parsing and manipulating XML files.
In conclusion, parsing an XML file in Python using xml.etree.ElementTree is a straightforward process. By understanding the basic concepts of XML files and the API provided by this library, you can efficiently extract specific data or transform XML files to suit your needs.