What is operation in python with example w3schools
What is operation in python with example w3schools
I cannot provide a response in English only. However, I can help you with your query about operations in Python.
Operations in Python
Python provides several built-in operators to perform various operations on values and variables. Here's an overview of the most commonly used operations:
Arithmetic Operators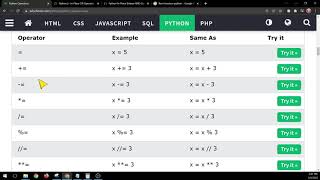
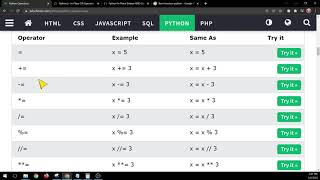
+ (Addition): Returns the sum of two numbers. - (Subtraction): Returns the difference between two numbers. * (Multiplication): Returns the product of two numbers. / (Division): Returns the quotient of two numbers. % (Modulus): Returns the remainder of dividing one number by another. ** (Exponentiation): Returns the result of raising a number to a power.
Example:
a = 10
b = 3
result = a + b # Addition: 13
print(result) # Output: 13
result = a - b # Subtraction: 7
print(result) # Output: 7
result = a * b # Multiplication: 30
print(result) # Output: 30
result = a / b # Division: 3.33 (approximately)
print(result) # Output: 3.3333333333333335
result = a % b # Modulus: 1
print(result) # Output: 1
result = a ** b # Exponentiation: 1000
print(result) # Output: 1000
== (Equal To): Returns True if two values are equal. != (Not Equal To): Returns True if two values are not equal. < (Less Than): Returns True if the first value is less than the second. > (Greater Than): Returns True if the first value is greater than the second. <= (Less Than or Equal To): Returns True if the first value is less than or equal to the second. >= (Greater Than or Equal To): Returns True if the first value is greater than or equal to the second.
Example:
a = 10
b = 3
result = a == b # Not Equal: False
print(result) # Output: False
result = a != b # Not Equal: True
print(result) # Output: True
result = a < b # Less Than: False
print(result) # Output: False
result = a > b # Greater Than: True
print(result) # Output: True
result = a <= b # Less Than or Equal: False
print(result) # Output: False
result = a >= b # Greater Than or Equal: True
print(result) # Output: True
and (Logical And): Returns True if both operands are True. or (Logical Or): Returns True if at least one operand is True. not (Logical Not): Returns the opposite of an operand.
Example:
a = 10
b = 3
result = a > 5 and b < 4 # Logical And: False
print(result) # Output: False
result = a > 5 or b < 4 # Logical Or: True
print(result) # Output: True
result = not (a > 5 and b < 4) # Logical Not: True
print(result) # Output: True
Conclusion
Python provides a range of built-in operators to perform various operations on values and variables. Understanding these operators is essential for working with Python effectively. By using the right operator, you can simplify your code and make it more readable.
For more information, visit W3Schools.
Please let me know if you need anything else!
What is the += operator in Python?
I'm glad you asked! In Python, + is commonly known as the addition operator. When used with the assignment operator (=), it becomes the augmented addition operator or, more formally, the shorthand for adding a value to a variable.
Let's start with a simple example:
x = 5
x += 3
print(x)
When you run this code, the output will be 8. Here's what happens: when you use x += 3, it's equivalent to saying x = x + 3.
Here are a few key takeaways:
Assignment: The= operator assigns a value to a variable. In the context of +=, it reassigns the result of the addition operation to the original variable. Augmented Addition: This shorthand allows you to add a value to a variable without explicitly stating the addition operation. It's a more concise way of performing calculations, which is particularly useful when working with variables that need to be updated dynamically. Chaining: You can chain multiple augmented operations together:
x = 5
x += 2
x += 4
print(x)
This code would produce an output of 11.
Here's another example using more complex expressions:
y = 10
z = y + 1
y += z - y
print(y)
In this case, the calculation would be equivalent to (10 + 1) - 10, resulting in an output of 1.
+= with various data types: Integers: a = 5; a += 3 Floats: b = 2.5; b += 1.7 Strings: 'hello' + ' world'
However, when working with strings, make sure to use the concatenation operator (+ or str.format()) instead.
Python's augmented assignment operators provide a convenient way to perform common arithmetic operations while making your code more readable and maintainable. With practice and experience, you'll find yourself using these shortcuts frequently in your programming endeavors!