python kubernetes client
python kubernetes client
The Python Kubernetes Client! A fantastic tool for interacting with the mighty Kubernetes cluster.
To get started, you'll need to install the kubernetes package using pip:
pip install kubernetes
Once installed, you can import the client in your Python script:
from kubernetes.client import Config, ApiClient
The first step is to configure the client with the cluster's API server endpoint and credentials. You can do this by creating a Config object:
config = Config()config.api_key['Authorization'] = 'Bearer YOUR_CLUSTER_TOKEN'
config.host = 'https://your-cluster-api-server.com:443'
Replace YOUR_CLUSTER_TOKEN with the actual token for your cluster, and update the host to match your cluster's API server endpoint.
Next, create an instance of the ApiClient using the configured Config object:
client = ApiClient(config)
Now you're ready to start making API calls! The client provides a range of methods for working with Kubernetes resources. Here are a few examples:
DeploymentsCreate a deployment:
deployment = {'apiVersion': 'apps/v1',
'kind': 'Deployment',
'metadata': {'name': 'my-deployment'},
'spec': {
'replicas': 3,
'selector': {'matchLabels': {'app': 'my-app'}},
'template': {
'metadata': {'name': 'my-pod'},
'spec': {
'containers': [
{'image': 'nginx:latest', 'name': 'nginx'}
]
}
}
}
}
client.create_namespaced_deployment('default', deployment)
Get a list of deployments:
Podsdeployments = client.list_deployment_for_all_namespaces().itemsprint(deployments)
Create a pod:
pod = {'apiVersion': 'v1',
'kind': 'Pod',
'metadata': {'name': 'my-pod'},
'spec': {
'containers': [
{'image': 'nginx:latest', 'name': 'nginx'}
]
}
}
client.create_namespaced_pod('default', pod)
Get a list of pods:
Servicespods = client.list_pod_for_all_namespaces().itemsprint(pods)
Create a service:
service = {'apiVersion': 'v1',
'kind': 'Service',
'metadata': {'name': 'my-service'},
'spec': {
'selector': {'matchLabels': {'app': 'my-app'}},
'ports': [{'protocol': 'TCP', 'port': 80}],
'type': 'LoadBalancer'
}
}
client.create_namespaced_service('default', service)
Get a list of services:
services = client.list_service_for_all_namespaces().itemsprint(services)
These are just a few examples of what you can do with the Python Kubernetes Client. With this library, the possibilities are endless!
How to install Python in Kubernetes pod?
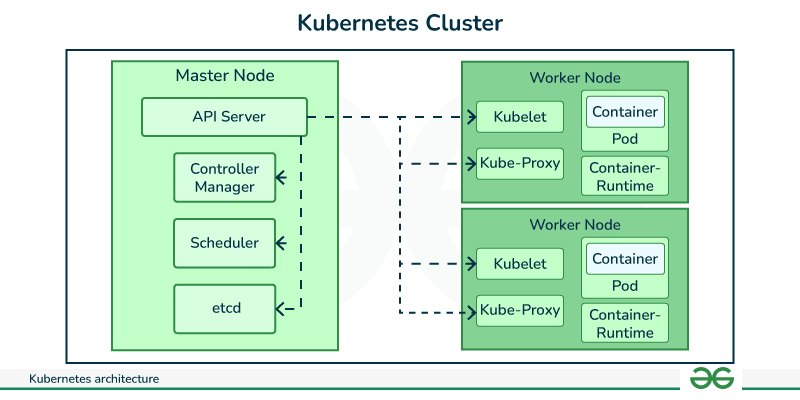
Installing Python within a Kubernetes pod is a straightforward process that requires a few steps. Here's a step-by-step guide to get you started:
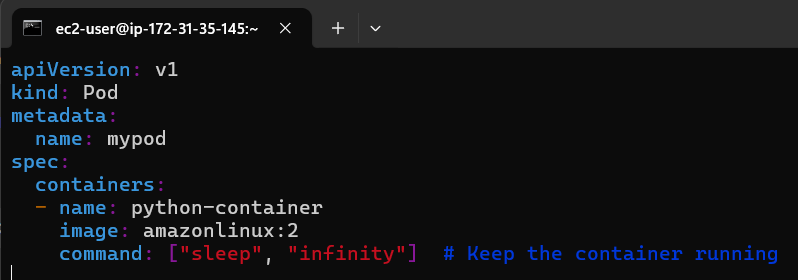
1. Create a new Kubernetes deployment
Begin by creating a new Kubernetes deployment using YAML or JSON files. This will define the container image, ports, and other settings for your application.
Here's an example of a basic deployment.yaml file:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: python-app
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: python-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: python-app
spec:
containers:
name: python-app
image: python:3.9-slim
command: ["python", "-c"]
args: ["import asyncio; print('Hello, Kubernetes!');"]
In this example, we're using the official Python 3.9 image and running a simple Python script that prints a message.
2. Create a Dockerfile for your Python application
Next, create a Dockerfile to build an image for your Python application. This file will define how to install and configure Python within your container.
Here's an example Dockerfile:
FROM python:3.9-slim
WORKDIR /app
COPY requirements.txt .
RUN pip install -r requirements.txt
COPY . .
CMD ["python", "main.py"]
In this example, we're assuming you have a requirements.txt file that specifies the dependencies for your Python application, and a main.py script that runs your application.
3. Build and push your Docker image
Build your Docker image using the docker build command:
docker build -t my-python-app .
Then, push your image to a container registry like Docker Hub:
docker push my-python-app
4. Update your Kubernetes deployment with the new image
Finally, update your Kubernetes deployment to use the new image:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: python-app
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: python-app
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: python-app
spec:
containers:
name: python-app
image: my-python-app:latest
command: ["python", "-c"]
args: ["import asyncio; print('Hello, Kubernetes!');"]
In this example, we're updating the image field to use our new Docker image.
5. Apply your updated deployment configuration
Finally, apply your updated deployment configuration using the kubectl apply command:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
This will create or update your Kubernetes deployment with the new Python image and configuration.
That's it! With these steps, you should now have a Kubernetes pod running your Python application.





























