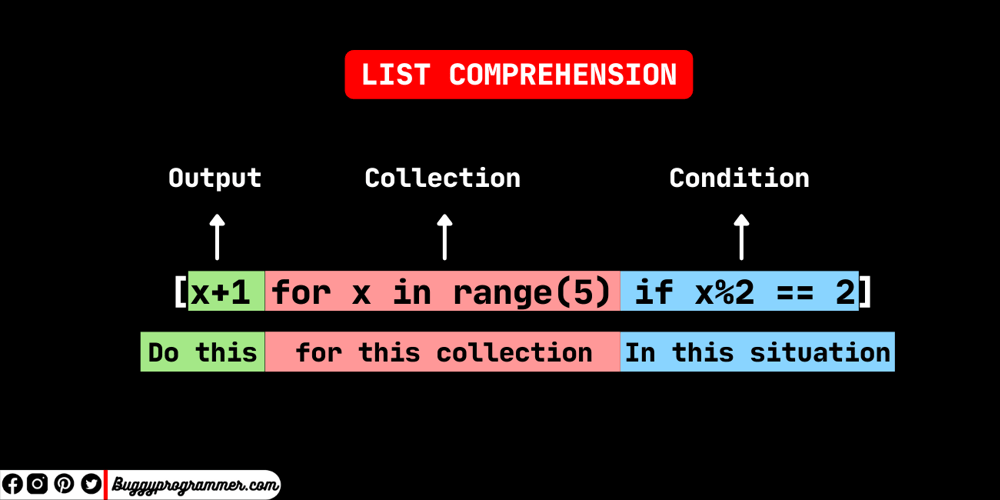
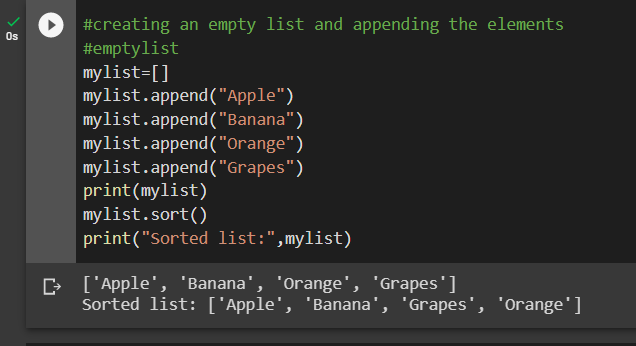
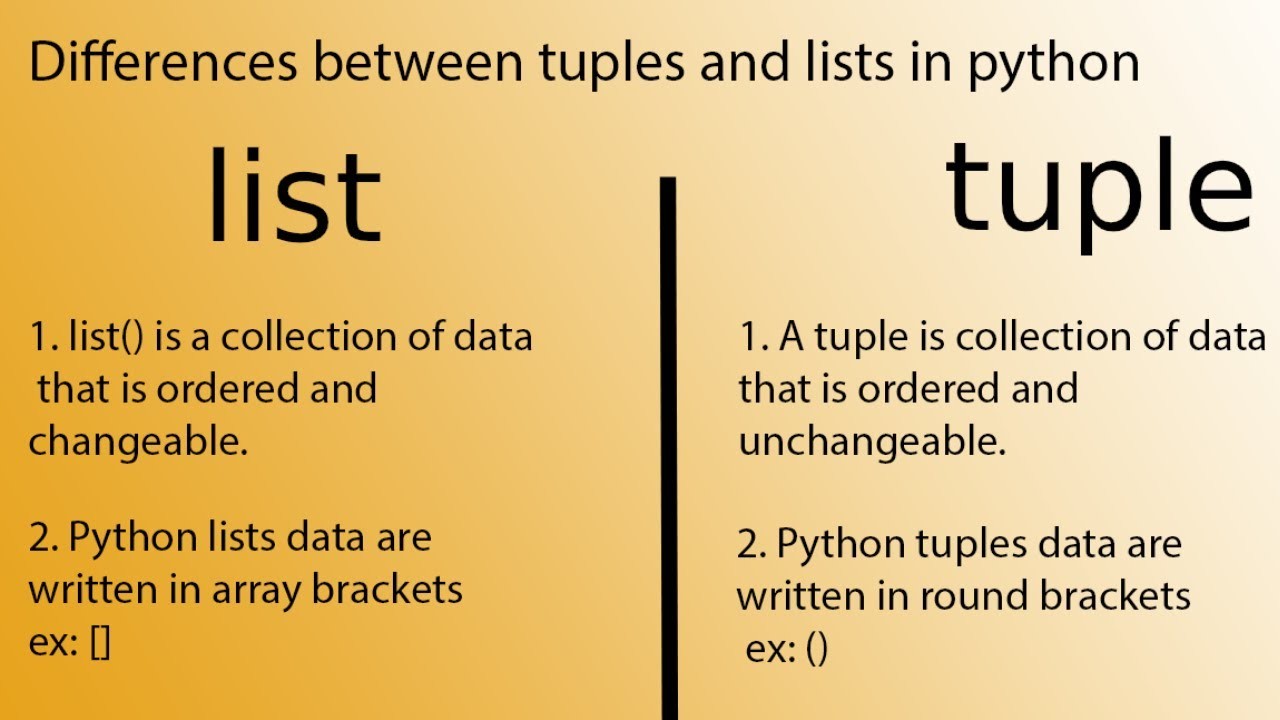
What is _ in for loop in Python?
What is _ in for loop in Python?

I'd be happy to explain what a for loop is in Python!
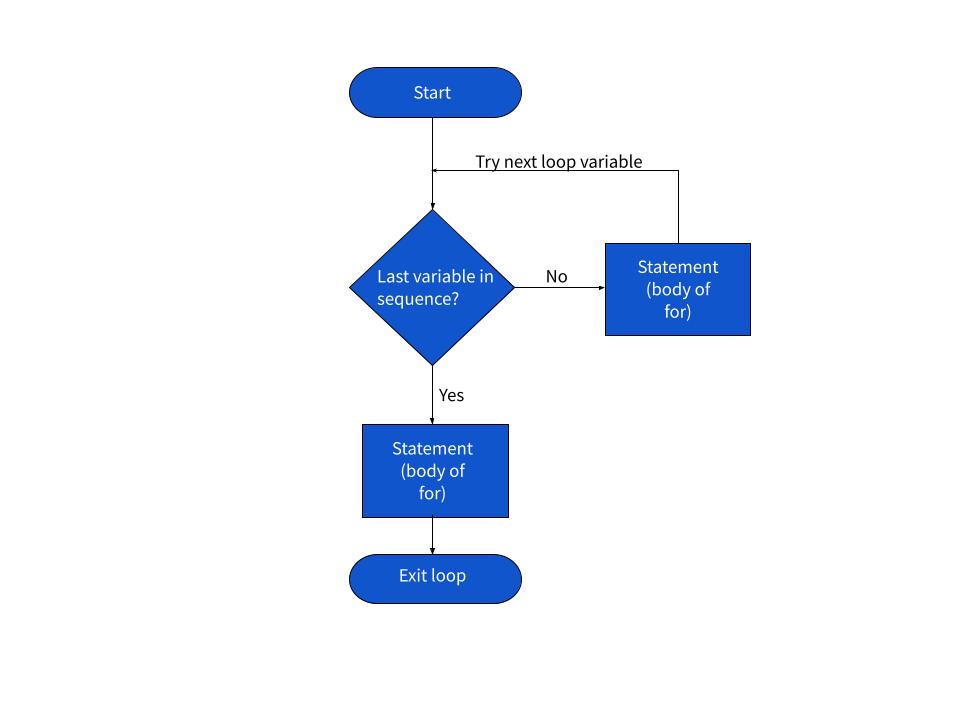
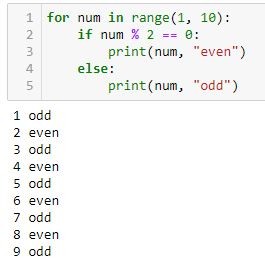
In Python, a for loop is used to iterate over a sequence (such as a list, tuple, or string) and execute a block of code repeatedly until the end of the sequence has been reached.
The general syntax for a for loop in Python is:
for variable_name in iterable: code to be executed
Here's what each part means:
variable_name: This is the name given to the current element being processed. You can use this name inside the loop to access the value of the element.
iterable: This is the sequence you want to iterate over, such as a list or tuple.
When the loop starts, Python assigns the first element in the iterable to the variable_name and executes the code indented under the for statement. Then, it moves on to the next element in the sequence, assigning it to variable_name, and repeats the process until the end of the iterable has been reached.
Here's an example:
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)
This code will output each fruit in the list on a new line. The variable fruit takes on the value of each element in the sequence, one at a time.
Some key features to keep in mind:
Iteration: Afor loop iterates over the elements of a sequence, allowing you to perform some action for each element.
Python also supports nested for loops:
nested_list = [['a', 'b'], ['c', 'd']]for outer_list in nested_list:
for inner_item in outer_list:
print(inner_item)
This code will output each item in the nested list, one at a time.
When deciding which loop to use (either for or while), ask yourself:
for. Do I need to repeat a block of code based on some condition that changes during iteration? -> Use while.
Now you know the basics of using for loops in Python!
Python for loop condition

I'm happy to help you with that!
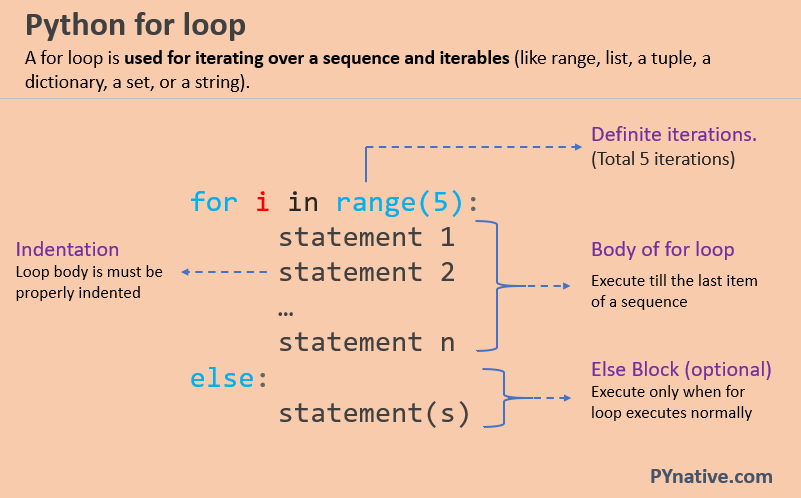
In Python, a for loop is used to iterate over a sequence (such as a list, tuple, or string) and perform an action for each item in the sequence.
The basic syntax of a for loop in Python is:
for variable in iterable:
code block
Here, variable is assigned the value from the iterable (like a list or string) on each iteration. The # code block is executed for each item in the sequence.
Let's break it down:
Variable: This is the name given to the variable that will take on the values from the iterable. Iterable: This can be any type of sequence, such as: A list (e.g.,[1, 2, 3]) A tuple (e.g., (1, 2, 3)) A string (e.g., "hello") A dictionary (more on this later)
Here's an example of a simple for loop:
fruits = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry']
for fruit in fruits:
print(fruit)
This will output:
apple
banana
cherry
When to use for loops:
Iterating over a sequence: For loops are perfect when you need to do something with each item in a list, tuple, or string. Processing data structures: You can iterate over dictionaries (more on this later) and process the key-value pairs. Performs repetitive tasks: Loops are great for performing repetitive tasks, like printing numbers from 1 to 10:for i in range(1, 11):
print(i)
How to use for loops:
Usein keyword: Always specify the iterable (like a list or string) using the in keyword. Define your variable: Choose a meaningful name for your variable that will take on the values from the iterable. Indicate what you want to do: Write the code block that will be executed for each item in the sequence.
Tips and Tricks:
Useenumerate() if you need both the index and value of each item in the sequence. Use zip() or itertools.zip_longest() to iterate over multiple iterables at once (like two lists). If you want to skip certain items in the iterable, use a conditional statement (e.g., if fruit != 'banana':) within your loop.
Now that we've covered the basics and some best practices, I hope this helps! Do you have any specific questions about for loops?