What is while () in Python?
What is while () in Python?
I'm glad you asked!
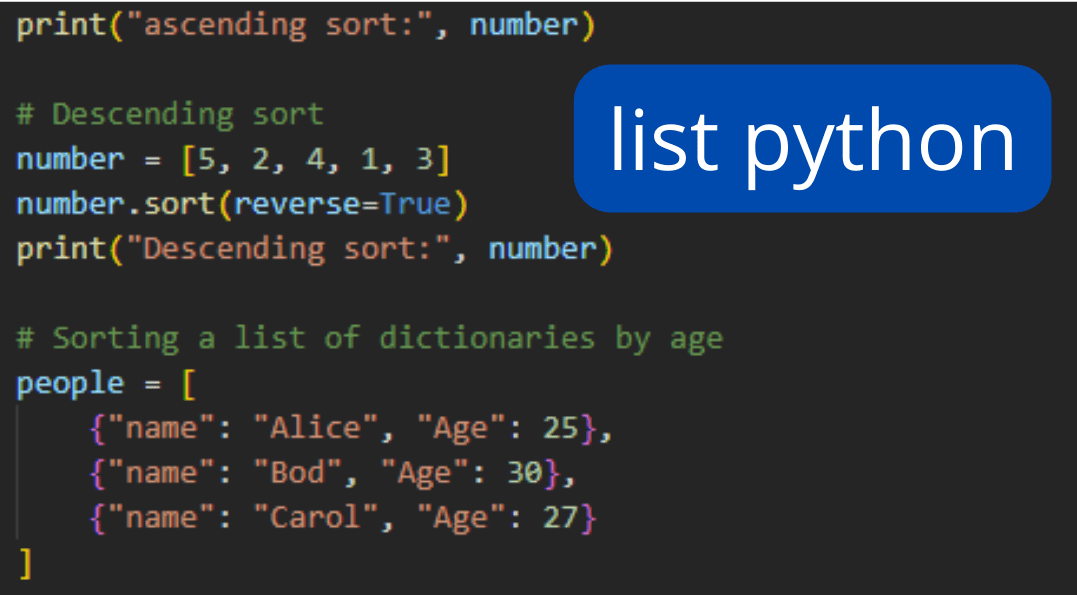
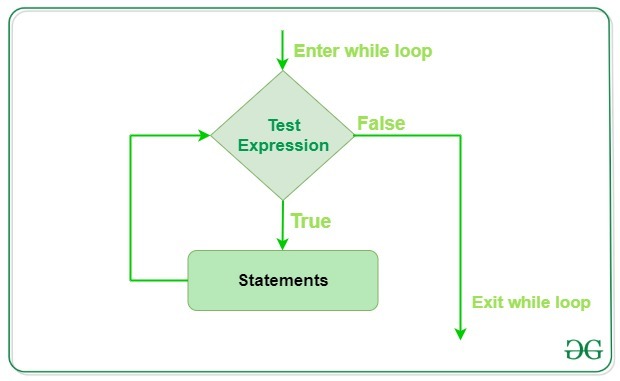
In Python, the while statement is a type of loop that allows you to execute a block of code repeatedly as long as a certain condition is met. The basic syntax of a while loop is:
while condition:
code to be executed
...

The condition is a boolean expression that is evaluated at the beginning of each iteration of the loop. As long as the condition is true, the code inside the loop will continue to execute. When the condition becomes false, the loop will exit.
Here's a breakdown of how you can use the while loop in Python:
==, <, >). Code block: The code inside the loop is executed as long as the condition is true. You can have multiple statements in this block, separated by semicolons (;).
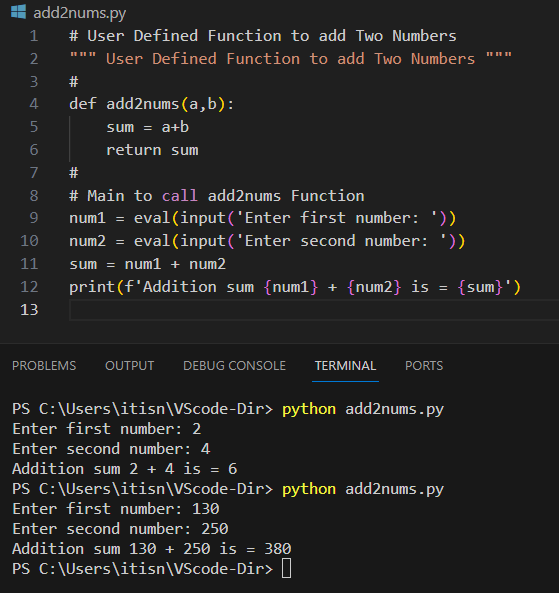
Here's a simple example of a while loop that counts from 1 to 5:
i = 1while i <= 5:
print(i)
i += 1
When you run this code, it will output the numbers 1 through 5.
Common uses of while loops:
Counting: As shown in the example above,while loops are great for counting from a starting value to an ending value. Reading files or input: You can use while loops to read a file line by line, parse user input, or process data as long as it's available. Processing data: Loops can be used to manipulate or transform data while certain conditions are met (e.g., processing all elements in a list). Implementing logic: You might use while loops to implement logical flows that depend on certain conditions being true.
Best practices:
Use meaningful variable names: Choose descriptive names for your loop control variables. Keep the condition simple: Make sure your condition is easy to understand and maintain. Avoid infinite loops: Double-check your condition to ensure it will eventually become false, preventing an infinite loop.In summary, while loops are a powerful tool in Python that allow you to execute code repeatedly based on a specific condition. By understanding the basic syntax and best practices for using these loops, you can write efficient, readable, and maintainable code!
python while loop break
I'm happy to help!
The break statement in Python is used to exit a loop (like while, for, or try-except) prematurely, skipping the rest of the code within the loop.
Here's an example of using break with a while loop:
i = 0while i < 5:
print(f"Current value: {i}")
if i == 3:
break
i += 1
print("Loop terminated!")
When you run this code, the output will be:
Current value: 0
Current value: 1
Current value: 2
Current value: 3
Loop terminated!
As you can see, the loop stopped at i == 3, even though it was supposed to go up to 5. The break statement effectively "killed" the loop, making it exit early.
Now, here are some scenarios where you might use break:
break to stop the loop and move on. Invalid input: When dealing with user input (e.g., from a file or console), you might encounter invalid data. You could use break to stop processing further if that happens. Detection of certain conditions: Let's say you're searching for a specific pattern in text, and when you find it, you can stop the search process.
Some important things to remember about break:
while, for, or try-except). If you use it outside a loop, Python will raise a SyntaxError. You should be careful when using break, as it can make your code less readable. Try to avoid breaking out of loops unless absolutely necessary. There's no equivalent to continue in other languages; if you're familiar with other programming languages, keep this in mind.
In conclusion, the break statement in Python allows you to exit a loop prematurely, giving you more control over the flow of your program. Just be mindful of its limitations and use it wisely!