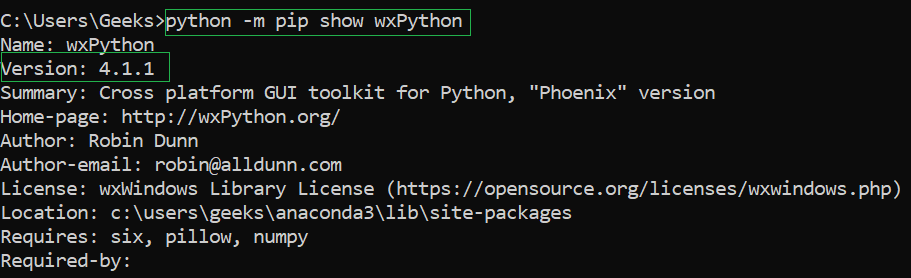
pip install wxpython
pip install wxpython
I'd be happy to help you with installing wxPython!
pip install wxPython
To start, let's begin by understanding what wxPython is and why we might want to install it.
What is wxPython?
wxPython (also known as Phoenix or Phoenixx) is a set of Python extensions that provide access to the GUI (Graphical User Interface) functionality of the wxWidgets C++ library. It's primarily used for building cross-platform desktop applications with a native look and feel on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
Why would I want to install wxPython?
Well, here are some reasons why you might consider installing wxPython:
wxPython is an excellent choice. It abstracts away many of the platform-specific details, allowing your code to be portable. Native look and feel: wxWidgets has been designed to mimic the native UI of each supported platform. This means that your application will blend seamlessly with the rest of the desktop environment, providing a consistent user experience across platforms. Extensive library support: wxPython comes with an impressive range of libraries and tools for creating GUI applications, including support for multimedia, printing, networking, and more.
How do I install wxPython?
Installing wxPython is relatively straightforward using pip (Python's package manager). Here are the steps:
cd ~Documents Run the following command: pip install wxPython Wait for the installation to complete. This might take a few minutes, depending on your internet connection and system resources.
Troubleshooting
In case things don't go as planned during installation, here are some common issues you might encounter:
Version mismatch: Ensure that you're running Python 3.7 or later. Dependency conflicts: Try installing wxPython withpip install --user wxPython if you have other packages installed globally. Installation failure: Check your internet connection and system resources. You can also try re-running the installation command.
Conclusion
In summary, wxPython is a powerful tool for building cross-platform GUI applications in Python. With its extensive library support, native look and feel, and ease of use, it's an excellent choice for creating desktop applications that need to run on multiple platforms. I hope this guide has helped you understand the process of installing wxPython using pip. Good luck with your projects!
wxPython Linux
Here's a comprehensive guide on using wxPython for building GUI applications on Linux:
Introduction
wxPython is a Python extension that allows you to build cross-platform GUI applications. It's based on the popular wxWidgets C++ library and provides a native-looking GUI on Windows, Mac OS X, and Unix platforms, including Linux. In this article, we'll explore how to use wxPython for building GUI applications on Linux.
Getting Started
To start using wxPython on Linux, you'll need to install it first. You can do this by running the following command in your terminal:
sudo pip install wxpython
Once installed, you can create a new Python script and import the wx module:
import wx
Creating a GUI Application
To create a GUI application using wxPython, you'll need to create a wx.Frame or wx.Dialog object. Here's an example of how to create a simple "Hello World" window:
import wx
class HelloWorldFrame(wx.Frame):
def init(self, parent=None, id=-1):
super(HelloWorldFrame, self).init(parent, id, title="Hello World")
sizer = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL)
label = wx.StaticText(self, label="Hello, world!")
sizer.Add(label, 0, wx.ALL, 10)
self.SetSizer(sizer)
app = wx.App()
frame = HelloWorldFrame(None)
frame.Show()
app.MainLoop()
In this example, we create a HelloWorldFrame class that inherits from wx.Frame. We then create a wx.BoxSizer and add a static text label to it. Finally, we show the frame using the Show() method and start the app's main loop with app.MainLoop().
Handling Events
wxPython provides several ways for handling events in your application. For example, you can use the Bind() method to bind an event handler to a specific event:
import wx
class HelloWorldFrame(wx.Frame):
def init(self, parent=None, id=-1):
super(HelloWorldFrame, self).init(parent, id, title="Hello World")
sizer = wx.BoxSizer(wx.VERTICAL)
button = wx.Button(self, label="Click me!")
sizer.Add(button, 0, wx.ALL, 10)
self.SetSizer(sizer)
def on_button_clicked(self, event):
print("Button clicked!")
app = wx.App()
frame = HelloWorldFrame(None)
frame.Show()
button = frame.FindWindowOfType(wx.Button)
button.Bind(wx.EVT_BUTTON, frame.on_button_clicked)
app.MainLoop()
In this example, we create a wx.Button and bind the on_button_clicked() method to its wx.EVT_BUTTON event. When the button is clicked, the method will be called.
Conclusion
In conclusion, wxPython provides a powerful way for building cross-platform GUI applications on Linux. By following the examples provided in this article, you should now have a good understanding of how to use wxPython for creating your own GUI applications.
Additional Resources
For more information and tutorials on using wxPython, I recommend checking out the official wxPython documentation and the wxWidgets website. You can also find many online resources, such as tutorials, code snippets, and example projects, that can help you get started with wxPython.
I hope this helps! Let me know if you have any further questions or need more clarification on any of these topics.