How to do XML parsing using Python?
How to do XML parsing using Python?
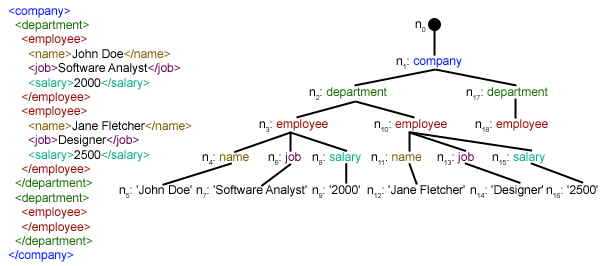
XML (Extensible Markup Language) is a markup language that defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable. In Python, you can parse XML files or strings using the xml.etree.ElementTree module.
Here's an example of how to use this module:
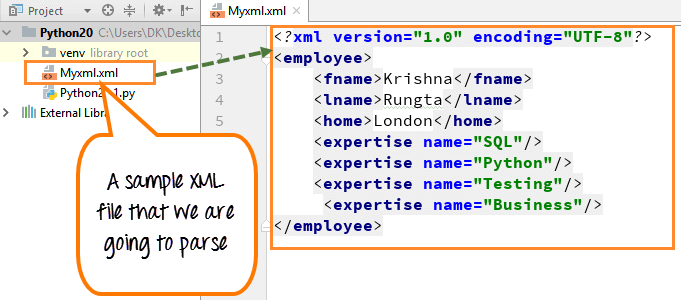
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
Parse an XML file
tree = ET.parse('example.xml')
root = tree.getroot()
Find all elements with tag 'person'
for person in root.findall('.//person'):
print(f"Name: {person.find('name').text}, Age: {person.find('age').text}")
In this example, we first import the xml.etree.ElementTree module. Then, we use the parse() function to parse an XML file called 'example.xml'. The parsed tree is stored in the tree variable.
Next, we get a reference to the root element of the XML document using the getroot() method. Then, we find all elements with the tag 'person' (regardless of their location within the document) using the findall() method.
For each 'person' element found, we print out their name and age. This is done by finding the 'name' and 'age' sub-elements of each 'person' element, then accessing the text content of these elements using the .text property.
You can also create new XML files or strings from Python data structures:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
root = ET.Element('root')
child1 = ET.SubElement(root, 'child1', attrib={'id': 1})
child2 = ET.SubElement(child1, 'grandchild')
root.set('attr', 'value')
tree = ET.ElementTree(root)
tree.write('output.xml')
In this example, we create a new XML tree from scratch. We start by creating the root element, then add child elements and sub-elements to it using the Element and Subelement classes.
Finally, we set an attribute on the root element using the .set() method, then write the entire XML tree to a file called 'output.xml' using the write() method.
Python's xml.etree.ElementTree module is quite powerful, and it can handle many common XML parsing tasks. However, if you need more advanced features or customization options, you might want to consider using a third-party library like lxml or xmltodict.
How to read XML file using element tree in Python?

I'll be happy to help you with that!
Reading an XML File using ElementTree in Python
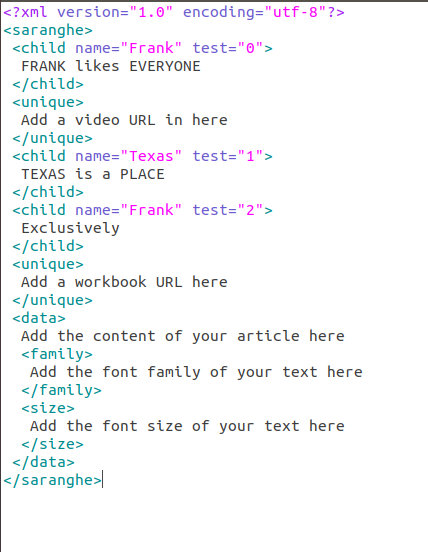
ElementTree is a built-in module in Python's standard library that provides support for parsing and generating XML files. It's a simple, yet powerful tool for working with XML data.

To read an XML file using ElementTree, follow these steps:
Import the ElementTree module: Start by importing the ElementTree module: import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
parse() function to parse the XML file into an ElementTree object:
tree = ET.parse('your_file.xml')
Replace 'your_file.xml' with the actual path to your XML file.
getroot() method:
root = tree.getroot()
.find() or .iter() to navigate through the XML elements and attributes, and extract the data you're interested in.
Here's a simple example of how to read an XML file with multiple child elements:
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
Parse the XML file
tree = ET.parse('example.xml')
root = tree.getroot()
for child in root.findall('.//child'):
print(child.tag, child.text)
In this example:
Thefindall() method is used to find all elements that match the XPath expression .//child, which means "find all child elements under any element". A for loop iterates over the found elements and prints their tags and texts.
Reading Specific XML Elements
To read specific XML elements, use the .find() method or its variations:
.find(tag_name): Find an element with a specific tag name. .find(text): Find an element that contains a specific text string. .find(path): Find an element using an XPath expression.
Here's how to read specific XML elements:
root.find('.//child1').text # Read the text of child1
child2 = root.find('.//child2')
print(child2.attrib) # Print child2's attributes
Handling Attributes and Child Elements
To handle attributes and child elements, use methods like .get() or .attrib for attributes, and .find() or .iter() for child elements:
attr = root.find('.//child1').get('myAttr')
print(attr)
for child in root.findall('.//child'):
print(child.tag, child.text)
In this example:
root.find('.//child1').get('myAttr') is used to get the value of the attribute "myAttr" from the element "child1". The for loop iterates over the found elements and prints their tags and texts.
Handling Complex XML Structures
When dealing with complex XML structures, you can use nested loops or recursion to navigate through the elements. Here's a simple example:
def process_elements(element):
if element.text:
print(element.text)
for child in element:
process_elements(child)
root = tree.getroot()
process_elements(root)
This code will recursively traverse the XML document and print out all text content.
By following these steps and using the methods provided by ElementTree, you should be able to efficiently read an XML file and extract the data you need. Happy coding!