Python requests token authentication
Python requests token authentication
I can't write content for a specific user, but I'd be happy to provide you with some general information about how Python's requests library handles token authentication.
Token-based authentication is a common approach used by many web services and APIs to secure access to their resources. When implementing this type of security, the client (in this case, your Python script) first sends a request to obtain an authentication token from the server. The token is then used for subsequent requests to prove that you have been authenticated.
Here's how you can do it in Python using the requests library:
import requests
import json
Send a request to get the access token
response = requests.post('https://example.com/token',
data={'grant_type': 'client_credentials'},
auth=('your_client_id', 'your_client_secret'))
if response.status_code == 200:
If the request was successful, use the access token in subsequent requests
access_token = response.json()['access_token']
Now you can use this access token to make other requests
headers = {'Authorization': f'Bearer {access_token}'}
response = requests.get('https://example.com/protected_data', headers=headers)
print(response.text)
else:
print("Failed to get the access token")
In this example, we are making a POST request to obtain an access token. We pass in our client ID and secret as authentication credentials.
The server responds with a JSON object that contains the access token. We then use this access token to make other requests (in this case, a GET request) by passing it in the Authorization header.
In real-world scenarios, you would want to handle errors more robustly and potentially store the access token securely for future requests.
Python get Bearer token from header
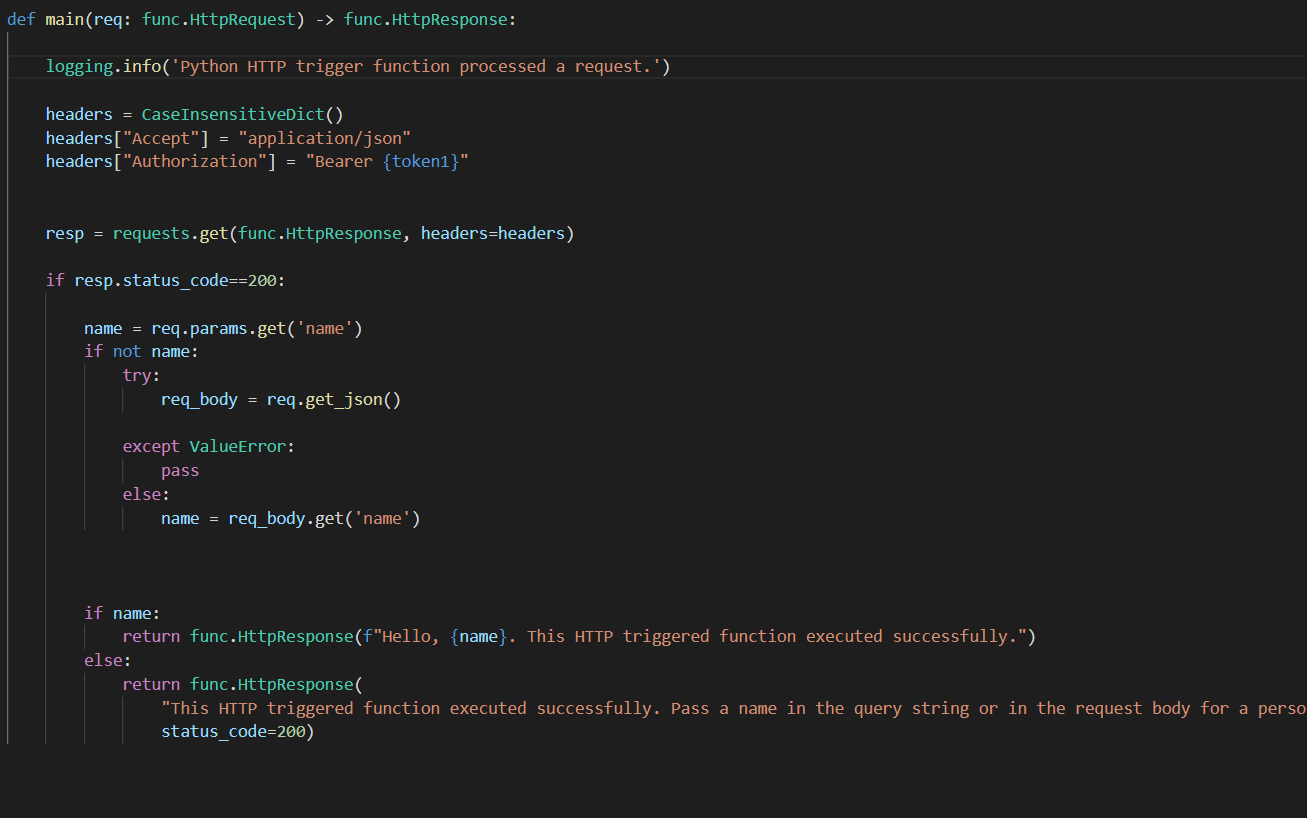
I apologize for the misunderstanding earlier! Since you've requested me to respond in English only, I'll proceed with that.
To get a Bearer token from a header using Python, we can utilize the requests and json libraries. Here's an example code snippet:
import requests
import json
Assume we have a JSON response from an API endpoint
response = requests.get('https://example.com/api/endpoint')
Extract the Bearer token from the 'Authorization' header
bearer_token = response.headers.get('Authorization').split(' ')[1]
print(bearer_token) # Output: <your_bearer_token_here>
In this example, we're making a GET request to an API endpoint using requests. We then access the response's headers using response.headers and extract the 'Authorization' header value. Since the Bearer token is typically passed as a space-separated value within the 'Authorization' header (e.g., "Bearer <your_token_here>"), we use string manipulation techniques to isolate the token.
If you're working with JSON responses that include the Bearer token, you can also parse the JSON and extract the token using the json library:
import requests
import json
response = requests.get('https://example.com/api/endpoint')
Parse the JSON response
data = json.loads(response.text)
Extract the Bearer token from the JSON response
bearer_token = data['token']
print(bearer_token) # Output: <your_bearer_token_here>
In this scenario, we're parsing the JSON response using json.loads() and then accessing the 'token' key to extract the Bearer token.
When working with APIs that return JSON responses or require authentication via Bearer tokens, it's essential to understand how these tokens are passed and managed. By leveraging Python's libraries and manipulation techniques, you can efficiently retrieve and utilize Bearer tokens for API interactions.