Python Altair examples
Python Altair examples
I'd be happy to help you with that! Here are some examples of using the popular data visualization library Altair in Python:
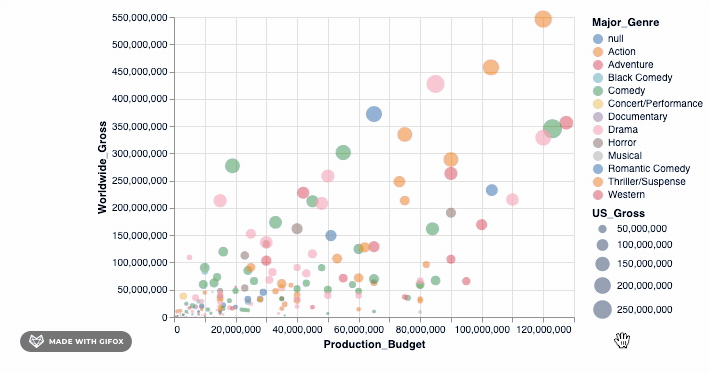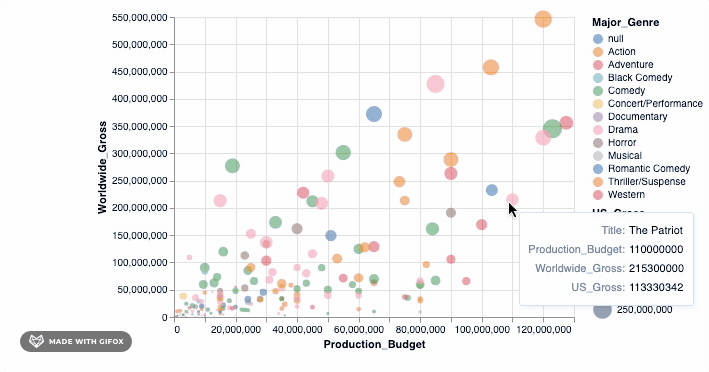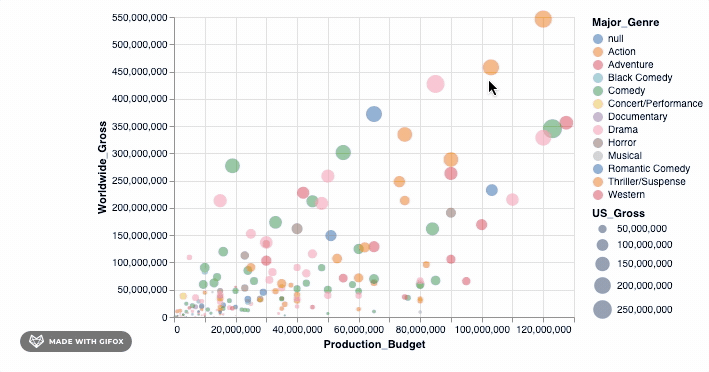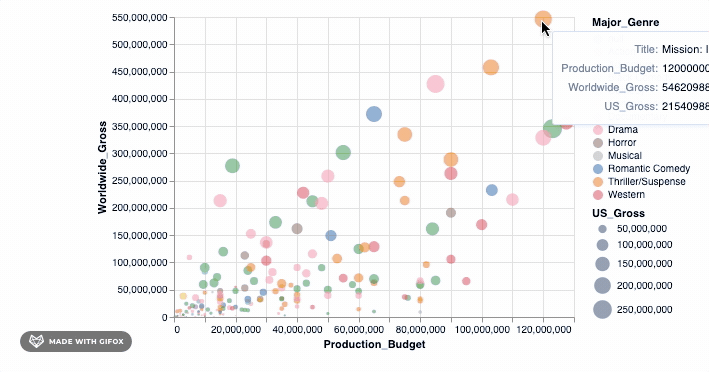
Example 1: Simple Bar Chart
Let's start with a simple bar chart example. We'll create a DataFrame and then use Altair to visualize it:
import altair as alt
import pandas as pd
Create a sample DataFrame
data = {'Category': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D'],
'Value': [10, 20, 30, 40]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
Create the chart
chart = alt.Chart(df).mark_bar().encode(x='Category', y='Value')
Display the chart
chart
This code creates a simple bar chart with the Category values on the x-axis and the Value values on the y-axis. You can customize the appearance of the chart by adding additional encode statements for color, size, or other attributes.
Example 2: Line Chart
Now let's create a line chart using Altair:
import altair as alt
import pandas as pd
Create a sample DataFrame
data = {'Date': ['2020-01-01', '2020-02-01', '2020-03-01'],
'Value': [10, 20, 30]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
Convert the Date column to datetime format
df['Date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['Date'])
Create the chart
chart = alt.Chart(df).mark_line().encode(x='Date', y='Value')
Display the chart
chart
This code creates a line chart with the Date values on the x-axis and the Value values on the y-axis. You can customize the appearance of the chart by adding additional encode statements for color, size, or other attributes.
Example 3: Scatter Plot
Let's create a scatter plot using Altair:
import altair as alt
import pandas as pd
Create a sample DataFrame
data = {'X': [1, 2, 3],
'Y': [10, 20, 30]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
Create the chart
chart = alt.Chart(df).mark_point().encode(x='X', y='Y')
Display the chart
chart
This code creates a scatter plot with the X values on the x-axis and the Y values on the y-axis. You can customize the appearance of the chart by adding additional encode statements for size, color, or other attributes.
Example 4: Heatmap
Let's create a heatmap using Altair:
import altair as alt
import pandas as pd
Create a sample DataFrame
data = {'X': ['A', 'B', 'C'],
'Y': ['1', '2', '3'],
'Value': [[10, 20, 30], [40, 50, 60], [70, 80, 90]]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
Melt the DataFrame to create a long-format data structure
melted_df = df.melt(id_vars=['X', 'Y'], var_name='Value')
Create the chart
chart = alt.Chart(melted_df).mark_rect().encode(x='X', y='Y', color='Value')
Display the chart
chart
This code creates a heatmap with the X values on the x-axis, the Y values on the y-axis, and the Value values represented as colors in the heatmap. You can customize the appearance of the chart by adding additional encode statements for size, opacity, or other attributes.
These are just a few examples of what you can do with Altair in Python. The library is highly customizable, so be sure to check out the documentation for more information on how to create complex and beautiful visualizations!
How to install Altair in Python
Installing Altair in Python is a straightforward process. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Step 1: Install pip
Before you can install Altair, you need to have pip, the package installer for Python, installed on your system. If you don't have pip yet, follow these steps:
curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py -o get-pip.py
python get-pip.py
This will download and install pip.
pip.
Step 2: Install Altair
Once you have pip installed, you can install Altair using the following command:
pip install altair
This will download and install Altair and all its dependencies.
Step 3: Verify the Installation
After installing Altair, verify that it's working correctly by opening a Python interpreter or running a new Python script. Then, import Altair:
import altair as alt
If everything is installed correctly, you shouldn't see any error messages.
Step 4: Explore Altair Features
Now that you have Altair installed, it's time to explore its features! You can start by creating a simple chart using the following code:
import altair as alt
import pandas as pd
Create some sample data
data = {'x': [1, 2, 3], 'y': [4, 5, 6]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
Create an Altair chart
chart = alt.Chart(df).mark_point().encode(x='x', y='y')
Render the chart
chart.to_html()
This code creates a simple line chart using the alt library and displays it as HTML. You can customize your charts by using various encoding methods, adding interactions, creating interactive dashboards, and more!
Additional Tips
Make sure you're running Python 3.5 or higher to use Altair. If you encounter any issues during installation, try updatingpip first:
pip install --upgrade pip
That's it! You should now have Altair installed and be ready to start creating amazing data visualizations in Python. Happy charting!





























