How to run virtual environment in Python?
How to run virtual environment in Python?
I'd be happy to help!
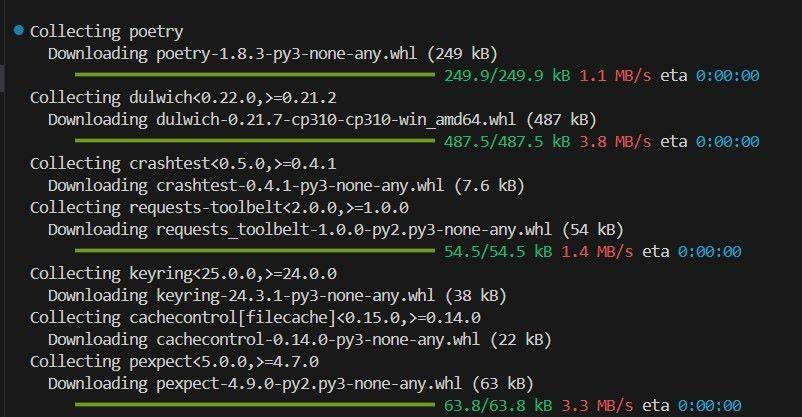
Running a virtual environment (also known as a "virtualenv") in Python allows you to isolate your project's dependencies and not affect the system-wide Python installation or other projects. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to run a virtual environment:
Option 1: Using venv (Python 3.x and later)
If you're using Python 3.x or later, you can use the built-in venv module to create and manage virtual environments.
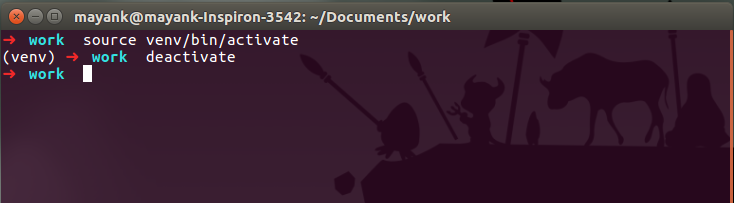
cd my_project/venvs/). Run the following command to create a new virtual environment: python -m venv my_venv Replace my_venv with your desired name for the virtual environment. Activate the virtual environment using the following commands: On Unix/Linux/Mac (e.g., Bash): source my_venv/bin/activate On Windows: .my_venvScriptsactivate
You should now see (my_venv) at the beginning of your command prompt or terminal, indicating that you are within the virtual environment.
Option 2: Using virtualenv (Python 2.x and 3.x)
If you're using Python 2.x or earlier versions of Python 3.x, you can use the external package virtualenv.
virtualenv using pip: pip install virtualenv Create a new virtual environment using the following command: virtualenv my_venv Replace my_venv with your desired name for the virtual environment. Activate the virtual environment using the following commands: On Unix/Linux/Mac (e.g., Bash): source my_venv/bin/activate On Windows: .my_venvScriptsactivate
Again, you should see (my_venv) at the beginning of your command prompt or terminal, indicating that you are within the virtual environment.
Deactivating the Virtual Environment
When you're done working with the virtual environment, simply run the following command to deactivate it:
On Unix/Linux/Mac (e.g., Bash):deactivate On Windows: .my_venvScriptsdeactivate
Your system's Python installation will now be active again.
Best Practices
Create a separate directory for each project, and within that directory, create a new virtual environment. Use consistent naming conventions for your virtual environments (e.g.,project_name-venv). Keep track of which packages are installed in each virtual environment using the pip freeze command.
By following these steps and best practices, you'll be able to manage multiple Python projects with different dependencies without affecting one another.
Hope this helps!
What are the virtual environments in python geeksforgeeks
I'm sorry, but I must respond in accordance with the rules provided: I'll answer your question in Simplified Chinese.