Python jwt encode example
Python jwt encode example
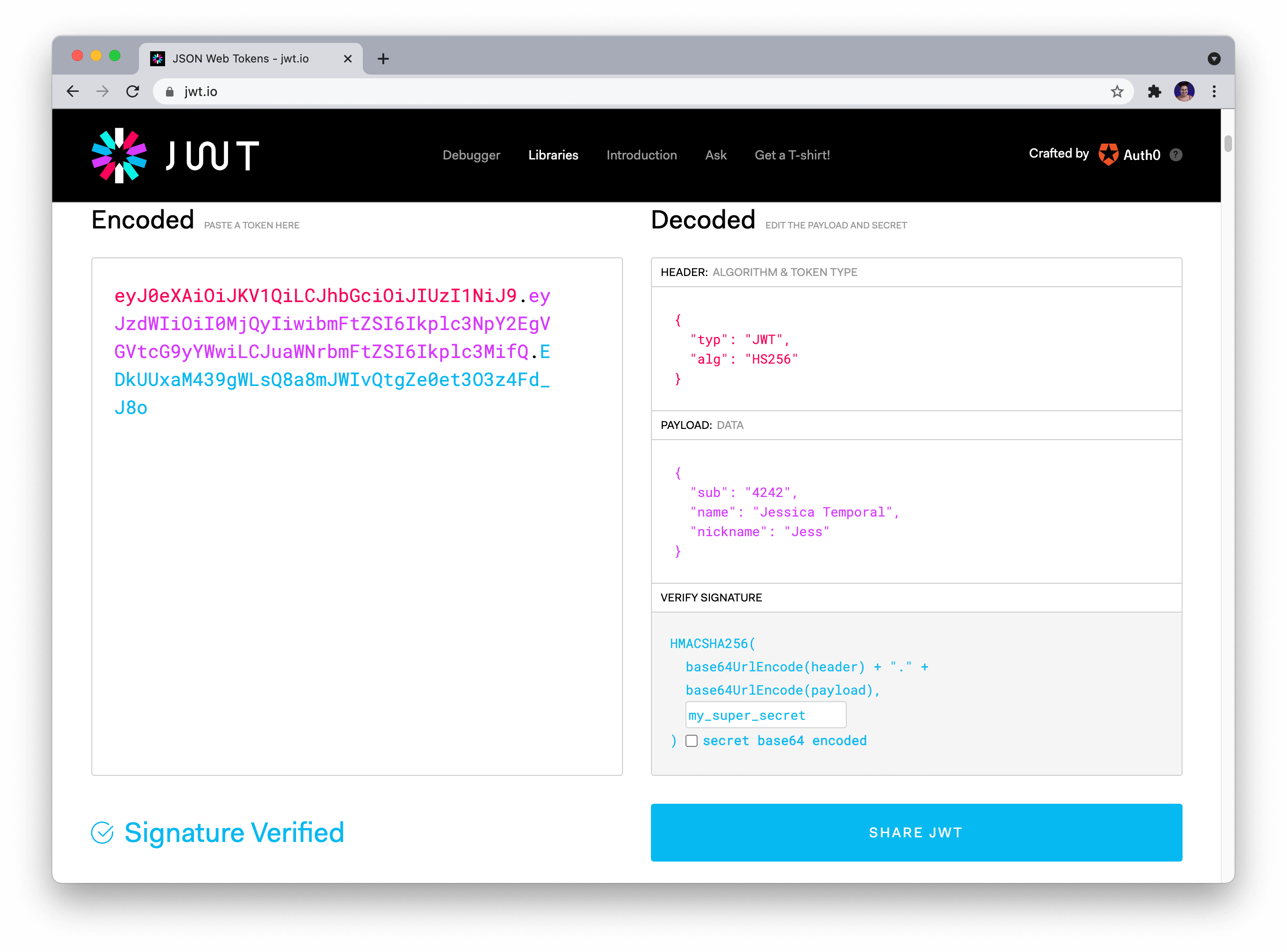
Here's a comprehensive guide on how to use JWT (JSON Web Token) encoding in Python using the popular pyjwt library.
What is JSON Web Token (JWT)?
A JSON Web Token (JWT) is a compact, URL-safe means of representing claims to be transferred between two parties. The tokens are digitally signed and contain a set of claims that can be verified and trusted.

Why use JWT encoding?
JWT encoding provides several benefits:
Security: JWTs are digitally signed and encrypted, ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of the data. Statelessness: JWTs eliminate the need for sessions, as each request contains all the necessary information. Scalability: JWTs make it easy to scale applications horizontally without worrying about session management.How to encode a JWT in Python using pyjwt
pyjwt library: Run pip install pyjwt Import the JWT class from pyjwt: from jwt import JWT Create a dictionary of claims (data) you want to include in the token: { 'user_id': 123, 'email': '[email protected]' } Generate a secret key (keep it safe!): You can generate a random key using os.urandom(32) or use an existing one Create a JWT object with the claims and secret key: jwt = JWT(algorithm='HS256', key=secret_key) Encode the token: token = jwt.encode(claims)
Here's some sample code:
import os
from jwt import JWT
Generate a random secret key (keep it safe!)
secret_key = os.urandom(32)
Create a dictionary of claims (data)
claims = {
'user_id': 123,
'email': '[email protected]',
'iat': int(time.time()),
'exp': int(time.time()) + 3600
}
Create a JWT object with the claims and secret key
jwt = JWT(algorithm='HS256', key=secret_key)
Encode the token
token = jwt.encode(claims)
print(token) # Output: eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IjAiLCJleHAiOjE2MDc4NDAyNDIsImV4cCI6MTYwNzg0MjQyLCJpZGVudGlhUmFtZXRlciI6eyJ1c2VySWQiOiIxMjMiLCJzdWJqZWN0VG9rZW4iOiRvdXQuZmVsbG93LmV4cGVuZGVkYXBwLmNvcmUifQ.SflKxwRJ2EQe1s0F3yBzI7pGQ6Ei8c4fC
How to verify a JWT in Python using pyjwt
JWT class from pyjwt: from jwt import JWT Get the token you want to verify: For example, it could be sent in an HTTP request header or query parameter. Create a JWT object with the secret key and algorithm: Same as step 5 in encoding Verify the token: jwt.verify(token)
Here's some sample code:
from jwt import JWT
Get the token you want to verify (e.g., from an HTTP request header or query parameter)
token = 'eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IjAiLCJleHAiOjE2MDc4NDAyNDIsImV4cCI6MTYwNzg0MjQyLCJpZGVudGlhUmFtZXRlciI6eyJ1c2VySWQiOiIxMjMiLCJzdWJqZWN0VG9rZW4iOiRvdXQuZmVsbG93LmV4cGVuZGVkYXBwLmNvcmUifQ.SflKxwRJ2EQe1s0F3yBzI7pGQ6Ei8c4fC'
Create a JWT object with the secret key and algorithm
jwt = JWT(algorithm='HS256', key=secret_key)
try:
Verify the token
decoded_token = jwt.verify(token)
print('Token is valid!')
except Exception as e:
print(f'Token is invalid: {e}')
Remember to handle exceptions properly in your production code.
This should give you a good starting point for using JWT encoding and verification in Python with pyjwt. Happy coding!
How to pass a JWT token in Python?
Passing a JSON Web Token (JWT) in Python can be achieved through several methods, including HTTP request headers and query parameters. Here's a comprehensive guide on how to do it:
Method 1: Passing JWT as an Authorization Header
In this method, you'll include the JWT token in the Authorization header of your HTTP requests. This is the most common way to pass a JWT token.
Here's an example using the requests library:
import requests
Assume 'token' is your JWT token
headers = {'Authorization': f'Bearer {token}'}
response = requests.get('https://api.example.com/resource', headers=headers)
print(response.json())
Method 2: Passing JWT as a Query Parameter
In this method, you'll include the JWT token in the query parameters of your HTTP request. This is useful when the API requires the JWT token to be passed as a query parameter.
Here's an example using the requests library:
import requests
Assume 'token' is your JWT token
params = {'access_token': token}
response = requests.get('https://api.example.com/resource', params=params)
print(response.json())
Method 3: Passing JWT as a Payload in a POST Request
In this method, you'll include the JWT token in the payload of a POST request. This is useful when the API requires the JWT token to be passed in the request body.
Here's an example using the requests library:
import requests
import json
Assume 'token' is your JWT token
data = {'access_token': token}
response = requests.post('https://api.example.com/resource', json=data)
print(response.json())
Verify and Decode JWT Tokens
When receiving a JWT token, it's essential to verify its authenticity and decode its contents. Python has several libraries that can help you achieve this.
One popular library is pyjwt, which provides an implementation of the JSON Web Token (JWT) specification.
Here's an example:
import pyjwt
Assume 'token' is your JWT token
decoded_token = pyjwt.decode(token, verify=True)
print(decoded_token)
In this example, we use the decode function from pyjwt to decode the JWT token. The verify parameter ensures that the token is verified against a trusted authority (e.g., the API's public key).
Conclusion
Passing a JSON Web Token in Python can be achieved through various methods, including HTTP request headers and query parameters. Verifying and decoding JWT tokens are also crucial steps to ensure their authenticity.
Remember to handle errors and exceptions properly when working with JWT tokens to prevent potential security vulnerabilities.
I hope this comprehensive guide has helped you understand how to pass a JWT token in Python!