activate virtual environment python windows vscode
activate virtual environment python windows vscode
Activating a Virtual Environment (VE) in Python on Windows using Visual Studio Code (VSCode) is a straightforward process. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Prerequisites:
Python installed: Ensure you have Python installed on your system. If not, download the latest version from the official Python website. Visual Studio Code (VSCode): Make sure you have VSCode installed and launched. Python extension for VSCode: Install the Python extension for VSCode by opening the Extensions panel (Ctrl + Shift + X on Windows/Linux or Cmd + Shift + X on macOS), searching for "Python", and installing the extension.Activating Virtual Environment:
Open Command Prompt or PowerShell: Open Command Prompt (on Windows) or PowerShell (on Windows 10+). Navigate to your project directory: Use thecd command to navigate to the directory where you want to create a new VE. Install the virtual environment package: Run the following command:
pip install virtualenv
virtualenv myenv # Replace "myenv" with your desired VE name
This will create a new VE named myenv in a directory called myenv in the current working directory.
.myenvScriptsactivate.bat # For Command Prompt
Or, on PowerShell:
.myenvScriptsactivate.ps1 # For PowerShell
You should see a prompt indicating that you are now in the myenv VE.
Verify your Virtual Environment:
Run Python: Run Python from within the VE using the following command:python --version
This will print the version of Python installed in your VE.
Check the Virtual Environment name: To verify you are still in the VE, run the following command:echo %VIRTUAL_ENV%
You should see the path to your myenv directory.
Deactivate and remove (if needed):
To deactivate the VE, simply run:
deactivate
To remove the VE, use the following command:
rm -rf myenv # On Windows or Linux
Now you have successfully created, activated, and verified a Virtual Environment in Python using VSCode on Windows!
activate virtual environment python windows cmd
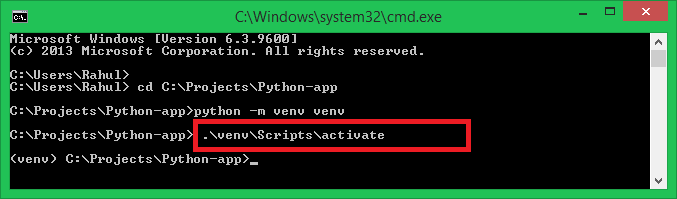
Activating a virtual environment in Python on Windows using the Command Prompt (cmd) is a straightforward process. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Install Python and pip
If you haven't installed Python and pip yet, you can download the installation package from the official Python website: https://www.python.org/downloads/. Follow the installation instructions to install Python and pip.
Step 2: Open Command Prompt (cmd)
Open the Start menu and search for "Command Prompt" or type cmd in the Run dialog box (Windows key + R). This will open a new command prompt window.
Step 3: Navigate to your Python installation directory
Use the cd command to navigate to the directory where you installed Python. The default installation location is typically C:PythonXX, where XX represents the version number (e.g., C:Python39). For example:
cd C:Python39
Step 4: Activate the virtual environment
Once you're in the Python installation directory, run the following command to create a new virtual environment. Replace <env_name> with your desired virtual environment name (e.g., myenv):
python -m venv
For example:
python -m venv myenv
This will create a new directory with the specified name and set up the virtual environment. You'll know it's successful when you see a (myenv) prompt in your command prompt window.
Step 5: Activate the virtual environment (optional)
To activate the virtual environment, run the following command:
.Scriptsactivate
Replace <env_name> with the name of your virtual environment. For example:
.myenvScriptsactivate
You should see a (myenv) prompt in your command prompt window indicating that you're now working within the activated virtual environment.
Tips and Variations:
If you're using Python 3.x, you can usepython3 -m venv <env_name> instead of python -m venv <env_name>. You can activate the virtual environment by running .<env_name>Scriptsactivate in PowerShell as well. To deactivate the virtual environment and return to your system's Python installation, simply type deactivate in your command prompt window.
That's it! You've successfully activated a virtual environment in Python on Windows using the Command Prompt (cmd).





























