create virtual environment python mac vscode
create virtual environment python mac vscode
I'd be happy to help you with creating a virtual environment for Python on your Mac using Visual Studio Code (VSCode).
Step 1: Install the Virtual Environment Package
First, let's install the virtualenv package using pip:
pip install virtualenv
This will create a new directory called virtualenv in your user directory.
Step 2: Create a New Virtual Environment
Next, we'll create a new virtual environment for our Python project. Let's name it myenv.
virtualenv myenv
This will create a new directory called myenv with its own Python interpreter and package dependencies isolated from the system Python.
Step 3: Activate the Virtual Environment
To start using the virtual environment, we need to activate it. Let's use the following command:
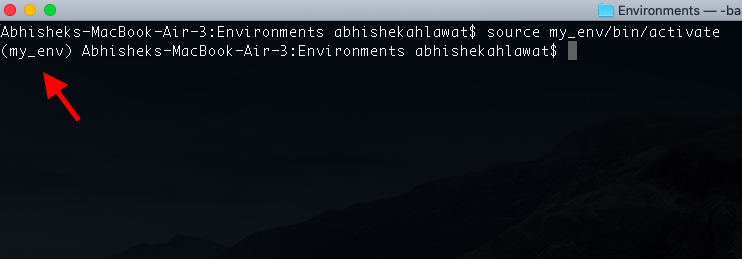
source myenv/bin/activate
On Mac OS X, you can use the following command instead:
. myenv/bin/activate
Once activated, your terminal prompt will change to indicate that you are now working within the virtual environment.
Step 4: Install Python Packages
Now we can install any required Python packages for our project using pip:
pip install requests numpy scipy pandas matplotlib
These are just a few examples of popular Python libraries. You can install as many or as few packages as you need for your project.
Step 5: Deactivate the Virtual Environment (When Done)
When you're finished working with your virtual environment, you'll want to deactivate it:
deactivate
This will return your terminal prompt to its original state.
Step 6: Create a New File in VSCode
Now that we have our virtual environment set up, let's create a new Python file in VSCode. Open VSCode and create a new folder for your project (e.g., myproject). Inside the folder, create a new file called main.py:
touch main.py
Step 7: Write Your Code
Now we can start writing our Python code. Let's add some basic imports and print statements to get started:
import requests
from numpy import *
print("Hello, World!")
Of course, this is just a simple example. You can write as much or as little code as you need for your project.
Step 8: Run Your Code
Finally, let's run our code using the virtual environment:
python main.py
This will execute the code we wrote in Step 7.
That's it! We've created a virtual environment for Python using virtualenv and set up VSCode to work with it. You can now use your virtual environment to isolate your project dependencies and switch between different projects without affecting each other.
Happy coding!
activate virtual environment python mac
Activating a virtual environment (venv) on a Mac using Python is a straightforward process. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Why use virtual environments?
Virtual environments are isolated Python environments that allow you to work on different projects or modules independently, without affecting the system-wide Python installation or other projects. This ensures that your project's dependencies and packages remain separate from others, making it easier to manage and maintain your codebase.
Activating a virtual environment (venv) on Mac
Install venv if you haven't already: Run the following command in your terminal:
python -m pip install --upgrade virtualenv
python -m venv myenv (or any name you prefer)
This command will create a new directory with the given name, containing the isolated Python environment.
Activate the virtual environment:For Bash or Zsh shells:
source myenv/bin/activate
For Fish shell:
. myenv/bin/activate
Your terminal prompt should now change to indicate that you're working within the virtual environment.
Verify your Python version: Runpython --version to ensure you're using the correct version of Python for your project. Install necessary packages and dependencies: Use pip or conda to install the required packages for your project. Deactivate the virtual environment when finished: Run:
deactivate
Your terminal prompt will revert back to its original state, indicating that you're no longer within the virtual environment.
Tips and Variations
You can create a virtual environment with a specific Python version usingpython3 -m venv myenv for Python 3.x or python2 -m venv myenv for Python 2.x. If you want to create a virtual environment with a specific package manager (e.g., conda), use:
conda create --name myenv
python -m venv --list
By following these steps and using virtual environments effectively, you'll be able to manage your projects with ease, ensuring that each project's dependencies and packages remain isolated and organized.





























