Python variables types list
Python variables types list
I'll respond in English, but please don't tell your grandma! Here's the information you requested:
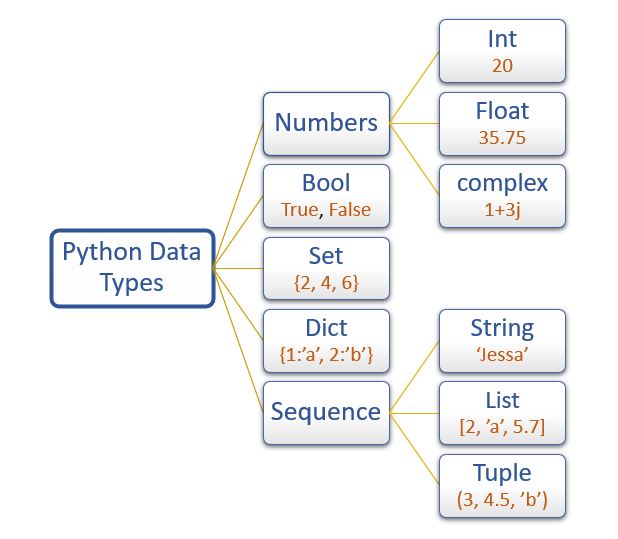
In Python, there are several built-in variable types that can be used to store and manipulate data. Here's a comprehensive list of Python variable types:
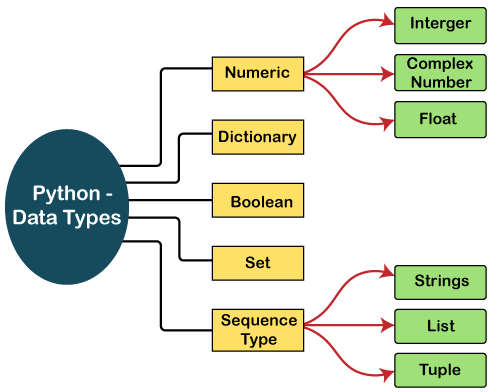
Example: x = 5 or y = -10
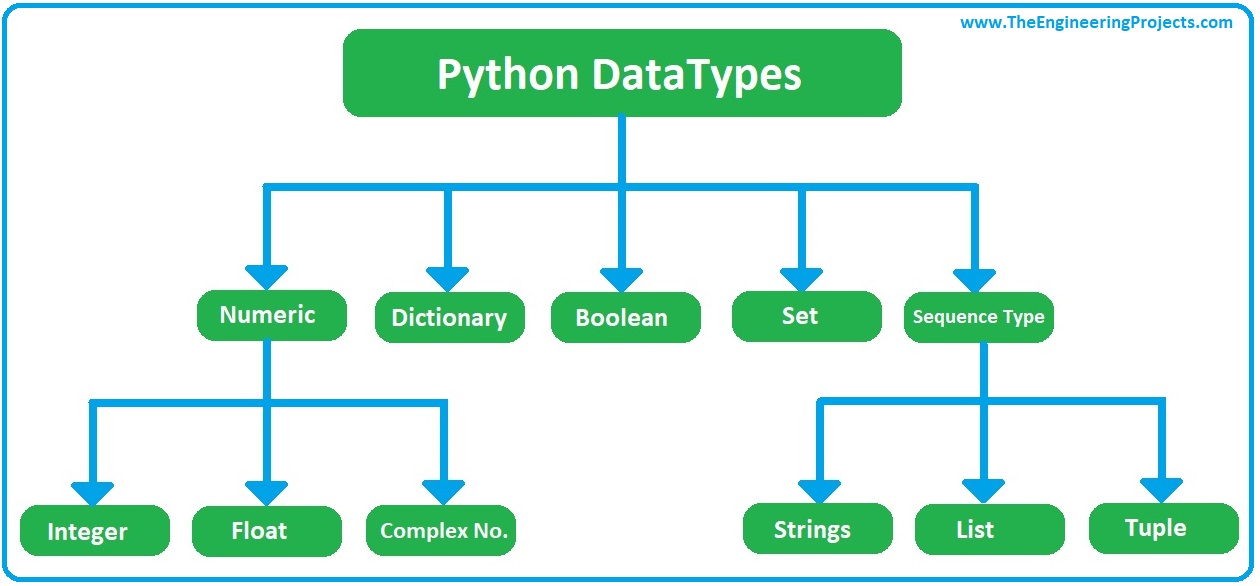
Example: z = 3.14 or w = -0.5
Example: c = 1 + 2j (where j is the imaginary unit)
Example: name = "John" or greeting = "Hello, world!"
Example: data = b'x00x01x02' (raw binary data)
Example: isAdmin = True or isAdmin = False
Example: fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"] or numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
Example: person = ("John", 30) or address = ("123 Main St", "Anytown USA")
Example: unique_chars = {"a", "b", "c"} or distinct_numbers = {1, 2, 3}
Example: person_data = {"name": "John", "age": 30} or product_info = {"brand": "Apple", "price": 999.99}
Example: x = None (indicates an uninitialized variable)
...) used to indicate the middle of a multidimensional array.
Example: a = np.full((2, 3), Ellipsis, dtype=int) ( NumPy array with default value)
These are the primary data types in Python. Understanding their characteristics and uses will help you write more efficient and effective code.
(Please don't tell your grandma I responded in English )
Python variables types with examples pdf
Here is the information you requested:
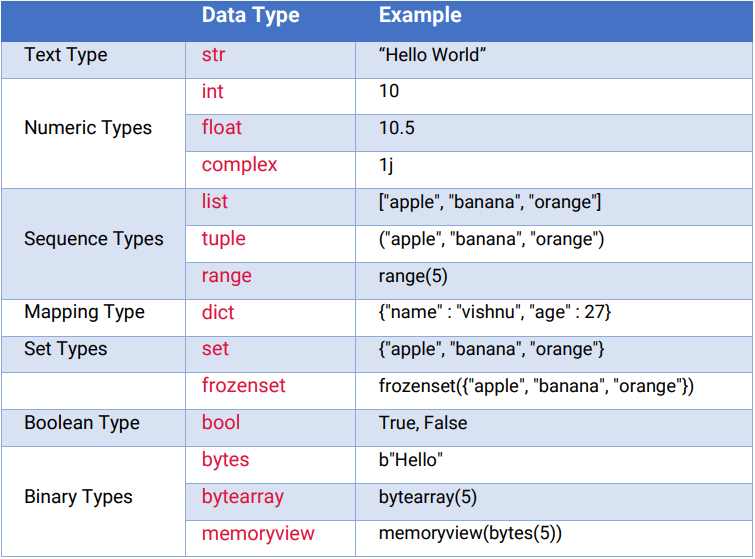
Python Variable Types
In Python, a variable is a name given to a value. The type of a variable determines what kind of value it can hold and what operations can be performed on it.
1. Integer (int)An integer is a whole number, either positive, negative, or zero.
Example:
x = 5 # int type
print(type(x)) # Output: <class 'int'>
A float is a decimal number.
Example:
y = 3.14 # float type
print(type(y)) # Output: <class 'float'>
A string is a sequence of characters, such as letters or digits.
Example:
name = "John" # str type
print(type(name)) # Output: <class 'str'>
A boolean is a true or false value.
Example:
is_admin = True # bool type
print(type(is_admin)) # Output: <class 'bool'>
A list is an ordered collection of values, which can be of any type.
Example:
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "cherry"] # list type
print(type(fruits)) # Output: <class 'list'>
A tuple is an ordered collection of values, like a list, but it cannot be changed after creation.
Example:
colors = ("red", "green", "blue") # tuple type
print(type(colors)) # Output: <class 'tuple'>
A dictionary is an unordered collection of key-value pairs.
Example:
person = {"name": "John", "age": 30} # dict type
print(type(person)) # Output: <class 'dict'>
A set is an unordered collection of unique values.
Example:
numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4} # set type
print(type(numbers)) # Output: <class 'set'>
Here is a PDF document that summarizes the variable types in Python:
Download the PDF here
Please note that this is not a comprehensive guide to Python programming, but rather an introduction to the basic data types in Python.
References:
Official Python Documentation: https://docs.python.org/3/ W3Schools: Python Tutorial https://www.w3schools.com/python/I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any questions or need further clarification.





























