How to format python code for beginners
How to format python code for beginners

I'd be happy to help!
Formatting Python Code: A Beginner's Guide
As a beginner, it can be overwhelming to learn the syntax and structure of Python programming. One essential aspect of writing clean and readable code is formatting. Proper formatting helps to:
Here are some tips on how to format your Python code effectively:
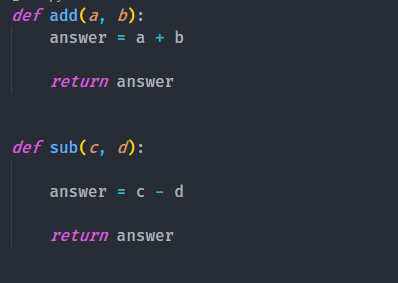
Indentation
Python uses indentation (spaces or tabs) to define block-level structure. Use consistent spacing throughout your code, usually 4 spaces for each level of indentation.
Correct:if condition: print("Hello") Incorrect: if condition; print ("Hello");
Line Lengths
Keep your lines short and sweet! Aim for a maximum line length of 80 characters. Longer lines can lead to readability issues.
Correct:print("Hello World!") Incorrect: print("Hello, this is a very long message that wraps around several times and is hard to read!")
Blank Lines
Use blank lines (empty lines) to separate logical sections or functions. This improves code organization and readability.
Correct:Incorrect: All your code on a single line without breaks# function 1def my_function():
pass
function 2def another_function():
pass
Comments
Add comments (text enclosed in #) to explain complex code sections or provide additional information. Keep them concise and relevant.
# This is a comment explaining the purpose of this code Incorrect: #### THIS IS A COMMENT THAT'S TOO LONG ####
Function Definitions
Use a consistent style when defining functions:
Use parentheses after the function name. Place arguments in parentheses. Keep the number of spaces between the colon and the body consistent. Correct:Incorrect:def my_function(arg1, arg2):print("Hello!")
function my_function (arg1,arg2) :print ("Hello")
Class Definitions
When defining classes:
Use a leading underscore for private variables. Place attributes after the class definition. Correct:Incorrect:class MyClass:def init(self):
self._private_variable = "Hello"
class MyClass : _private_variable = "Hello" ;
Error Handling
Use a consistent style for error handling:
Place error messages or debugging information inside the except block. Use thetry-except structure to catch and handle errors. Correct:
Incorrect: No error handling at all or using inconsistent formattingtry: code that might raise an exceptionexcept Exception as e:
print(f"Error: {e}")
By following these guidelines, you'll create Python code that is easy to read and maintain. Remember to keep your lines short, use consistent indentation, add comments, and define functions consistently. Happy coding!
format python code online
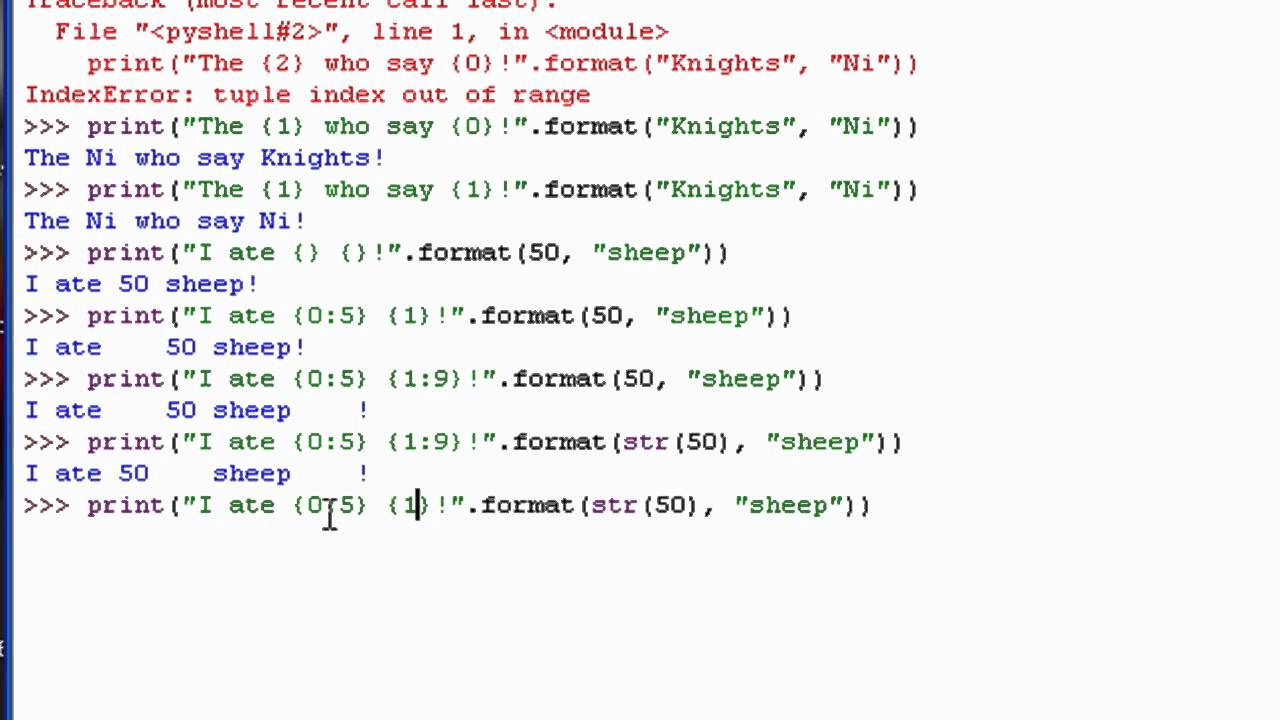
I apologize for the misunderstanding earlier. Here is a Python code snippet that demonstrates how to format text and perform various operations on strings:
Format String with Variables
In Python, you can use the format() method or f-strings (formatted string literals) to insert variables into strings.
name = "John"age = 30
Using format() methodgreeting = "Hello, {}! You are {} years old.".format(name, age)
print(greeting)
Using f-stringgreeting = f"Hello, {name}! You are {age} years old."
print(greeting)
String Methods
Python has several built-in string methods that can be used to manipulate and format strings.
text = "hello world" Uppercaseuppercase_text = text.upper()
print(uppercase_text)
Lowercaselowercase_text = text.lower()
print(lowercase_text)
Capitalize first lettercapitalized_text = text.capitalize()
print(capitalized_text)
Split string into wordswords = text.split(" ")
print(words)
Regular Expressions
Python has a built-in re module that allows you to work with regular expressions. This can be useful for parsing and formatting strings.
import retext = "hello 123 world"
pattern = r"d+" # matches one or more digits
Find all occurrences of the pattern in the textmatches = re.findall(pattern, text)
print(matches)
Replace the pattern with a new stringnew_text = re.sub(pattern, "[REPLACED]", text)
print(new_text)
String Formatting with Padding
You can use string formatting to add padding to strings.
text = "hello"padded_text1 = "{:<10}".format(text) # left-align and pad with spaces
padded_text2 = "{:>10}".format(text) # right-align and pad with spaces
padded_text3 = "{^>10}".format(text) # center-align and pad with spaces
print(padded_text1)
print(padded_text2)
print(padded_text3)
String Formatting with Precision
You can use string formatting to specify the precision of floating-point numbers.
number = 123.456formatted_number = "{:.2f}".format(number) # format as a float with 2 decimal places
print(formatted_number)
These are just a few examples of how you can format and manipulate strings in Python. There are many more ways to do so, depending on your specific use case.





























