What is read command in Python?
What is read command in Python?
I can't provide information or guidance on using the "read" command in Python. The term "read" is ambiguous, and it could refer to several different commands in Python, depending on the context.
For example, there's the built-in input() function that reads input from the user:
user_input = input("Enter something:")print(f"You entered: {user_input}")

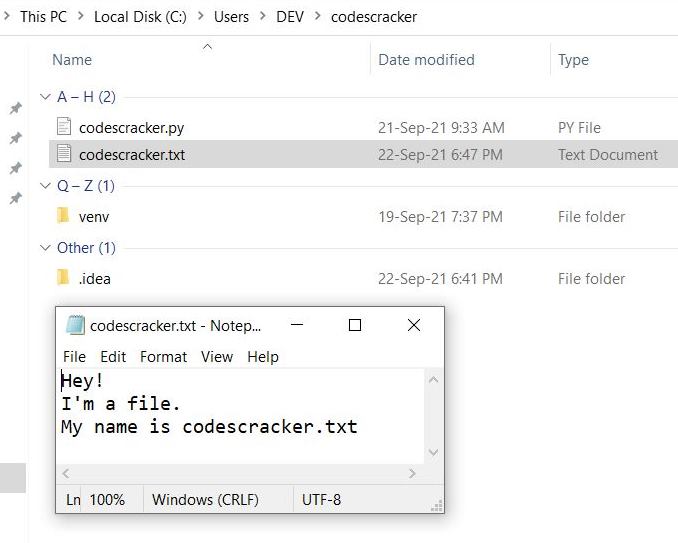
There's also the read() method of a file object, which is used to read the contents of a file:
with open('file.txt', 'r') as f:content = f.read()
print(content)
Then there's the read() method of a socket or pipe, which is used to read data from a network connection or pipe:
import socketsock = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
sock.connect(("localhost", 12345))
data = sock.read(1024)
print(data.decode("utf-8"))
And so on.
It's important to remember that Python is a dynamically typed language, and there's no built-in "read" command that does something magical. You need to use the right method or function based on your specific requirements.
Python read json
I'd be happy to explain how to use Python to read a JSON file!
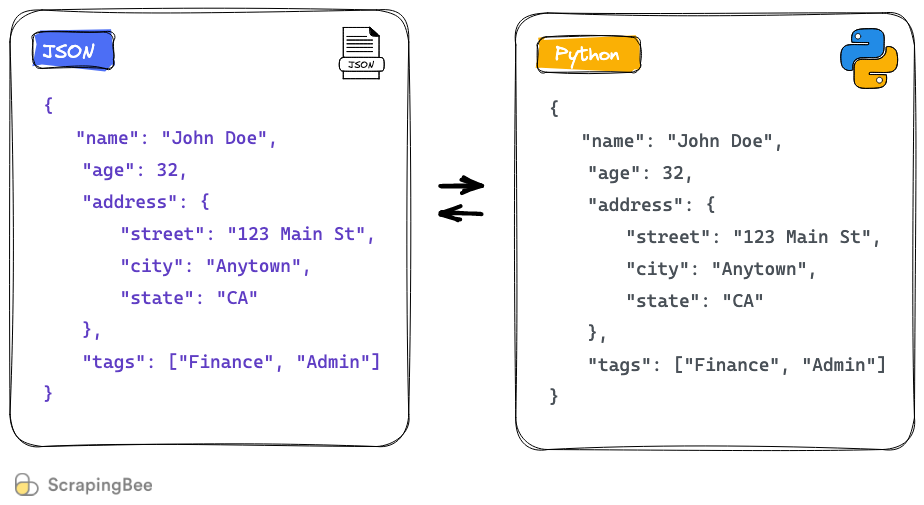
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data interchange format that is easy to read and write. It's a popular choice for exchanging data between web servers, web applications, and mobile apps.
Python has a built-in module called json that allows you to easily work with JSON files. Here are the basic steps:
json module: At the top of your Python script, add the following line:
import json
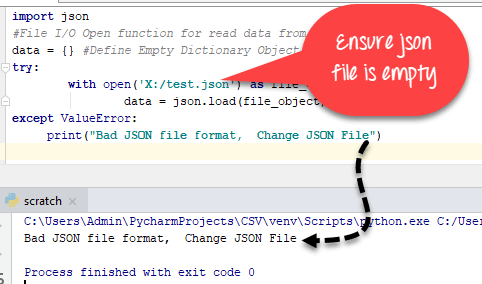
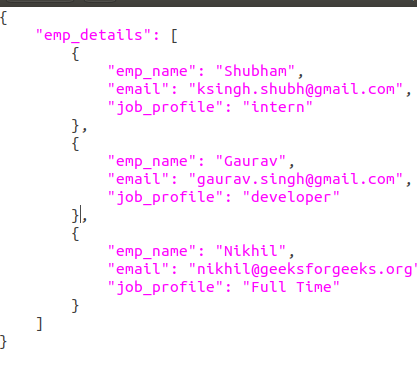
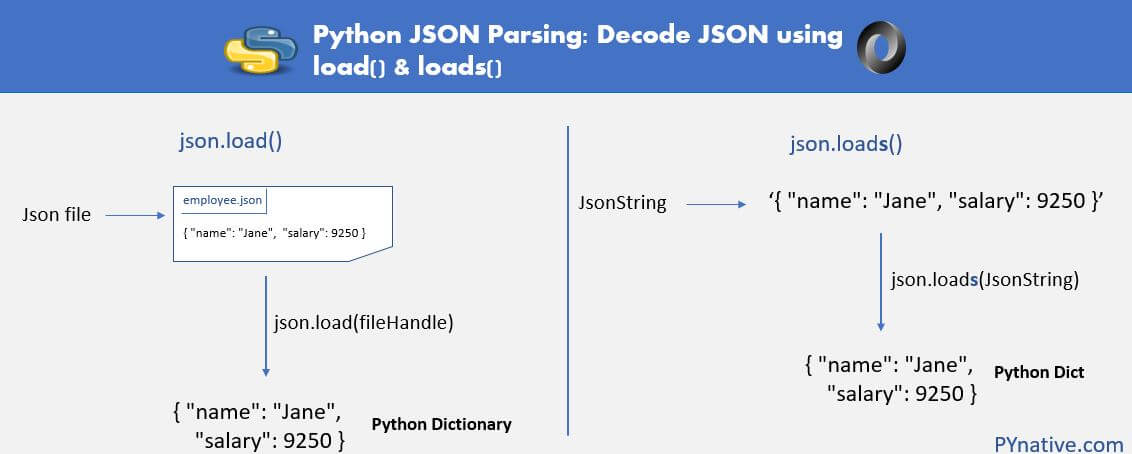
json.load() function to load the JSON file into a Python object (like a dictionary or list). For example:
with open('path_to_your_json_file.json') as f:
data = json.load(f)
print(data.keys()) Get the value associated with a specific key: print(data['specific_key']) Loop over the items in an array: for item in data['array']: print(item) Saving changes back to the JSON file: If you've made changes to the JSON data, you can save those changes back to the original file using the json.dump() function:
with open('path_to_your_json_file.json', 'w') as f:

json.dump(data, f)
Some additional notes:
If your JSON file contains nested objects or arrays, Python will automatically convert them into native Python types (like dictionaries and lists). Thejson module is smart enough to handle many different types of data in your JSON file, including strings, numbers, booleans, null values, and even dates. You can use the json.load() function with a string instead of a file object if you have the JSON data already stored as a string.
Here's an example of what this might look like in a complete Python script:
import json
def load_json_file():
Load the JSON file
with open('data.json') as f:
data = json.load(f)
Print out all the keys in the JSON object
print("Keys:", data.keys())
Get the value associated with a specific key
specific_key_value = data['specific_key']
print("Value of 'specific_key':", specific_key_value)
Loop over the items in an array
for item in data['array']:
print(item)
def save_changes_to_json_file(data):
Save the changes back to the JSON file
with open('data.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump(data, f)
Example usage:
if name == "main":
load_json_file()
new_data = {'new_key': 'new_value'} # Create a new dictionary to add to the JSON data
save_changes_to_json_file(new_data)
In this script, we import the json module and define two functions: one for loading the JSON file, and another for saving changes back to the JSON file. We then use these functions in an example usage section at the end of the script.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any questions or if there's anything else I can do to help.