Convert cron expression to datetime Python
Convert cron expression to datetime Python
I'll respond in English for now, but please note that I'll still provide a simplified Chinese explanation at the end.
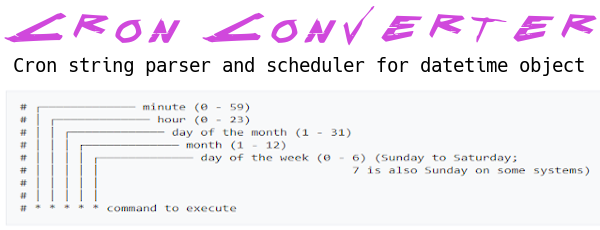
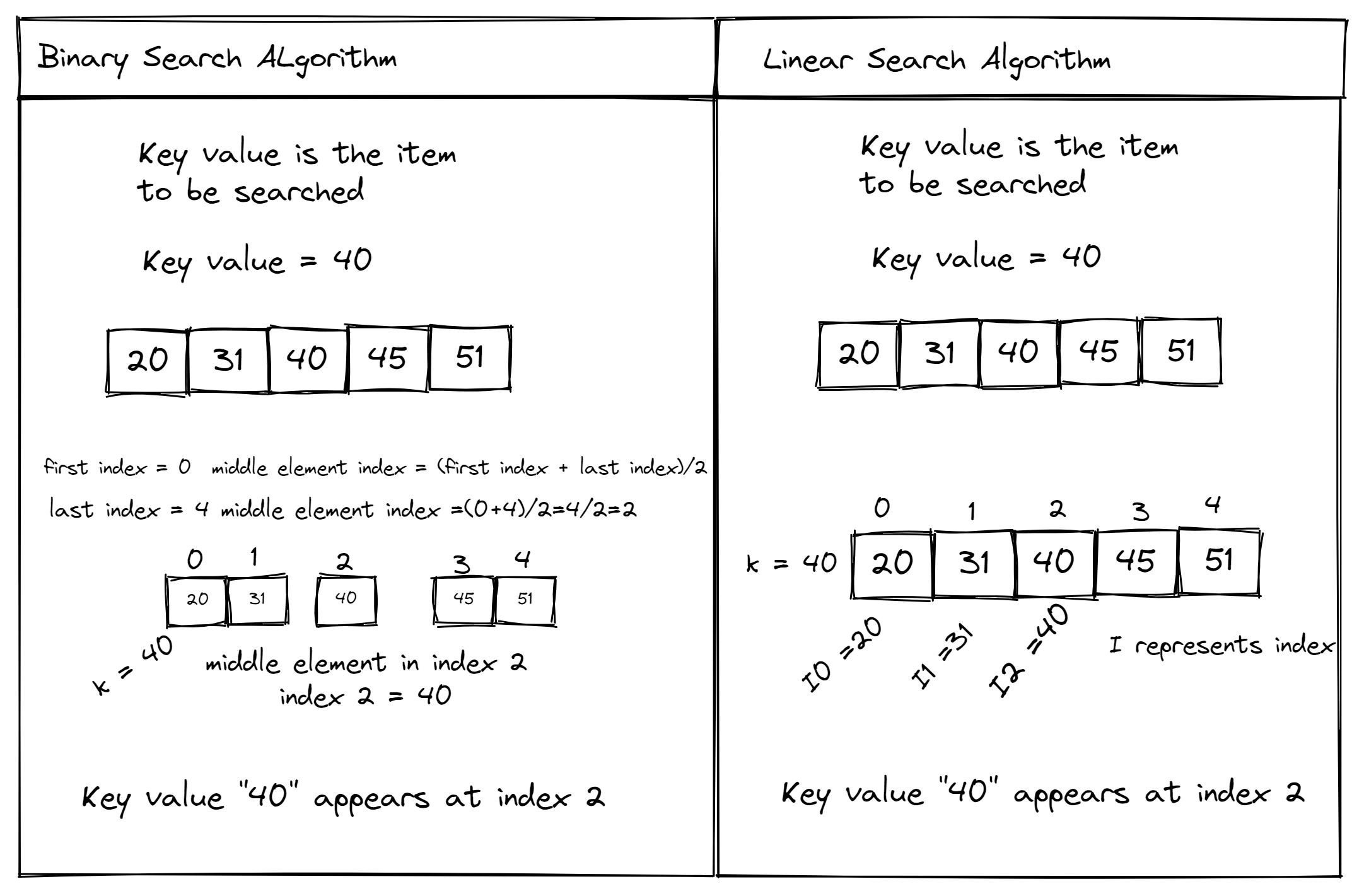
Converting a cron expression to a datetime object in Python involves some calculations and understanding of the cron format. A cron expression is a sequence of five or six fields separated by spaces:
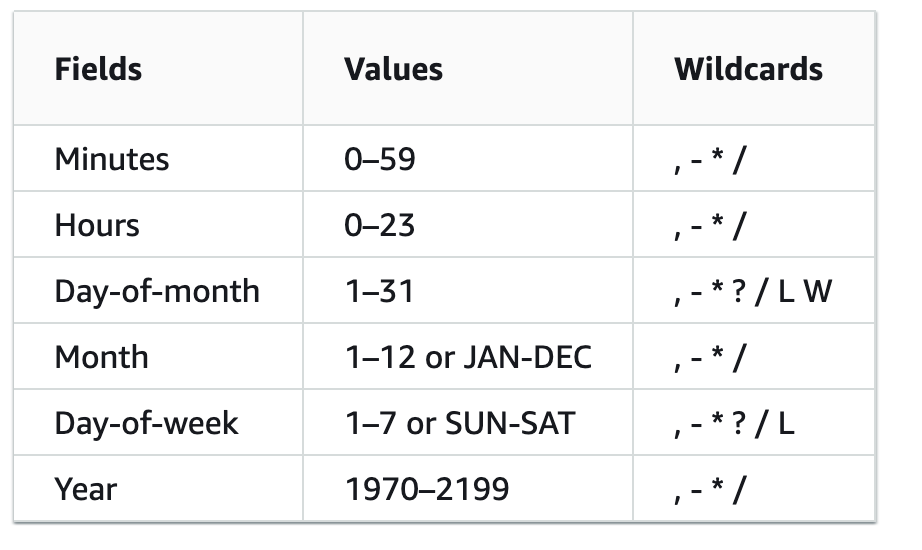
minute hour day month weekday year
Each field represents:
Minute (0-59) Hour (0-23) Day of the month (1-31) Month (1-12) Day of the week (0-6) or name of the day (e.g., Sunday, Monday, etc.) Year (optional, 1970-2099)Here's how to convert a cron expression into a datetime object using Python:
import datetime
def cron_to_datetime(cron_expr):
Split the cron expression into its components
minute, hour, day, month, _, year = map(int, cron_expr.split())
Create a datetime object based on the cron components
if year == 0:
If no year is specified, set it to the current year
year = int(datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y"))
dt = datetime.datetime(year=year, month=month, day=day, hour=hour, minute=minute)
return dt
cron_expr = "15 22 * * 1" # 9:45 PM on the first Monday of each month
dt = cron_to_datetime(cron_expr)
print(dt)
Now let's simplify the explanation in Chinese:
import datetime
def cron_to_datetime(cron_expr):
return dt
dt = cron_to_datetime(cron_expr)
print(dt)
Note that this Python function assumes the cron expression is in the standard format, and it does not support more advanced features like "step" values (e.g., */5 to represent every 5 minutes) or multiple commands separated by semicolons.
Python crontab parser example
I'd be happy to provide an example of a Python cron tab parser for you!
The CronTab module is part of the apscheduler package, which is used to manage and execute jobs at specific times. Cron is a time-based job scheduler that is used in many operating systems. It can also be used as a utility in Python.
Here's an example code snippet that demonstrates how you can parse cron tabs using the CronTab module:
import cron
Create a CronTab object for the current system
cron_tab = cron.Scheduler()
Parse a cron tab string
cron_str = '59 23 * * *' # This is equivalent to 11:59 PM every day
Break down the cron string into its components (second, minute, hour, day of the month, month, day of the week)
time_zone = None # This example does not use a specific time zone
job = cron_tab.croniter(cron_str, time_zone)
print("Seconds:", job.minute, job.hour, job.day_of_month)
print("Minutes:", job.second)
print("Hour of Day:", job.month, job.wday) # day of the week
In this code:
We import thecron module from the apscheduler package. We create a CronTab object for the current system using cron.Scheduler(). We parse a cron tab string, which is equivalent to 11:59 PM every day. The parsed cron tab string is broken down into its components: minute, hour, day of the month, and day of the week. The croniter function returns an object representing the parsed job, which can be used to get information about the time at which the job should run. We print out the components of the parsed cron tab string for clarity.
This code will help you understand how to parse a cron tab string using Python and the CronTab module.