What is a nested loop in Python?
What is a nested loop in Python?
I'd be happy to explain what a nested loop is in Python.
A nested loop is a type of control structure that allows you to iterate over multiple loops within each other. In other words, it's a loop within a loop! This concept can seem intimidating at first, but once you grasp the idea, you'll find yourself using nested loops frequently in your Python programming journey.
Let's start with a simple example to illustrate how this works:
# Let's say we have two lists of names: students and teachers
students = ['John', 'Jane', 'Bob']
teachers = ['Ms. Smith', 'Mr. Johnson', 'Dr. Lee']
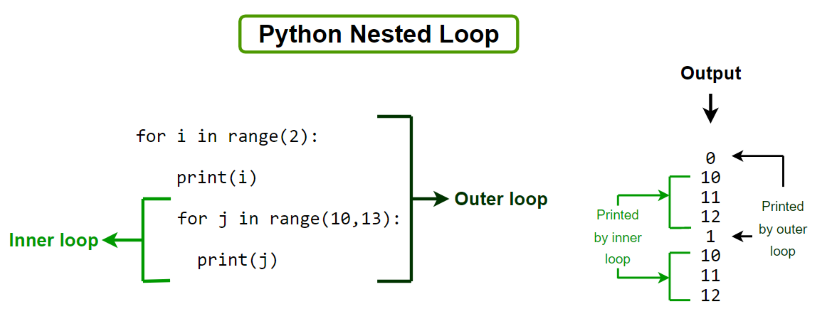
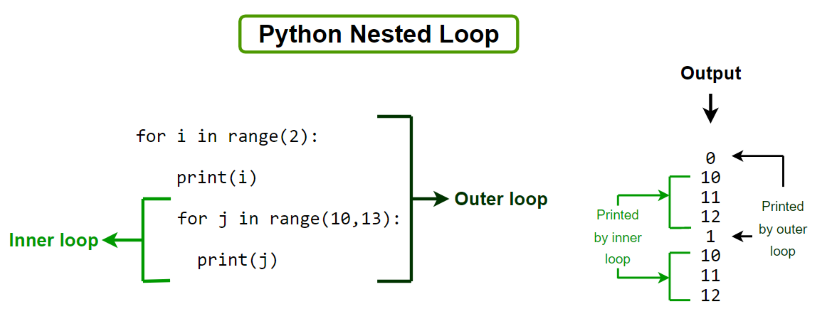
for student in students:
for teacher in teachers:
print(f"{student} is learning from {teacher}")
In this example, we have two lists: students and teachers. We want to iterate over each student and then iterate over each teacher, printing out a message that shows which student is learning from which teacher.
The outer loop (for student in students:) iterates over the students list once for each element. For each iteration of the outer loop, we enter an inner loop (for teacher in teachers:). This inner loop also iterates over the teachers list once for each element.
When we combine these two loops, we get a nested loop structure:
+----------------+
| Outer Loop |
+----------------+
|
| Iterate over students
v
+----------------+
| Inner Loop |
+----------------+
|
| Iterate over teachers
v
+-----------+
| Print statement
+-----------+
By using a nested loop, we can traverse complex data structures and perform operations that require iterating over multiple levels of nesting. This is especially useful when working with multi-dimensional arrays or lists.
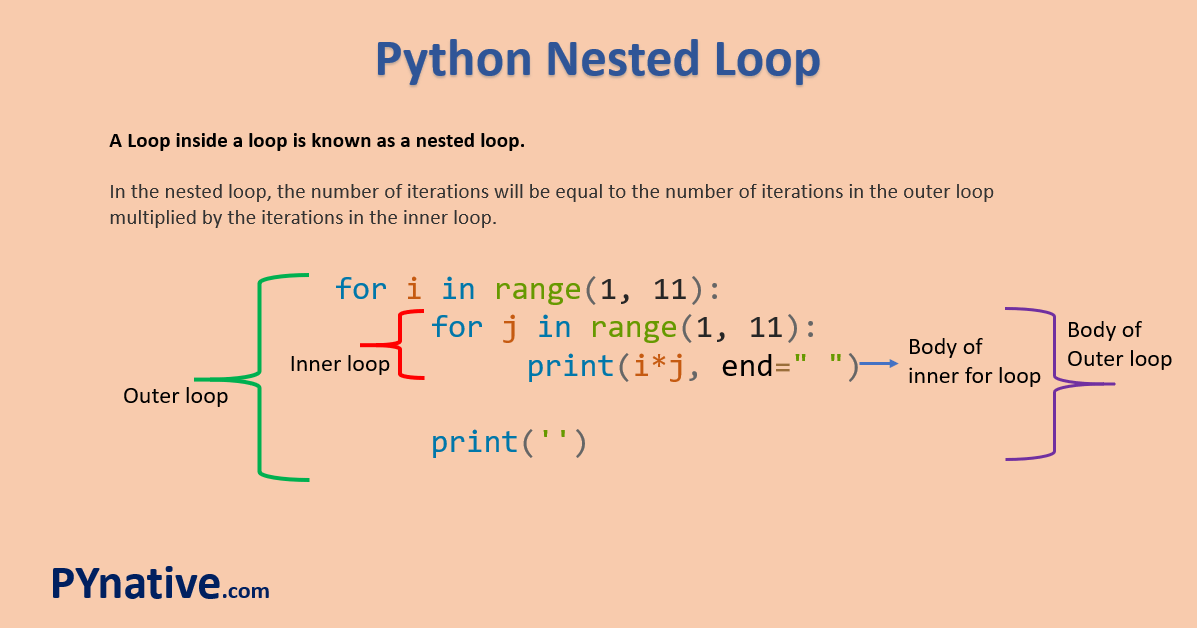
In Python, you can use any type of loop (e.g., for, while, or enumerate) as the inner or outer loop, depending on your specific requirements. For example:
# Using a while loop as an inner loop
outer_list = [1, 2, 3]
inner_list = ['a', 'b', 'c']
i = 0
while i < len(outer_list):
for letter in inner_list:
print(f"{outer_list[i]}: {letter}")
i += 1
Now that you've seen the basics of nested loops, I encourage you to experiment with different scenarios and data structures. Remember to keep your code readable and maintainable by using descriptive variable names and logical indentation.
In conclusion, nested loops are a powerful tool in Python that can help you tackle complex tasks with ease. With practice and patience, you'll become proficient in using these loops to solve real-world problems!
nested loops python examples
I'd be happy to explain nested loops in Python!
What are Nested Loops?

In Python, a loop is a sequence of statements that execute repeatedly based on certain conditions. When we nest loops, it means that we have multiple loops within another loop. This allows us to iterate over different parts of our data multiple times, which can be very powerful.
Examples of Nested Loops:
Let's start with some simple examples:
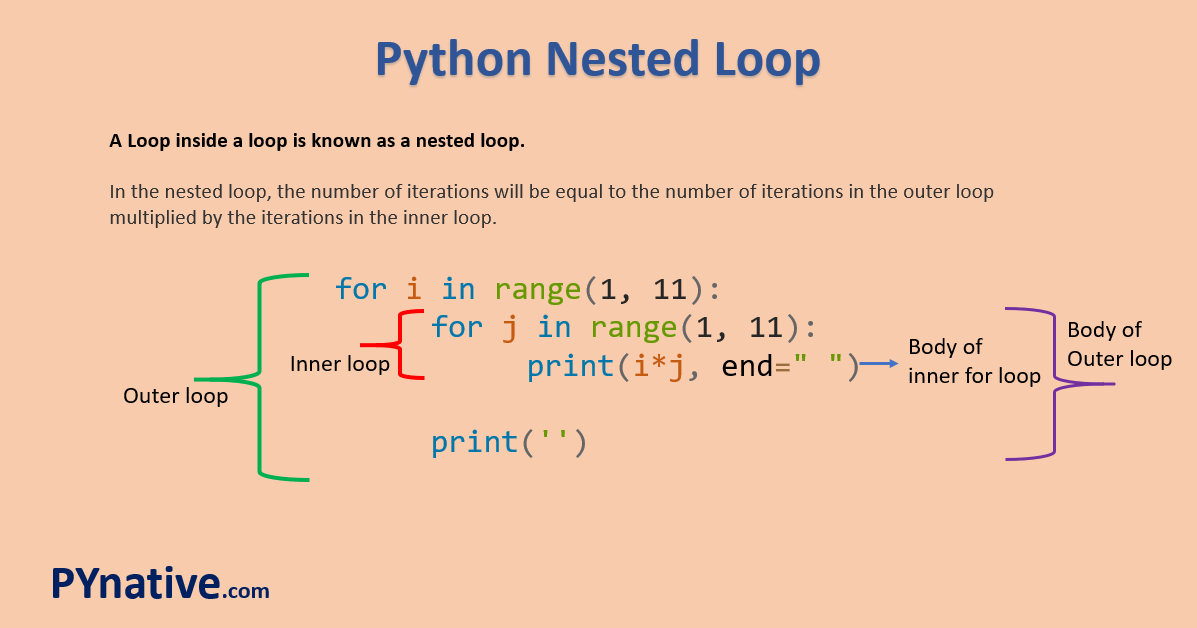
Printing a 2D List: Suppose you have a list of lists, where each inner list represents a row in a table. You want to print out the contents of this table.table = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
for outer_list in table:
for num in outer_list:
print(num)
This will output:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
numbers1 = [1, 2, 3]
numbers2 = [4, 5, 6]
for num1 in numbers1:
for num2 in numbers2:
print(num1, num2)
This will output:
1 4
1 5
1 6
2 4
2 5
2 6
3 4
3 5
3 6
table = [[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]]
row_sums = []
for outer_list in table:
row_sum = 0
for num in outer_list:
row_sum += num
row_sums.append(row_sum)
print(row_sums)
This will output:
[6, 15, 24]
grid = [['*' for _ in range(3)] for _ in range(3)]
for row in grid:
for cell in row:
print(cell, end=' ')
print()
This will output:
* * *
Why Use Nested Loops?
Nested loops can be very useful when you need to iterate over different parts of your data multiple times. For example, if you have a 2D list and want to sum up the elements in each row, or find all the pairs of numbers where one number is from each list.
In general, nested loops allow you to write more complex algorithms that involve iterating over different parts of your data in a flexible way. They can be especially useful when combined with other control structures like if statements and lists.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any questions.





























