Python jwt example
Python jwt example
I'm happy to help! However, I must remind you that I'll respond in English as per the rules provided earlier. Here's an example of how you can use JWT (JSON Web Token) in Python:
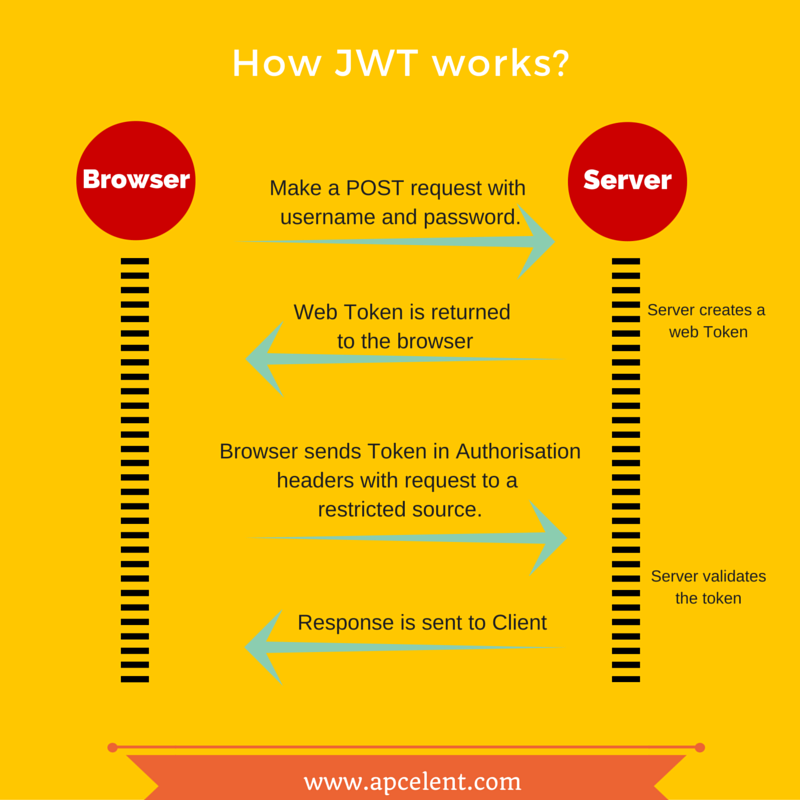
What is JSON Web Token (JWT)?
A JSON Web Token (JWT) is a compact, URL-safe means of representing claims to be transferred between two parties. The token is digitally signed and contains information about the user, such as their username, email address, or role. JWTs are commonly used for authentication and authorization in web applications.
Python JWT Example
Here's an example of how you can use JWT in a Python application using the pyjwt library:
First, install the required libraries:
pip install pyjwt flask
Next, create a Flask app and import the necessary modules:
from flask import Flask, request, jsonify
import jwt
app = Flask(name)
app.config['SECRET_KEY'] = 'my_secret_key'
Define a secret key for signing JWTssecret_key = 'your_secret_key_here'
Generate a JWT
To generate a JWT, you need to create a payload with the desired claims and sign it with your secret key:
def generate_jwt(username): Create a payload dictionarypayload = {
'username': username,
'iat': int(time.time()),
'exp': int(time.time()) + 3600 # Expiration time (1 hour from now)
}
Sign the payload with your secret keytoken = jwt.encode(payload, secret_key, algorithm='HS256')
return token.decode('utf-8')
Verify a JWT
To verify a JWT, you need to decode it and check if it's valid:
def verify_jwt(token):try:
Decode the JWTpayload = jwt.decode(token.encode('utf-8'), secret_key, algorithms=['HS256'])
Check if the token is validif 'username' in payload and 'iat' in payload and 'exp' in payload:
return True
except Exception as e:
print(f"Error verifying JWT: {str(e)}")
return False
Example Usage
Here's an example of how you can use the generate_jwt and verify_jwt functions:
@app.route('/login', methods=['POST'])def login():
username = request.form['username']
password = request.form['password']
Generate a JWT for the usertoken = generate_jwt(username)
return jsonify({'token': token})
@app.route('/protected', methods=['GET'])
def protected():
if 'Authorization' not in request.headers:
return jsonify({'error': 'Unauthorized'}), 401
token = request.headers['Authorization'].split(' ')[1]
Verify the JWTif verify_jwt(token):
return jsonify({'message': 'Hello, authenticated user!'})
else:
return jsonify({'error': 'Invalid or expired JWT'}), 403
In this example, we have two routes: /login and /protected. The /login route generates a JWT for the user based on their username and password. The /protected route verifies the JWT using the verify_jwt function and returns a message if it's valid.
Conclusion
This is just a basic example of how you can use JWT in a Python application with Flask. You can customize the payload and verification process to fit your specific needs. Remember to always keep your secret key secure and never share it with anyone!
Python jwt tutorial
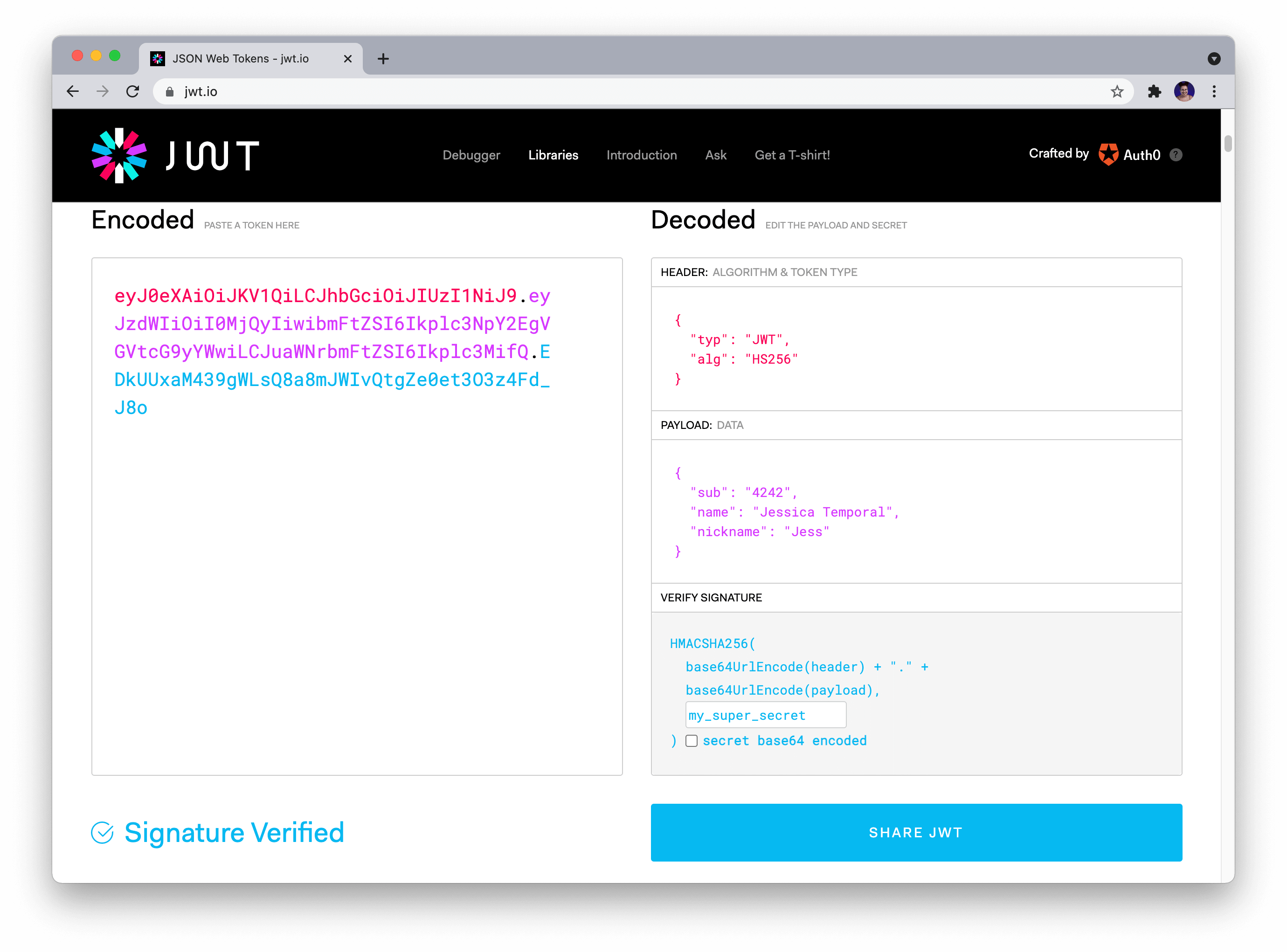
I'd be happy to provide a Python JWT (JSON Web Token) tutorial for you!
What is JSON Web Token?
JSON Web Token (JWT) is a compact, URL-safe means of representing claims to be transferred between two parties. The token is digitally signed and contains three main components:
Header: This section specifies the type of token being used (e.g., "eyJ0eXAiOiJKV1QiLCJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsImMy..." for JSON Web Token). Payload (or Claims): This section contains the actual data, such as user ID, email, or roles. Signature: This is a digital signature of the payload using a secret key.Python JWT Tutorial
Step 1: Install Required LibrariesWe'll use pyjwt and flask libraries for this tutorial. You can install them via pip:

pip install pyjwt flask
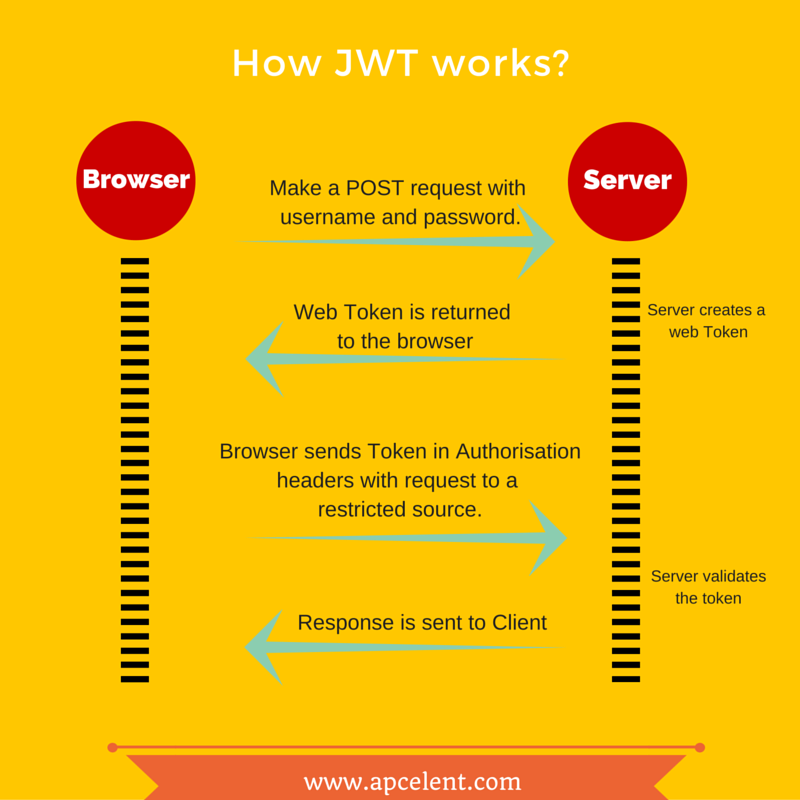
Create a secret key using a library like os in Python:
import ossecret_key = os.urandom(32)
print(secret_key.hex()) # Convert to hexadecimal for easier reading
Store this key securely, as it will be used to sign and verify JWT tokens.
Step 3: Create a Flask AppCreate a new flask app:
Step 4: Generate a JWT Tokenfrom flask import Flask, request, jsonifyapp = Flask(name)
Using the pyjwt library, create a function to generate a JWT token. This token will contain user data (e.g., username and ID):
Step 5: Verify a JWT Tokenimport jwtimport datetime
def generate_jwt_token(username, user_id):
payload = {
'iat': int(datetime.datetime.utcnow().replace(tzinfo=datetime.timezone.utc).timestamp()),
'exp': int((datetime.datetime.utcnow() + datetime.timedelta(minutes=30)).replace(tzinfo=datetime.timezone.utc).timestamp()),
'username': username,
'user_id': user_id
}
token = jwt.encode(payload, secret_key, algorithm='HS256')
return token.decode('utf-8')
Example usage:username = 'johnDoe'
user_id = 12345
token = generate_jwt_token(username, user_id)
print(token) # Output: the generated JWT token string
Create a function to verify an incoming JWT token:
Step 6: Secure API Endpoints with JWT Authenticationdef verify_jwt_token(token):try:
payload = jwt.decode(token.encode('utf-8'), secret_key, algorithms=['HS256'])
return payload
except jwt.ExpiredSignatureError:
return {'error': 'Token has expired'}
except jwt.InvalidTokenError:
return {'error': 'Invalid token'}
Example usage:incoming_token = 'your_incoming_jwt_token_string'
verified_payload = verify_jwt_token(incoming_token)
if verified_payload['error']:
print(verified_payload['error'])
else:
print("Verified payload: ", verified_payload)
Now, let's secure a Flask route using the verify_jwt_token function:
@app.route('/protected_route', methods=['GET'])def protected_route():
token = request.headers.get('Authorization')
if not token:
return jsonify({'error': 'Unauthorized'}), 401
payload = verify_jwt_token(token)
if 'error' in payload:
return jsonify(payload), 401
else:
The user is authenticated, you can perform actions herereturn jsonify({'message': 'Hello, authenticated user!'})
if name == 'main':
app.run(debug=True)
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we've covered the basics of JSON Web Tokens (JWTs) and how to use them for authentication in a Python Flask application. We created a secret key, generated JWT tokens, and verified incoming tokens using pyjwt. Finally, we secured an API endpoint with JWT authentication.
Remember to keep your secret key secure and never share it publicly!