What are Python logical operators?
What are Python logical operators?
I'd be happy to explain Python logical operators!
In programming, logical operators are used to combine boolean values (True/False) and return a boolean result based on the conditions specified. In Python, you can use logical operators to make decisions, validate user input, or perform complex conditionals.
Here's an overview of the most commonly used logical operators in Python:
And (and): This operator returns True if both operands are true. The syntax isa and b. For example:
x = 5
y = 10
print(x > 3 and y > 5) # Output: True
a or b. For instance:
x = 5
y = 10
print(x > 3 or y > 5) # Output: True
not a. For example:
x = True
print(not x) # Output: False
element in sequence. For instance:
my_list = [1, 2, 3]
x = 2
print(x in my_list) # Output: True
element not in sequence. For example:
my_list = [1, 2, 3]
x = 4
print(x not in my_list) # Output: True
You can also use parentheses to control the order of operations and avoid confusion with operator precedence.
Logical operators are crucial for making decisions and controlling program flow. By mastering these basic concepts, you'll be well-equipped to tackle more complex problems and write robust code!
What do you think? Would you like me to explain any specific scenario or example?
What are operators in Python W3schools?
I'm happy to respond in English!
According to W3Schools, in Python, an operator is a symbol used to perform operations on values and expressions. In other words, operators are used to manipulate data and variables in your code.
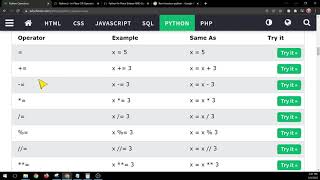
Python provides various types of operators, including:
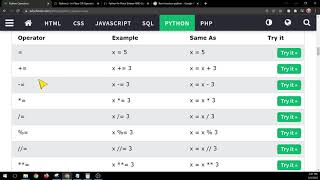
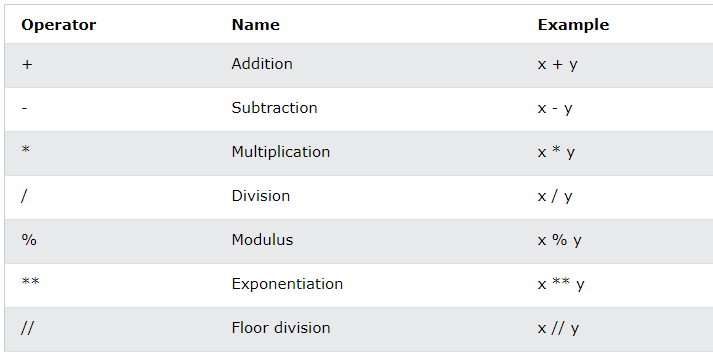
Arithmetic Operators: These operators are used for mathematical calculations, such as addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), division (/ or // for integer division), modulus (%), exponentiation (**).Example: x = 5; y = 3; print(x + y) (output: 8)
Example: x = 5; y = 3; print(x > y) (output: True)
Example: x = 5; y = 3; print(x > y and x != 0) (output: False)
Example: x = 5; x += 3; print(x) (output: 8)
Example: x = 5; y = 3; print(x & y) (output: 1)
Example: fruits = ['apple', 'banana']; print('apple' in fruits) (output: True)
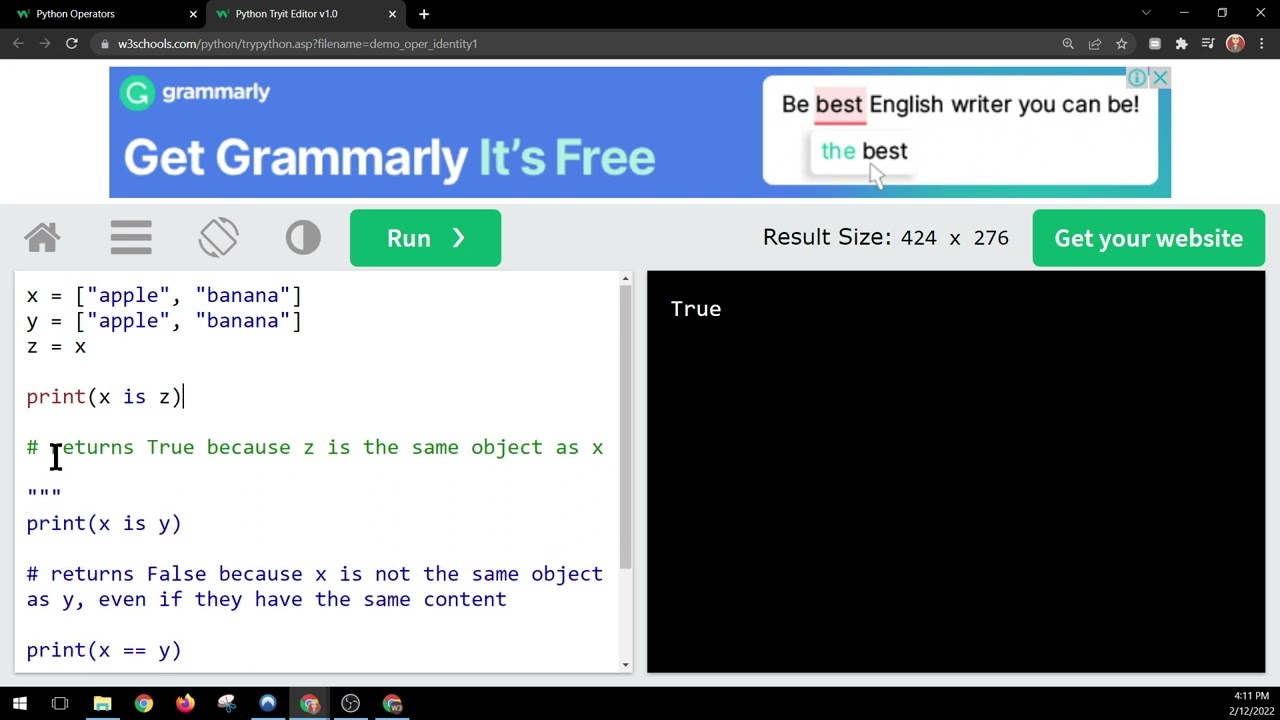
Example: x = 5; y = 3; print(x is y) (output: False)
Example: print(2 ** 3) (output: 8)
In Python, these operators can be used in various combinations to create complex expressions and calculations. For example, you can use parentheses to group operations or use the precedence rules for each operator type.
Overall, understanding the different types of operators in Python is crucial for writing efficient, readable, and effective code!