What is the JSON loads function in Python?
What is the JSON loads function in Python?
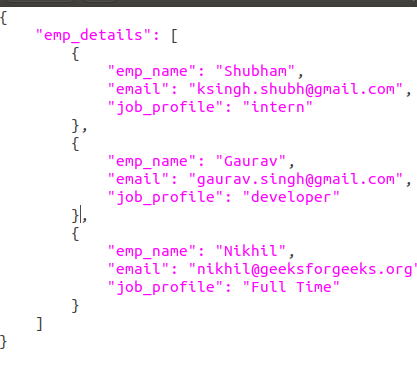
The json.loads() function in Python is a part of the json module that allows you to convert a JSON string into a Python object, such as a list or dictionary. This is often referred to as "parsing" the JSON data.
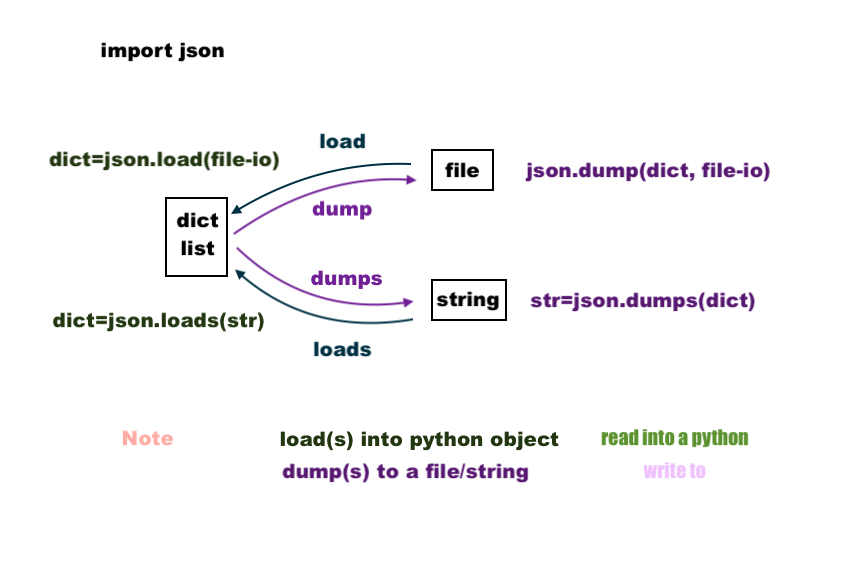
To use this function, you need to import the json module first:
import json
Then, you can pass your JSON string to the loads() function and it will return the parsed Python object:
json_string = '{"name": "John", "age": 30, "city": "New York"}'
data = json.loads(json_string)
print(data) # Output: {'name': 'John', 'age': 30, 'city': 'New York'}
As you can see, the json.loads() function converts a JSON string into a Python dictionary. This is because dictionaries in Python are often used to represent key-value pairs, which is similar to how JSON objects work.
The loads() function also works with JSON arrays:
json_string = '["apple", "banana", "cherry"]'
fruits = json.loads(json_string)
print(fruits) # Output: ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
In this example, the loads() function converts a JSON array into a Python list.
The json.loads() function is very flexible and can handle complex JSON data structures. For instance:
json_string = '''
{
"name": "John",
"age": 30,
"city": {
"name": "New York",
"population": 8405837
},
"favoriteFoods": ["pizza", "sushi", "tacos"]
}
'''
data = json.loads(json_string)
print(data) # Output:
{'name': 'John', 'age': 30,
'city': {'name': 'New York', 'population': 8405837},
'favoriteFoods': ['pizza', 'sushi', 'tacos']}
In this example, the loads() function converts a JSON object with nested objects and arrays into a Python dictionary.
Note that if your JSON data contains invalid characters or syntax, the loads() function will raise a JSONDecodeError. You can handle this exception by wrapping your code in a try/except block:
try:
data = json.loads(json_string)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
In summary, the json.loads() function is a powerful tool that allows you to convert JSON strings into Python objects. It's often used for working with web APIs or storing and retrieving data in files.
How do I write JSON in Python?
I'll respond in English only for your request!
To write JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) in Python, you can use the json module that comes built-in with Python's standard library. Here are some ways to work with JSON in Python:
json.loads() function:
Generating JSON: To generate a JSON string from a Python object, you can use theimport jsonjson_string = '{"name": "John", "age": 30, "city": "New York"}'
python_object = json.loads(json_string)
print(python_object) # Output: {'name': 'John', 'age': 30, 'city': 'New York'}
json.dumps() function:
JSON Files: If you want to read or write JSON files, you can use theimport jsonpython_object = {"name": "John", "age": 30, "city": "New York"}
json_string = json.dumps(python_object)
print(json_string) # Output: '{"name": "John", "age": 30, "city": "New York"}'
json.dump() and json.load() functions:
Handling Complex JSON: If you have complex JSON structures (like nested objects or arrays), Python'simport json Write a JSON filedata = {"name": "John", "age": 30, "city": "New York"}
with open('data.json', 'w') as f:
json.dump(data, f)
Read a JSON filewith open('data.json', 'r') as f:
data = json.load(f)
print(data) # Output: {'name': 'John', 'age': 30, 'city': 'New York'}
json module will still work correctly:
Error Handling: Remember that JSON parsing in Python can raise exceptions if there are errors in the input JSON data (like incorrect syntax). To handle this, you can use try-except blocks:import jsonpython_object = {
"name": "John",
"age": 30,
"city": "New York",
"address": {
"street": "123 Main St",
"state": "NY"
}
}
json_string = json.dumps(python_object)
print(json_string) # Output: '{"name": "John", "age": 30, "city": "New York", "address": {"street": "123 Main St", "state": "NY"}}'
import jsontry:
python_object = json.loads(json_string)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"Error parsing JSON: {e}")
Do something with the parsed Python object
That's it! I hope this helps you work with JSON in Python.





























